How to measure the chemical resistance of paint film?
1 Definitions, Purpose and Significance

2 Relevant Standards
GB/T 4893.1-2005 Determination of refrigerant resistance on furniture surface
GB/T 9274-88 Determination of liquid resistance of basecoats and varnishes (eqv]1S02812-1974)
IS0/FDIS 2812-1:2006(E) Paints and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part I: Immersion in liquids other than water
IS0/FDIS 2812-3:2006(E) Pigments and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part III. Absorbent medium method
IS0/FDIS2812-4:2006 (E) Pigment and varnish - Determination of resistance to liquid media - Part IV drip method
IS0/FDIS2812-5:2006 (E) Pigments and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part 5: Oven test with temperature gradient
GB/T 9265-88 Determination of alkali resistance of architectural coatings
GB/T 10834-89 Determination of salt water resistance of ship paints by salt water and hot brine immersion method
3. Introduction to the key points of the test method
3.1 GB/T4893.1-2005 Determination of refrigerant resistance on furniture surface
3.1.1 Test Principle
Place the filter paper soaked in the test solution on the surface of the specimen (common to all cured surfaces of finished furniture, regardless of material.) Do not apply to hand leather coatings and coatings of coated fabrics) and cover the surface with a tempered glass cover. After the required amount of time, remove the paper, wash and dry the surface. Check the damage (discoloration, discoloration, bubbling, etc.). The test results were evaluated according to the table of grading criteria described.
3.1.2 Materials and Equipment
Round paper sheet: flexible filter paper with a diameter of about 25mm, and its gram weight is (400-500) g/m2;
Tempered glass cover: edging, no flanging, inner diameter of about 40mm, height of about 25mm;
Tweezers;
Absorbent paper or absorbent cotton: has good absorption properties;
Self-colored, soft absorbent cloth;
Diffuse light source: provide uniform diffuse light, the brightness of irradiating the test area is 2000lx-5000lx, and diffuse natural light or diffuse artificial light can be used;
Direct light source: 60W frosted bulb, after frosting treatment to ensure that the light only shines on the test area, will not directly into the test eye. The light projected to the test area is 30° to 60° and the level can be evaluated by using an observation box (see Figure 34).
Test solution: the temperature is (23±2)°C;
Purified water or steamed water: the temperature is (23±2) °C;
Clear liquid: an aqueous solution prepared with detergent, with a concentration of 15ml/1, which should be freshly prepared each time it is used;
Cleanser. According to GB9985-2000 B1.4.3 standard tableware, deep washing agent.
3.1.3 Operational Points
The coated specimen should be stored at least 48 hours at a temperature of (23±2) °C and a relative humidity of (50±5)%.
Place the test surface horizontally, carefully wipe the test surface with a dry cloth, apply the selected test solution to the test position, the center of the two test positions should be 60mm away from each other, if possible, the center of the test position should be 40mm away from the edge of the test surface.
Put the round paper piece into the selected test solution for 30s, pick it up with a silver clip, wipe off the liquid along the edge of the container containing the test solution, quickly place it on the test area, and immediately cover it with an inverted tempered glass cover, and the round paper should not touch the glass cover.
After reaching the specified test time, remove the glass sheet and remove the round paper with silver, do not remove the paper that adheres to the test area, blot the residual liquid with absorbent paper (do not wipe with coal), and let it stand for 16h~24h.
After 16h-24h, the test surface is gently scrubbed with an absorbent cloth and cleaning solution, then the cloth is used to absorb pure water or steamed water, and finally the test surface is wiped dry with a dry cloth. At the same time, scrub and dry a position (contrast area) on the test surface without test solution, and then let it stand for 30 minutes before inspecting the test area
During the inspection, one of the surface light sources is used to reflect the light from the test surface into the observer's eye (if the test surface has a texture direction, the light rays are parallel or perpendicular to the texture direction), and the inspection is carried out from different angles, including the area between the angles, and the observation distance is 0.25mm-1.0mm.
