Application of Water Quality Analyzer in Swimming Pool Water Quality Detection
Water quality testing is essential for the management of swimming pools. It ensures the hygiene and safety of swimming pool water bodies, protects the health of swimmers, and provides a good swimming experience. Through water quality testing, key indicators in swimming pool water can be monitored, such as residual chlorine, pH value, dissolved oxygen, total alkalinity, turbidity, etc., as well as possible bacteria, viruses and other pollutants. In this way, water quality problems can be detected in a timely manner, and necessary regulatory measures can be taken to ensure that the swimming pool water body is clean, sterile, and meets hygiene standards and regulatory requirements. This not only helps prevent the spread of pool-related diseases, but also improves swimmer comfort and satisfaction, while protecting the long-lasting use of the pool facility.
Swimming pool water quality testing needs to pay attention to the following indicators to ensure that the water quality meets health and safety standards:
Free residual chlorine: Disinfectants added to swimming pools, such as chlorine, can form free residual chlorine. Appropriate concentrations of free residual chlorine can effectively destroy bacteria and viruses in water.
Total residual chlorine: Total residual chlorine includes free residual chlorine and bound residual chlorine and is used to assess the overall effect of disinfectants.
pH: The pH of swimming pool water should be in the appropriate range (usually 7.2-7.8) to ensure that the water body is not irritating to the skin and eyes, and to maintain the effectiveness of the disinfectant.
Water temperature: Control of water temperature is critical to swimmer comfort.
Turbidity: Turbidity indicates the amount of suspended matter in the water, and high turbidity may affect the transparency and visual effects of the water.
Pool pH (TA): TA is an overall indicator of the pH of swimming pool water and is essential for maintaining the stability and suitability of the water body.
Pool Hardness (CH): Hardness indicates the amount of calcium and magnesium ions in the water, and the right hardness helps prevent scale and corrosion problems.
Swimming Pool Alkalinity (CYA): CYA is the amount of stabilizer in swimming pools that protects free residual chlorine from the sun's UV rays.
Swimming Pool Cyanuric Acid (CYA): CYA is the amount of sunscreen that can help reduce the sensitivity of swimmers' skin to UV rays.
In addition, the water quality of swimming pools needs to be regularly tested and monitored in accordance with relevant regulations and standards to ensure that the water quality meets hygiene and safety requirements. The frequency and requirements of water quality testing may vary by region and regulations. Therefore, it is recommended to follow local water quality testing requirements when operating and maintaining swimming pools, and regularly test and adjust swimming pool water. Generally, a water quality analyzer is used for testing, and a Detector with corresponding parameter functions should be selected.
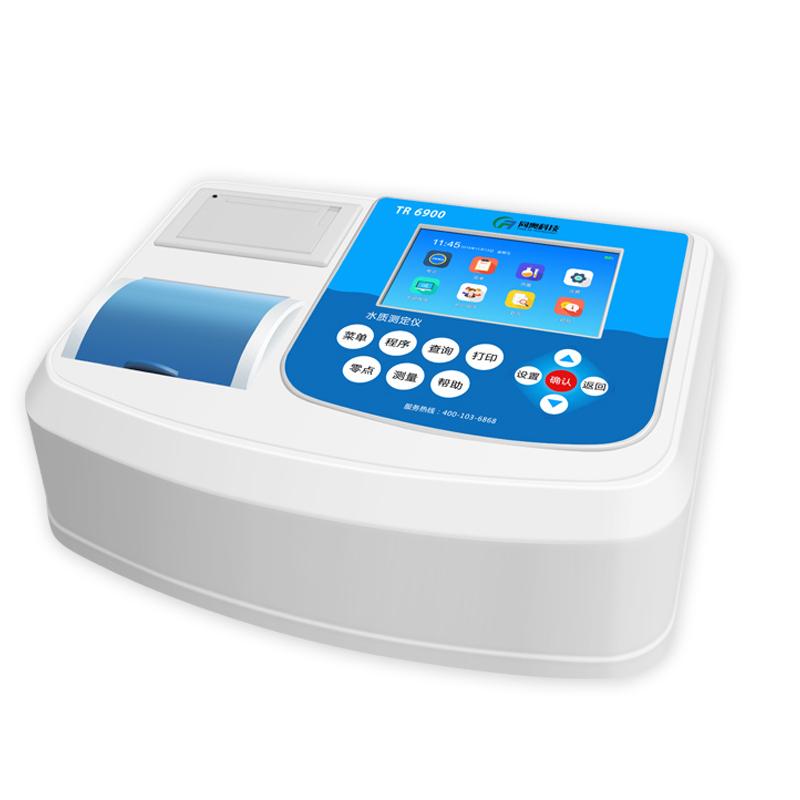

Detection method
When using a water quality Tester to test the water quality of a swimming pool, you can follow the steps below:
Prepare the test instrument: Make sure the water quality test instrument is calibrated and prepare the required sensors, electrodes or test boxes according to the instruction manual.
