Waterborne architectural coatings detection method
Water-based architectural coatings, especially interior and exterior architectural latex paints, play an important role in modern architectural decoration. In order to ensure that the quality and performance of these coatings meet expected standards, a series of scientific testing methods must be used. This article will delve into the main testing methods of water-based architectural coatings, covering container status, dispersion fineness, pH value, consistency, freeze-thaw stability, drying time, contrast ratio, sag resistance, roller spray paint, paint film appearance, Alkaline resistance and resistance to scrubbing and cleaning.
State in the container: Ensure the initial state of the paint
The condition in the container is an important indicator for evaluating the primary quality of paint. Skinning, thickening, gelling, delamination, settling, agglomeration and other phenomena may affect the use and performance of the coating. Through visual methods, such as the condition in the container of 3011 in the US Federal Test Method Standard No. 141, you can quickly determine whether the paint is in good condition.
Dispersion fineness: measures the degree of dispersion of paint pigments
Dispersion fineness is an important parameter for the degree of dispersion of pigments and extender pigments in coatings. The size of the fineness directly affects the hiding power and appearance finish of the paint. The scraper Fineness Meter method, such as the national standards GB/T1724, GB/T6753.1 and the American standard ASTM D1210, uses the scraper Fineness Meter method, which provides us with a reliable means of measuring dispersion fineness.
pH value: an indicator of stability
pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a coating solution and is critical to the stability of the coating. The pH value of latex paint generally ranges from 5 to 10, and changes in it can indicate acceptable changes in the stability and performance of the paint. GB/T 1717, ASTM E70 and other standards adopt the pH meter method to ensure that the product remains stable during storage.
Consistency: Key to spreadability and flow
Consistency refers to the internal resistance of paint when flowing and is a key parameter to measure the spreadability and fluidity of paint. GB/T 9269 and ASTM D562 use Stormer viscometer to measure the consistency of coatings to ensure the uniformity and workability of the product.
Freeze-thaw stability: resistance to cycle testing
The ability of latex paint to maintain its original properties after it undergoes freeze and thaw cycles is called freeze-thaw stability. This performance index is evaluated through a series of cyclic tests, such as GB/T 9268 and ASTM D2245, to ensure that the coating can still maintain its excellent performance under extreme conditions.
Drying Time: Master Construction and Maintenance Time
Drying time refers to the time required for paint to form a solid paint film under specified conditions. This indicator is affected by the composition of the paint and environmental conditions, and is directly related to the construction schedule and maintenance cycle. Methods such as GB/T 1728, GB/T 6753.2, GB/T 9273, GB/T 9280 and ASTM D1640 provide us with multiple ways to measure drying time.

Contrast Ratio: Determine the hiding power of a coating
Contrast ratio is the ratio of reflectance of the same paint film on black and white substrates. This ratio is used to determine whether a coating completely covers the substrate, eliminating human error and suitable for white and light-colored paints. Standards such as GB/T 9270, GB/T 5211.17 and ASTM D2805 use the reflectometer method to measure contrast ratio.

Anti-sag: Prevent the coating film from flowing unevenly
When paint is applied on a vertical surface, due to poor sagging resistance or improper application, the paint film may flow locally, forming an uneven coating, which is called sagging. GB/T 9264 and ASTM D4400 use multi-tooth scrapers of different specifications to evaluate coatings to ensure their sag resistance.