3.1.4 Result Judgment
The test areas were graded by comparison with the comparison areas. The grading criteria are shown in Table 5
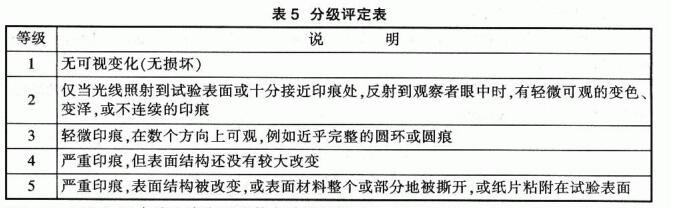
3.2 GB/T 9274-88 Determination of the resistance of color paints and varnishes to liquid media
This standard is divided into three test methods: method A (immersion method), method B (absorbent medium method), and method C (drip method).
3.2.1 Test principle
The paint test plate or test rod is in contact with the liquid medium at a certain temperature, and the surface change of the paint film is observed after reaching the specified time, and whether it meets the requirements of the product standard is judged, or the time that can be lasted until the coating is damaged and failed to a certain extent can be determined.
3.2.2 Materials
Tinplate: 120mmx50mmx(0.2~0.3)mm;
Steel plate: 120mmx50mmx(0.45-0.55)mm;
Aluminum plate: 12()mmx50mmx(1-2)mm;
Test rod (only for the immersion method) Unless otherwise specified, the rod shall be of steel or aluminum, one end shall be rounded, the radius of its arc is close to that of the rod itself, and the other end shall have a hole or ring;
Hygroscopic disc: It should not be affected by the test liquid, and laminated cardboard with a thickness of 1.25mm and a diameter of about 25mm can be used;
Surface dish: The size is about 40mm.
3.2.3 Handling and painting
Test board: Unless otherwise specified, it should be handled in accordance with the provisions of GB9271. Painted according to product standards. The back of the test plate should be coated with appropriate P-retention paint or test coating, and the edge of the test board should be sealed in this way.
Test stick: Unless otherwise specified, it should be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB1727.
Placement time: according to the product standard or according to the provisions of GB1727, generally at least 16 hours (except for drying paint).
3.2.4 Operational points
3.2.4.1 Method A (Immersion Method)
(1) Procedure A: Use a single liquid
Immerse 2/3 or all of the specimen in the medium specified in the product standard at a temperature of (23i2)°C, and use this bracket to immerse the specimen sample in a near-vertical position and cap. If it is prescribed that the air should be stirred or circulated to the liquid, the air should be diffused with a slow flow of air to remove the grease. If so, the test solution or distilled water should be added at the specified time to maintain the original volume or concentration.
When soaking to meet the requirements of the product standard, take out the test plate, if it is an aqueous solution, effectively clean the test plate with water. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent known to be non-damaging to the coating, and blot dry with filter paper to immediately check the coating changes of the test plate. If a recovery period is prescribed, this check-and-contrast should be repeated after the recovery period.
If it is necessary to check the erosion of the substrate, the coating is removed by the prescribed method.
(2) Procedure B: Use a two-phase liquid
This can be used as a holder to immerse the specimen sample in a near-vertical position in the appropriate container, with the plate width in the horizontal position for the plate.
Unless otherwise specified, dense liquids are poured from the side of the container and the test plate is immersed to a depth of 60 mm, and care should be taken not to contaminate the test plate above this level.
Unless otherwise specified, add a second liquid of low density in the same way to the metal part of the test plate, cover it, and let it sit without agitation.
When the soaking specified in the product standard is reached, the sample specimen is taken out, dried with paper, and the change phenomenon of the coating of the test plate in contact with each liquid is immediately checked. If a recovery period is prescribed, this examination and comparison should be repeated after the recovery period. When the test plate is inspected in the middle of the test, it does not need to be taken out, otherwise it should be cleaned immediately and the soaking operation should be repeated.
