Process methods and characteristics of surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment
Both surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment are heat treatments on the surface of parts. Surface heat treatment only changes the surface structure and properties, while chemical heat treatment adjusts the different tissue properties of the surface and the core by changing the surface composition. Since most of the working conditions of the parts have high requirements on the surface properties, such as fatigue resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., the use of surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment technology can give full play to the potential of the material, improve the performance and prolong the service life. Improve security.
Surface heat treatment mainly includes induction hardening, flame quenching, etc. Chemical heat treatment mainly includes carburizing, nitriding, boronizing, sulfurizing, metalizing, etc. The quality control of surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment mainly includes process method selection, process parameter optimization, equipment, tooling and infiltration agent selection, production operation control, post-infiltration heat treatment control, etc.
(1) Process method selection
There are many methods of surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment, each of which has its own characteristics, and can endow the surface of parts with one or another excellent performance. However, any process method has limitations, and there is also a certain limit to the improvement of the surface properties of parts. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively analyze and compare according to the performance requirements and various heat treatment process characteristics, and select the appropriate process method.
The characteristics of commonly used surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment methods are shown in the table. Surface hardening such as induction hardening and flame hardening is mainly used to improve the fatigue resistance and wear resistance of parts (related instruments: wear-resistant testing machine), such as machine tool transmission gears, machine tool spindles, internal combustion engine crankshafts, camshafts and other parts, often using medium carbon steel Or medium-carbon alloy steel, surface quenching and low-temperature tempering after normalizing or quenching and tempering, while cold-rolled parts are mostly made of high-carbon steel surface quenching. The main purpose of carburizing is to improve wear resistance, improve fatigue resistance while maintaining good toughness (recommended instrument: bending Tester), and because of its fast penetration speed and strong bearing capacity, it is widely used in various mechanical manufacturing industries, such as Various gears of automobiles and tractors, etc. Carburizing mostly uses low carbon steel or low carbon alloy steel, quenching and tempering at low temperature after carburizing. Nitriding can increase the surface hardness of the parts to a greater extent, improve the wear resistance, seizure resistance, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of the parts. Medium carbon alloy steel or stainless steel is mostly used for nitriding. The parts need quenching and tempering treatment before nitriding. There is no need to quench after nitrogen, and the heat treatment deformation is small, but the hardened layer is shallow and the bearing capacity is low. It is mainly used for crankshafts, splines, valves, plungers and petrochemical machinery. The sulfurized layer has good anti-friction performance, and can be used for gears, bearing sleeves and tools and molds, significantly prolonging the service life. The hardness of the boronizing layer is extremely high, up to 1300-2000HV, with good abrasive wear resistance and good anti-seizing performance, and is used for high wear-resistant parts such as cold working molds. Aluminizing is mainly used to improve the high temperature oxidation resistance of parts, and chromizing can greatly improve the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of parts. In practical application, you can choose a suitable surface heat treatment or chemical heat treatment method according to the service conditions of the parts , or you can choose two or more methods to carry out composite surface heat treatment, such as carburizing - boronizing, carbonitriding - low temperature sulfurizing , Carburizing - high frequency induction hardening, etc.
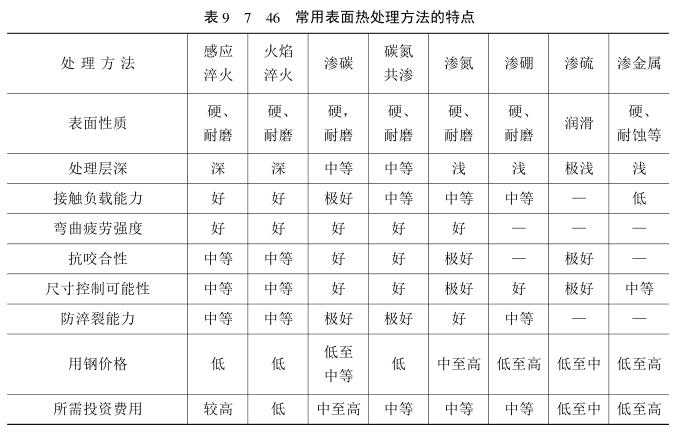
(2) Surface quenching quality control
1. Raw material composition and tissue control
Surface quenching heating is rapid heating, the phase change is insufficient, and the structure and composition are not uniform enough. In order to obtain stable heat treatment quality, the composition of the surface quenching steel and the structure state before treatment must be strictly controlled. The carbon content range of the surface quenching steel is often selected. For narrow selected steel, quenching and tempering treatment is recommended for preliminary heat treatment to obtain uniform sorbite with fine and uniform grain size, usually larger than grade #. Before quenching, there should be no decarburization and microcracks on the surface of the workpiece to avoid the formation of soft spots, insufficient hardness and cracking.