Roller Splatter: A measure of paint spatter during construction
Roller coating is a commonly used construction method for architectural coatings, and roller splash paint is a method to evaluate the splash resistance of paint. ASTM D 4707 uses drawings of certain specifications to collect the size and density of paint spots splashed on it, and compares them with standard drawings to evaluate the paint's splash resistance.
Paint film appearance: the key to decorative indicators
The appearance of the paint film is a key indicator of the decorative performance of the paint. After the paint film dries, conduct a visual inspection, including the flatness and uniformity of the paint film, as well as whether there are pinholes, shrinkage holes, sags, brush marks, etc. GB/T 11186.1~3, ASTM D 2244 and other methods provide standards for the measurement of gloss and color.
Alkali resistance: Prevent the influence of alkalinity of the substrate on the coating
Alkali resistance is the resistance of the paint film to alkali attack. The alkalinity of substrates such as cement may have adverse effects on coatings. Standards such as GB/T 9265 and ISO 2812 use saturated and calcium hydroxide dipping methods to determine the alkali resistance of coatings.
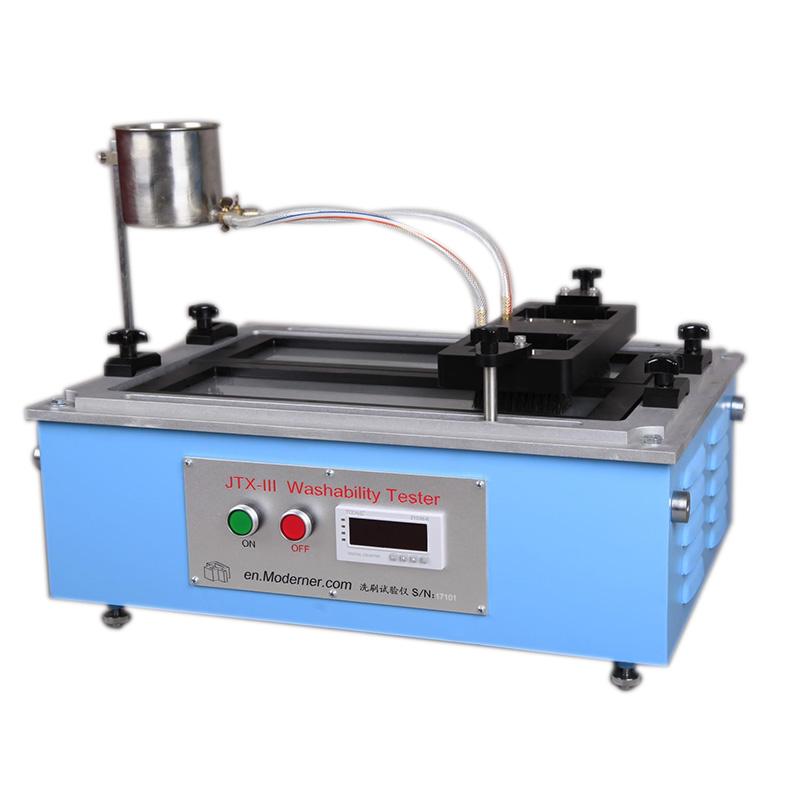
Scrub-resistant and washable: ensures long-lasting cleanliness
Scrubbing resistance is the ability of a paint film to remain undamaged by repeated scrubbing with detergent media, while cleanability is the ability of a paint film to maintain its original performance after being scrubbed to remove dust, dirt and surface stains. The two test methods include GB/T 9266, ASTM D 2486, ASTM D3450, ISO 11998, etc.

Testing methods for waterborne architectural coatings are a critical step in ensuring product quality and performance. By measuring the state of the container, dispersion fineness, pH value, consistency, freeze-thaw stability, drying time, contrast ratio, sag resistance, roller paint splash, paint film appearance, alkali resistance, and wash resistance and cleanability With an in-depth understanding of other aspects, we can better understand and control the properties of water-based architectural coatings. With the continuous advancement of science and technology, I believe that the coating industry will usher in more innovative detection methods to provide more reliable and efficient coating solutions for the construction industry.
- 1Basic Principle and Application Analysis of Paints drying time Tester
- 2Coating performance testing: leveling & sagging
- 3Summary of drying time determination method for paint film and putty film
- 4Several Determination Methods of Coating drying time
- 5Coating leveling and sagging
- 6Coating performance testing: ensuring the efficiency and mass of the painting process
- 7Film drying method: natural drying, heating drying, irradiation curing and gas phase curing
- 8Coating levelling and sagging performance test
- 9Explore the method and application of Coating sagging test
-
-
-
-
-
JINGKELIAN QNF Backtack Tester 3 pcs$ 190.00
-