If it is necessary to check the substrate invasion, remove the coating by the prescribed method.
3.2.4.2 Method B (Absorbent Medium Method)
Immerse the hygroscopic disc in the appropriate amount of test fluid and allow the excess liquid to drip dry. Evenly distribute the discs on the painted test plate and at least 12mrn away from the edge of the test board. Cover the disc with a surface dish whose curvature does not touch the disc, so that the test plate can be properly placed in a ventilated environment during the test period (no more than 7 days). If volatile liquids are used, it is necessary to replace the hygroscopic disc with a new absorbent disc (as such a test should be recorded in the report).
Remove the moisture absorbent plate at the time specified in the product standard, and if it is an aqueous solution, effectively clean the test plate with water. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent known to be non-damaging to the coating, blot it with a piece of paper, and immediately check the coating changes of the test plate. If a recovery period is prescribed, this examination and comparison should be repeated after the recovery period.
If it is necessary to check the erosion of the substrate, the coating is removed by the prescribed method.
3.2.4.3 Method C (drip method)
Place the painted test plate in a horizontal position, add several drops of test solution to the coating, each drop volume is about 0.1mL, the center of the droplets is at least 2 l) mm, and the edge of the test plate is at least 12 mm high.
If required, cover the test section with appropriate methods to prevent over-evaporation.
When the time specified in the product standard is reached, if it is an aqueous solution, the test plate is effectively cleaned with water. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent that is known to have no damage to the coating, and blot a thousand with a piece of paper to immediately check the coating changes of the test plate.
If it is necessary to check the corrosion of the substrate, remove the coating by the prescribed method.
3.2.5 Determination of Results
3.2.5.1 Determination of the results of Law A
Check the loss of light, discoloration, rust, blistering, falling off and other phenomena of the paint film, whether it is qualified or not according to the product standard, and no less than two samples meet the product standard for qualified.
The evaluation of the phenomenon of paint film loss of light, discoloration, rust, blistering, peeling and other phenomena can be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 1766-1995 "Grading Methods for Aging of Pigment and Varnish Coatings".
3.2.5.2 Determination of the result of Law B
Check the loss of light, discoloration, rust, blistering, falling off and other phenomena of the paint film in contact with the moisture absorbing plate, and whether it is qualified or not is specified in the product standard, and many hand two test plates meet the product standard for qualification.
The evaluation of the phenomenon of paint film loss of light, discoloration, rust, blistering, peeling, etc., can be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GBIT 1766-1995 "Rating Methods for the Aging of Pigments and Varnish Coatings".
3.2.5.3 Determination of the result of Method C
Check the loss of gloss, discoloration, rust, blistering, falling off and other phenomena of the paint film of the dropwise test solution part, and whether it is qualified or not according to the product standard, and no less than two test plates meet the product standard for qualification.
The evaluation of the phenomenon of paint film loss of light, discoloration, rust, blistering, peeling and other phenomena can be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 1766-1995 "Grading Methods for Aging of Pigment and Varnish Coatings".
3.3 IS0/FDIS2812-1:2006 (E) Paints and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part I: Immersion in liquids other than water
3.3.1 Test Principle
Same as 3.2.1
3.3.2 Materials
Container: made of temperamental material, suitable for test fluids and test plate 1
Oven: with artificial ventilation device;
Test board: in accordance with IS01514 regulations, the size is about 150mmx100mmx (0.7mm-1.0mm);
Test bar: steel bar, length of about 150mm, diameter of about 15mm, one end rounded.
3.3.3 Operational Points
3.3.3.1 Method A single liquid
Immerse half or the agreed immersion depth of the specimen in the specified medium and cap. If specified, the liquid can be shaken or stirred. If required, the test solution or distilled water should be supplemented at the specified time to maintain the original volume or concentration.
The test can also be carried out at high temperatures. The test solution is heated to a specified temperature with an accuracy of 13°C before immersion in the test piece.