Select the corresponding detection method according to the parameters to be measured: Common parameters of swimming pool water quality include residual chlorine, pH value, dissolved oxygen, total alkalinity, turbidity, etc. According to needs, select the corresponding detection method and test plan.
Take water samples: Take samples from the swimming pool to ensure that the water samples are representative. Dedicated water sample collection containers can be used to avoid contamination or other effects on the sample.
Carry out water quality testing: According to the selected detection method, add the water sample to the detection instrument, or insert the sensor or electrode into the water sample, and measure according to the instructions of the instrument.
Record and interpret results: Record measurements and interpret them according to set standards or guidelines. Compare measurements with applicable water quality standards and assess the hygiene of water bodies.
Take necessary measures: According to the measurement results, if water quality problems are found or exceed the allowable range, take corresponding measures to adjust and correct. This may include adding appropriate disinfectants, adjusting pH, increasing or decreasing the amount of chemicals, etc.
Regular Monitoring: Conduct regular water quality tests to ensure the continued hygiene and safety of swimming pool water bodies. As needed, a monitoring plan can be developed, including testing frequency and monitoring parameters.
It is important to use the correct instruments and methods for water quality testing and follow the relevant operating practices and safety measures. If you are not sure how to do this, it is recommended to consult a professional or follow the instructions for use of the instrument.
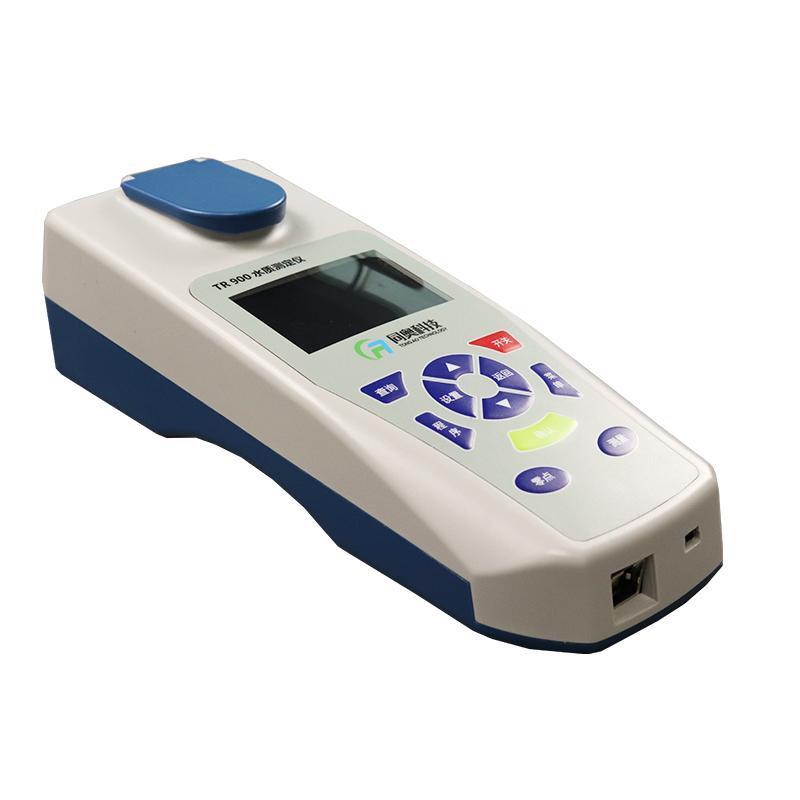

Through the use of water quality analyzers, swimming pool managers can keep abreast of the condition of swimming pool water bodies, and take necessary control measures to ensure that water quality meets hygienic standards and regulatory requirements, providing swimmers with a safe and clean swimming environment.
- 1Application of residual chlorine Detector in canned food factory
同奥科技
- 2Residual chlorine, total chlorine reagent simple operation process
同奥科技
- 3Basic principle and application of residual chlorine meter in waterworks
- 4How does a water quality Tester measure turbidity?
- 5What is ORP in solution testing?
- 6What are the water quality testing equipment required by the laboratory?
- 7American Ren's JENCO water quality analysis full series of instrument model selection table
- 8雷磁水质分析仪DZS-706A/706B/706C三种型号对比
- 9AQ3070 Portable Residual Chlorine and Total Chlorine Colorimeter Description