2. Process parameter selection
(1) Rapid heating makes the phase transition points of steel Ac1, Ac3, Acm, (increased, so the heating temperature of surface quenching is higher than that of ordinary quenching!))*, generally using Ac3+ (120-180°C).
(2) There are two different heating methods for surface quenching, namely time-directed heating and continuous heating. In mass production, in order to improve production efficiency, the simultaneous heating method should be used as much as possible under the condition of the equipment. For single or small batch production, for shaft and flat workpieces, the continuous heating method should be used so that Reduce the cost of tooling such as fixtures and sensors.
(3) Due to the poor heating uniformity of the surface quenching, in order to improve the heating uniformity and tissue uniformity, the heating device (induction coil or burner) and the workpiece should move back and forth multiple times.
(4) There are two ways of surface quenching cooling, spray cooling and immersion cooling. The workpieces with simple shapes and low deformation requirements are usually spray cooled, while the workpieces with complex shapes and strict deformation requirements are cooled with oil.
(5) Due to the rapid heating during surface quenching, the grains do not have time to grow, the composition is not very uniform, and the structure stability is poor, so the quenching medium with a faster cooling rate should be used for surface quenching. Carbon steel surface quenching can use water and organic quenching medium aqueous solution , alloy steel surface quenching can use organic quenching medium aqueous solution or oil.
(6) After surface quenching, the workpiece should usually be tempered at low temperature to reduce residual . Furnace tempering or self-heating tempering can be used.
(7) Induction surface hardening is easy to control and realize automation, with high quality and suitable for mass production. Flame surface quenching is simple and easy, and can handle a wide range of shapes, sizes, and weights of workpieces, but it is difficult to control during production. It can be used in small quantities and batch production, especially for large and complex special-shaped workpieces.
3. Equipment and tooling selection
(1) Induction hardening and flame hardening are respectively equipped with special induction heating power supply, combustion gas and oxygen gas supply devices, all of which need to meet the technical conditions and technical safety requirements.
(2) According to the shape and size of the workpiece, set up a one-time quenching machine tool or a mobile quenching machine tool, and it should meet the accuracy shown in the table
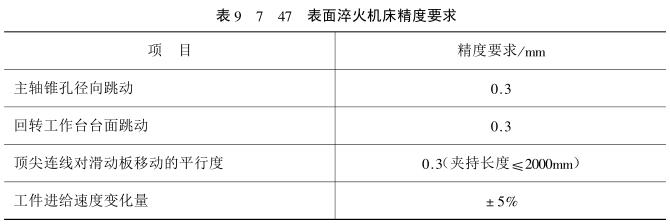
(3) Photoelectric pyrometer or infrared radiation thermometer (recommended instrument: temperature measuring paper) is used to measure the surface temperature of the workpiece, and the working parameters of the equipment are continuously tracked and measured to control or adjust
(4) Induction quenching requires a reasonable design of the inductor; flame quenching requires a reasonable design of the burner, and proper adjustment of the distance between the burner and the workpiece, the pressure and ratio of combustion gas and oxygen.
4. Production operation control
(1) The surface quenching operation should be carried out in strict accordance with the process regulations and operating procedures. Pay special attention to the reasonable and uniform gap between the sensor or burner and the workpiece , and the timing of cooling start and transfer speed should be appropriate.
(2) Since the corners of the workpiece have a more prominent sharp corner effect on the surface heating, in order to prevent local overheating, in addition to the chamfering required for the corners, additional rounded corners, cover plates, shields and stays can also be used for surface quenching. leftovers and other measures.
(3) During surface quenching, the surface quality of the workpiece before treatment is greatly affected. Before quenching, it must be cleaned strictly to remove the oxidation decarburization layer, and remove surface oil, water and other dirt.
(4) After surface quenching, the internal stress of the workpiece is relatively large. In order to prevent cracking, tempering or self-tempering should be carried out quickly to prevent placement cracks
- 1Working principle and application of UV coating Cupping testing device
- 2Application of shakeout Tester in organic polymer film abrasion resistance testing
- 3Application of shakeout Tester in aluminum surface coating abrasion resistance testing
- 4Paint film abrasion resistance and test method thereof
- 5Polyethylene (PE) coating indentation hardness inspection and its importance in pipeline corrosion protection
- 6Paint film abrasion resistance and its test method - rubber abrasive wheels method
- 7Determination of abrasion resistance of paint film
- 8Determination method of paint film abrasion resistance and its importance
- 9Coating performance testing: the key to ensuring quality coatings