3.3.3.2 Method B is a two-phase liquid
Pour the dense liquid from the side of the container until 40% of the specimen is submerged, and be careful not to contaminate the test plate above this level. In the same way, add a second, less dense liquid until the other 40% of the plate is submerged, cover, and do not agitate. 3.3.3.3 After the specified soaking time, take out the sample, wipe it dry with a cloth, and if the test solution is an aqueous solution, effectively clean the test plate with running water. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent that is known to be non-damaging to the coating. Immediately inspect coating changes.
3.4 IS0/FDIS2812-3:2006 (E) Pigment and varnish - Determination of resistance to liquid media - Part III: Absorption medium method
3.4.1 Test Principle
Same as 3.2.1
3.4.2 Materials
Oven;
Surface dish: the diameter is about 40mm, and the curvature cannot contact the absorbing medium;
Petri dishes: 60 mm in diameter with 20 mm high sides;
Filter paper: not affected by the test solution, the diameter is about 25mm;
Absorbent cotton: lint-free and not affected by the test solution, which can replace the filter paper and clean the test plate after the test by hand;
Test board: in accordance with the IS01514 regulations, the size is about 150mmx100mmx (0.7mm~1.0mm).
3,4.3 Operational Points
Soak the filter paper or absorbent cotton into the test solution and let the excess liquid drip dry. Place it on a horizontally placed plate and distribute it evenly on the painted board, at least 10 mm between them and from the edge of the board. Immediately cover the test area with a surface dish or Petri dish.
If a high-viscosity or book-like test medium is used, put 0.5cm3 of the test medium on the surface of the test plate, then put the paper or degreasing essence on the test medium, and cover the test area with a petri dish. After the specified time, remove the paper or absorbent cotton, dry the test area with dry absorbent cotton, and use the test solution if it is an aqueous solutionRunning water effectively cleans the test board. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent that is known to be non-damaging to the coating. Immediately check for coating changes.
3.5 IS0/FDIS 2812-4:2006 (E) Paints and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part IV: Drip method 3.5.l Test principleSame as 3.2.1
3.15.2 Materials
Pipette: suitable for pipetting about 0.1ml of test solution;
Burette: 50RN1 ;
Petri dish: 60 mm diameter, 20 nm high side;
Test board: in accordance with IS01514 regulations, the size is about 150mmx100mmXL (0.7mm-1.0mm).
3.5.3 Operational Points
3.15.3.1 Method A - Position the test board horizontally
Place the painted test plate in a horizontal position, and use a pipette to fill several drops of test solution on the coating, each drop volume is about 0.1mL, and the droplets are at least 12 mm between the droplets and from the edge of the test plate.
If a high-viscosity or green test medium is used, place 0.5 cm3 of test medium on the surface of the test plate and use a Petri dish to cover the test area. (Related Instrument: Viscometer)
3.5.3.2 Method B: Placing the template obliquely
Place the painted test plate in the collector at a 30° angle to the horizontal position, and use a burette to drop a drop of test solution at an interval of 1 s-2 s to the position near the center of the test plate for 10 minutes. The test solution flows into the collector with the plate.
3.5.3.3 After the specified question, wipe the test area of the test board with a dry degreasing phase, and clean the test plate with running water if the test liquid is an aqueous solution. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent that is known to be non-damaging to the coating. Immediately inspect coating changes.
3.6 ISO/FDIS2812_5:2006 (E) Pigments and varnishes – Determination of resistance to liquid media – Part V: Oven test with temperature gradient
3.6.1 Test Principle
The test solution is dropped onto a painted test plate and placed in an oven with a temperature gradient to assess its effectiveness according to an agreed standard.
