Painting calculation formula
Before the production, inspection and application of coatings, some theoretical calculations or estimates are often required. The calculation results can be used to guide coating design, verify coating testing results, and also be used as a reference for production feeding or construction planning to avoid blindness. Coating calculation mainly includes: calculation of coating formula, such as pigment volume solubility (PVC), solid content and volatile organic compound (voc) of coating, calculation of coating construction, such as theoretical spreading rate of coating, wet film thickness , dry film thickness, theoretical coating dosage, actual coating dosage, etc.
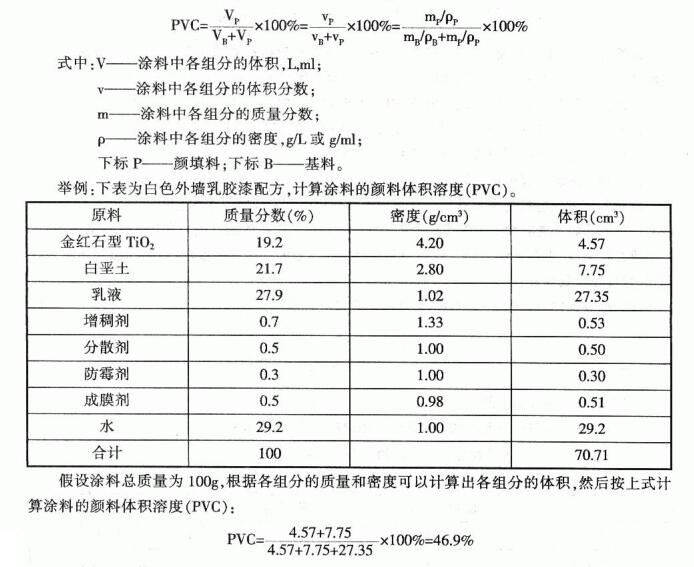
1. Pigment volume solubility of paint (Pvc)
Pigment volume solubility (PVC) of paint refers to the ratio of the volume of medium-frequency materials, extender pigments and other solid particles of paint to the total volume of non-volatile matter, usually expressed in percentage (%), and sometimes expressed in mass ratio.
By analyzing and changing the Pvc value of the paint formula, better pigment volume solubility can be obtained, so that the respective advantages of pigments, fillers and base materials can be fully utilized, and the cost of paint can be reduced. Therefore, calculating the pigment volume solubility (PvC) of paint is Very useful tool in paint design.
The theoretical calculation of the pigment volume solubility (Pvc) of coating is carried out as follows:
2. Solid content of coating
The solid content of the paint refers to the amount of non-volatile substances contained in the paint. Generally, it is expressed as the mass percentage of non-volatile matter, which is called the mass solid content, and it can also be expressed as a volume percentage, which is called the volume solid content.
The solid content of the paint is an important indicator of the paint. By calculating the solid content of the paint, it can be determined how much material in the paint will form the final coating, and it can also be determined how much coating area a certain amount of paint can form.

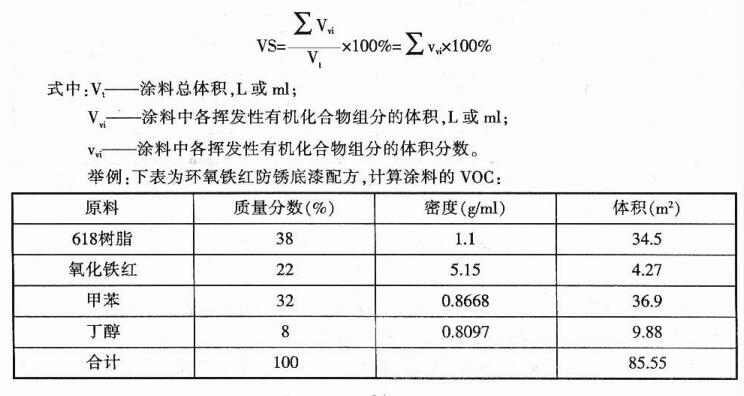
3. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) in Coatings
Volatile organic compounds in coatings refer to organic compounds that volatilize into the air during film formation and drying. Most coatings, including water-based coatings, contain volatile organic compounds. Volatile organic compounds make the air quality of the paint construction site poor, and seriously pollute the air, water and soil. Therefore, voc is also an important indicator that the paint needs to be controlled. voc can be expressed by volume fraction or mass fraction.
