Measurement of expansion coefficient of film
Changes in temperature have a significant effect on changes in paint film properties. In practice the temperature can vary from -60 to +60°C, ie the temperature can vary up to 120°C. Rapid changes in temperature cause the paint film to expand and contract alternately, resulting in reduced durability of the paint film. Therefore, particularly stringent requirements are imposed on coating films that are subject to sharp temperature changes.
The durability of the paint film is particularly significantly reduced when the material used to manufacture the painted object has a different coefficient of thermal expansion than the paint film. In this case, as the temperature changes, the degree of expansion of the painted object and the paint film is different, and the degree of shrinkage is also different accordingly. The tension generated in this way may be greater than the adhesion force, thus causing premature failure of the paintwork. When the elasticity of the paint film is not enough, this tension will cause the formation of cracks and strands. In the case of multilayer coatings, a more complex phenomenon occurs. Multilayer coatings are generally systems composed of several paint layers (not less than two layers) that differ in composition and physical and chemical properties. For example this multi-layer system could consist of a long oil base coat (1st coat), a short oil base coat (2nd coat) and nitro enamel (3rd coat). Each paint layer in this system has different expansion coefficients, which can cause severe internal stress when the temperature changes, resulting in damage to the coating film.
So far, there is no complete information that can show the special influence of temperature changes on the properties of paint films, because in fact, changes in temperature are often accompanied by changes in a series of factors (light, humidity, etc.).
Brusilovsky and other comrades and others devised a special apparatus for the study of the thermal expansion of nitrovarnish films. It has been affirmed that there is a certain relationship between the expansion coefficient and contraction coefficient of the oil-based varnish film, the composition of the film-forming material and the pigment composition, and also has a certain relationship with the aging degree of the film. For example, it has been found that when the oil-based varnish film is aging, its slow expansion coefficient and shrinkage coefficient are reduced; and after adding pigments, the swelling coefficient and shrinkage coefficient of the paint film increase sharply.
Since the expansion coefficient of organic matter is generally larger than that of metal, the change in the length of the paint film plays a greater role than the change in the length of the base plate. For example, if the bottom plate is made of iron, the length of the metal changes by about 0.02% when the temperature changes by 20°C; and when the temperature range reaches 60°C, the maximum secondary length of iron is only about 0.07% . Under the same conditions, the change in the length of the paint film is generally greater than the change in the length of the metal. (Related instrument: furnace temperature tracker)
It is of great interest to observe the behavior of the paint film at low temperatures which often make the paint film brittle. It has been proved by the research work that when the temperature changes from +20°C to -20°C, the expansion coefficients of various nitric acid vitrified paints, acid paints and phenolic paint films are much larger than those of metals. This difference is not very significant in aluminum and aluminum alloys whose coefficient of expansion is about twice that of iron. From this, it can be concluded that if the temperature expansion coefficient of the paint coating film is significantly greater than the corresponding coefficient of the metal, the expansion or contraction of the coating film will be much larger than that of the base plate when the temperature changes. Cause the corresponding deformation of the coating film (wrinkle, moiré, etc.). The more frequent the action of temperature changes, the faster the coating film should be damaged.
For example, when cooling different paint films to 40°C (the bottom plate is made of steel), the following deformation values can be obtained: nitro varnish - 0.28%, modified phenolic resin oil-based varnish - 0.41%, tung oil and Alkyl phenol resin-based oil-based varnish - 0.57%. With the help of the thermal expansion curve of the varnish film and its change with the degree of aging, the formula of paint materials with certain special purposes can be formulated.
Many instruments have been designed for the determination of the slow expansion coefficient of paint films. In Kogbetliev's apparatus, the stripped paint film to be tested is placed on a glass surface and heated by hot air. One end of the paint film is fixed in the movable center, while the other end is placed freely on the glass surface. Changes in the surface of the paint film caused by temperature changes can be measured using a microscope. The whole set of equipment is installed in a wind tunnel that can generate thermal air flow.
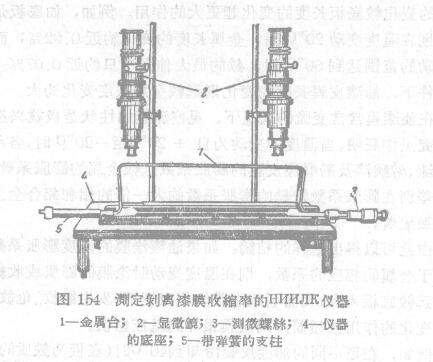
Use the HNNJIK instrument (Figure 154) to measure the shrinkage of the paint film, and the peeled paint film should be placed on the metal table 1. The stage device has two sets of microscopes 2 with an accurate and fixed distance between them. The metal table can be moved by measuring screws 3 .
When the shrinkage rate is determined according to the above method, the peeled paint film is placed on glass or metal, and the test results obtained are therefore inaccurate.
This shortcoming can be eliminated if the Orlov instrument is used for determination. On this instrument, the cut-off paint film is placed on the surface of the mercury. The tank containing mercury can be heated by an electric burner.
Using a metallographic microscope embedded with a special additional lens with controlled graduations under the objective lens, the change in the size of the paint film can be observed and measured.
HNNJIK has worked out a fairly accurate method for measuring the linear expansion coefficient of paint film, and designed an instrument without microscope for this purpose.
- 1Polyurethane-graphene composite prepative film
- 2The relationship between film with light, semi-light and no light and actual use
- 3Glossmeter for paints film gloss detection
- 4How can ultra-thin coating film ignore material fineness?
- 54 influencing factors of film precision control
南北潮商城 - 《www.nbchao.com》
- 6ASTM paint film physical properties related testing standards
- 7Film laminating FAQ and solution
- 8How-to video of preparing precise film layers with film rods
- 9Defect Analysis of Whitening Phenomenon in Coating Construction Process
-
JINGKELIAN QNF Backtack Tester 3 pcs$ 190.00