3.6.2 Materials and Equipment
Oven with temperature gradient (see Figure 35)
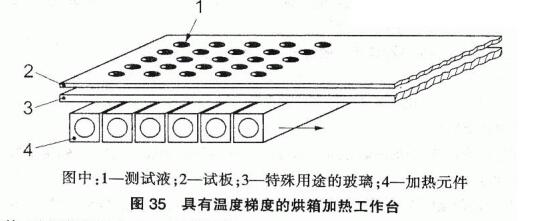
3.6.3 Operational Points
Place the test plate horizontally and add the test solution dropwise with a pipette, and the distance between the test droplets is generally equivalent to the distance between the heating sections of the gradient oven. Drip addition test. The test solution should be added at room temperature in the test room, not in the . Add dropwise in the fuel box. The temperature gradient range of the oven is 35 °C to 80 °C, and the temperature difference between each heating part should be 1 °C. Push the prepared test plate into the gradient oven, use a central tool to make the test plate close to the heating table, and take out the test plate from the oven after 30min.
Wipe the test area of the test board with a soft cloth, and if the test solution is an aqueous solution, use running water: effectively clean the test board. If it is a non-aqueous solution, rinse with a solvent that is known to be non-damaging to the coating. Immediately inspect coating changes.
3.7 GB/T 9265-88 Determination of alkali resistance of architectural coatings
3.7.1 Test Principle
Immerse the painted test plate in a liquid medium that maintains a certain temperature, observe the surface change of the paint film after reaching the specified time, and judge whether it meets the requirements of the product standard, or measure the time that can last until the coating is damaged and failed to a certain extent.
3.7.2 Materials
Asbestos cement board: 150mmx70mmx3
distilled or ionized-free water;
Calcium hydroxide (chemically pure);
Paraffin, rosin (industrial product);
pH Broad Test Strips: 1-14.
3.7.3 Operational Points
Preparation of alkali solution (saturated calcium hydroxide): under the condition of (23±2) °C, the solution is prepared with the ratio of 0.12g calcium hydroxide added to 100mL of distilled smoke water and stirred evenly, and the pH value of the solution should reach 12~13.
The substrate treatment shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of 5.3 in GB9271, and the painting shall be carried out in accordance with GB9271.
After the test plate is prepared, the edges and back of the test plate are closed with a mixture of stone and rosin 1:1.
Immerse 2/3 of the test plate in a saturated calcium hydroxide solution at a temperature of (23i2)°C. After soaking, take out the test plate and rinse it with water, shake off the water droplets on the board surface, and then blot it with filter paper, and immediately observe the coating surface.
3.7.4 Determination of Results
Check whether the paint film has discoloration, blistering, cracks, peeling, chalking, etc., and whether it is qualified or not is qualified according to the product standard, and no less than two test plates meet the product standard for qualification. The coating area within 5mm of the edge of the test board and 10mm below the liquid level is not evaluated.
The evaluation of paint film discoloration, loss of light, blistering, peeling and other phenomena can be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 1766-1995 "Rating Methods for Aging of Pigment and Varnish Coatings".
3.8 GB/T10834-89 Determination of salt water resistance of ship paint Salt water and hot brine immersion method
3.8.1 Test Principle
Same as 3.7.1
3.8.2 Materials and test setups
Ordinary carbon steel plate of hot car: 150mmx70mmx(2-3)mm, a small hole with a diameter of 3mm is opened at 5mm from the short side of the short side of the center line of the sample for suspension.
Test dregs: The salt solution constant temperature test tank is adopted, and the part in contact with the brine can be made of glass and plastic. Dimensions (500x400x300)mm, with lid, heater and thermostatic control system. At the same time, it should be considered that the flow speed and temperature of the brine in all parts of the dregs should be uniform, and a certain liquid level height should be maintained.
Stirring system: An electric batch mixer can be used for stirring, and the stirring paddle is added to shield the flow direction of the brine to achieve the purpose of fully stirring the brine and uniform temperature of the whole tank. Test plate bracket: The bracket is fixed in the slot and can be hung vertically. (Related Instrument: Magnetic Stirrer)
3.8.3 Test conditions
3.s.3.1 Salt water solution: Refined edible sea salt in accordance with GB2721 is used to prepare 3% brine solution; It is also possible to use natural seawater in accordance with the first category in GB 3097, but the transition should be made to the paper. The saline solution is changed every cycle (21d).