The theoretical calculation of the volatile organic compounds (voC) of the coating is carried out according to the following formula:
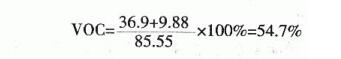
4. Wet film thickness and dry film thickness of coating
In construction quality management, monitoring film thickness is a relatively important item. The purpose of monitoring the film thickness is to make the thickness of the coating to meet the design specified thickness to ensure the protective performance, but also to avoid the waste caused by over-thickness. Coating film thickness can be divided into wet film thickness (wFT) and dry film thickness (DFr). Wet film thickness refers to the thickness of the coating film just after the coating is applied, and is mainly used to guide and supervise the coating construction process. Dry film thickness refers to the coating thickness after the coating film has dried, and is mainly used in the coating design and construction acceptance stages. The conversion relationship between dry film thickness and wet film thickness:
Dry film thickness (mn) = wet film thickness (mm) x coating volume solid content (%)
The volume solid content (%) of the coating in the above formula refers to the test result, not the theoretical volume solid content of the coating. Because the drying process of the coating film is very complicated, for volatile coatings and two-component coatings with high solid content, the above conversion relationship is more consistent with the actual situation. For volatile coatings with low solid content and inorganic zinc-rich coatings, the above conversion relationship is quite different from the actual one.
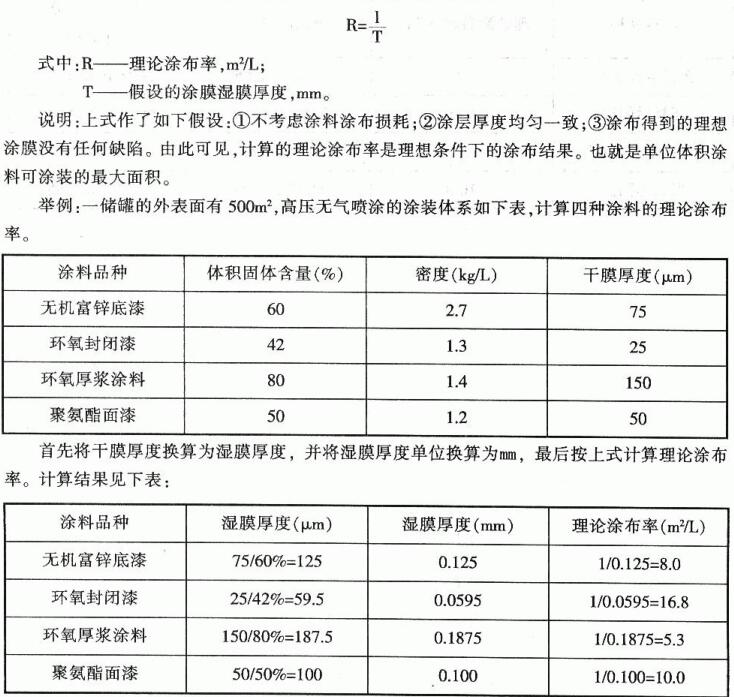
5. Theoretical spreading rate of coating
The theoretical spread rate of paint refers to the area that can be coated by a unit volume of paint when the thickness of the paint is constant.
The theoretical spread rate of paint is an important basis for calculating the amount of paint, which can be calculated according to the following formula
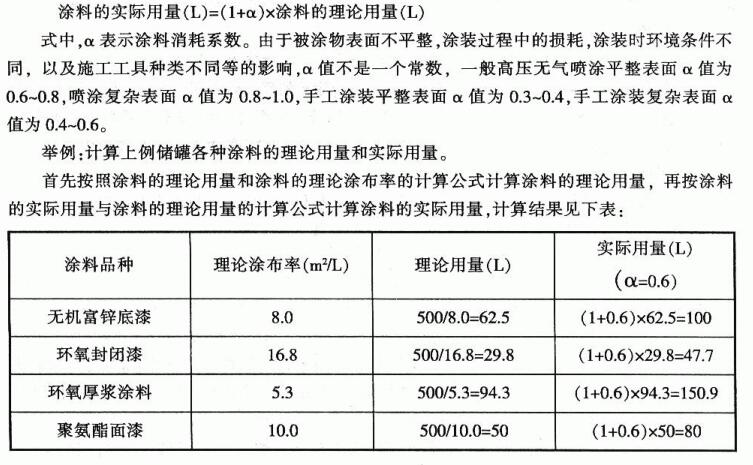
6. Theoretical and actual dosage of paint
After determining the paint matching system, before arranging painting, it is often necessary to estimate the amount of paint required. The theoretical dosage of paint can be calculated according to the following formula:
Theoretical dosage of paint (L) = coating area (㎡)/theoretical coating rate of paint (㎡/L)
The satisfactory conditions assumed in calculating the theoretical coating rate of coatings are impossible to achieve in actual construction, so it is also necessary to estimate the actual amount of coatings according to the actual application requirements. The conversion relationship between the actual amount of paint and the theoretical amount is as follows:
- 1Paint transparency detection method
- 2Importance and determination method of paraffin resistance of pigments
- 3Coating rheology and thixotropic
- 4How to determine pigment lightfastness
- 5How to assess the dispersion of pigments?
- 6Coating unit talk
- 7What are the main differences between Varnish and Paints?
- 8Pigment acid alkalinity test
- 9Paints gloss detection and measurement procedures