3.8.3.2 Temperature: generally kept at (23t2)°C. Unless otherwise specified for special coatings (such as oil energy and cutting chamber), the hot brine immersion test temperature should be kept at (40t2)°C
3.8.3.3 Stirring: When the solution reaches the constant temperature condition as required, the stirring will be stopped.
3.8.4 Operational Points
The surface treatment of the substrate is sandblasted or shot blasted, and the two sides of the steel plate reach GB8923 b1 grade, and the surface roughness Ra is (50~70) μm. It can also be used for surface treatment by grinding with abrasive cloth or acid and alkali method. The coating on both sides of the steel plate should be brushed or sprayed, and the number and thickness of the coating supporting system are shown in Table 6:
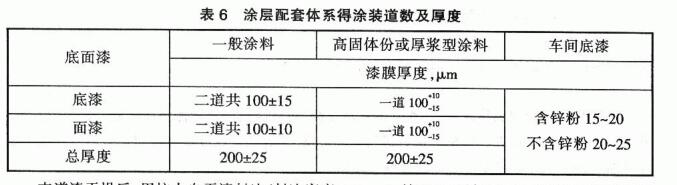
After the dry operation of the last paint, use the water-resistant self-drying paint to seal the edge (edge width 3~5mm), and place it for 7 days before testing. Inspect, record or photograph the sample before the test.
Inject a sufficient amount of brine into the test drum, open a stirring system, and after the temperature remains constant, hang the sample so that three-quarters of it is soaked in the brine solution. General brine immersion test per cycle (21d), of which the last 2 hours do (40t2) °C hot brine test (special requirements do (80, 2) °C), take out the sample at the end of each cycle, carefully rinse the sample with tap water, gently dry it with paper or soft cloth, check the damage phenomenon, and put the sample back in the test dregs.
When the test is carried out according to the specified period or time, the sample should be taken out, the sample should be rinsed with a tap water group, and gently dried with a paper or soft cloth to check the damage phenomenon.
3.8.5 Determination of Results
Check the discoloration, loss of light, blistering, rusting, falling off and cracks of the coating system, and compare the pre-test notes: table or photography, evaluate the damage phenomenon of the thousand membranes, and record or take pictures, without considering the influence of the edge (10mm around). Whether it is qualified or not, the product standard stipulates that no less than two samples meet the product standard requirements.
The evaluation of the phenomenon of loss of light, discoloration, blistering, rust, peeling and cracking in the lacquer belly can be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 1766-1995 "Rating Methods for Aging of Color Delivery and Varnish Coatings".
3.9 Precautions
3.9.1 The material of the substrate, the treatment of the substrate and the thickness of the paint film shall be strictly in accordance with the product standards. The uniformity of the film thickness, the good drying of the paint film: No, whether there are defects on the surface of the paint film (such as the size of brush marks, whether there are particles, shrinkage holes), and the quality of the back and edge sealing of the sample may have an impact on the test results of its performance.
3,9.2 For each test, the solution should be replaced again or carried out according to the regulations.
3.9.3 It is recommended to use a container for a sample, especially if the test liquid has a high electrolytic effect, the immersion sample should be at least 30mm away from the inner wall and bottom of the sample, and the interval between the samples should be at least 30mm, so as to avoid the interaction between the samples, electrochemical corrosion, and accelerate the damage.
- 1Overview of resistant coatings
- 2Characteristics and construction points of corrosion resistant Coatings
- 3Application of corrosion resistant coatings on reinforced concrete surfaces
- 4Technological development and application of heavy anticorrosive coatings
- 5Application and performance analysis of silicon diffusion coatings
- 6Research and application of chromium diffusion coatings
- 7High temperature oxidation and corrosion resistance performance and application of aluminum diffusion coatings
- 8Zinc diffusion coating performance process and application
- 9Chromate coating technology and its application








