Liquid viscosity measurement and application
Viscosity is the ability of a liquid to hinder the relative motion of molecules due to the interaction between its molecules under the action of external forces, that is, the resistance to the flow of liquids. This resistance is usually expressed as the ratio of the external force exerted on the liquid to the resulting flow velocity gradient. The viscosity of a liquid can be defined as the ratio of its shear force to the shear rate, i.e., the dynamic viscosity, which is measured in pa·seconds (Pa·s). If the effects of viscosity and density are taken into account, kinematic viscosity is used, which is defined as the ratio of dynamic viscosity to liquid density in square meters per second (m²/s).
The importance of viscosity
Viscosity is one of the important indicators of coating products and is a reliable method for determining the molecular weight of polymers in paints. In the process of lacquering, too high viscosity will produce gelatinization, and too low viscosity will make the solvent that should be added unable to be added, which will seriously affect the performance of the paint film. In the construction of coatings, too high viscosity will make the construction difficult, and the leveling of the paint film is poor; Too low viscosity can cause sagging and other ills. Therefore, the determination of the viscosity of the coating is necessary for the control of the coating production process and to ensure the quality of the final coating product.
Methods for measuring the viscosity of liquid coatings
There are many viscosity testing methods for liquid coatings, which are suitable for different varieties. Common detection methods include outflow method, vertical ball drop method, bubble method and set shear rate method.
1. Outflow method
The principle of the outflow method is to use the gravity flow of the sample itself to measure its outflow time to convert it into viscosity. According to the provisions of GB/T 1723-93 "Paint Viscosity Determination Method", the specific operation is to plug the Viscosity Cup outflow hole with a plug rod or finger, pour in the sample, and measure the time required from the beginning of the outflow to the interruption of the flow column, and the result is measured in seconds (s). This method is suitable for liquid coatings with Newtonian or near-Newtonian types, such as low-viscosity varnishes and basecoats.
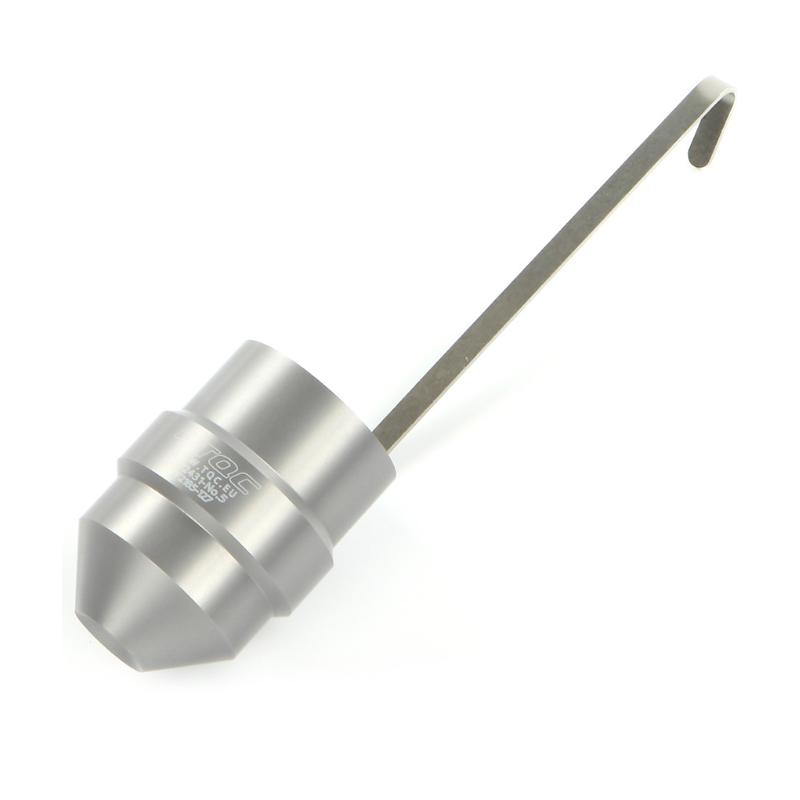

2. Drop the ball
The principle of the falling ball method is to determine the viscosity of a liquid by using the speed of the vertical descent of the solid ball in the liquid under the action of gravity. The specific operation is to measure the time it takes for a steel ball to pass through the distance between the upper and lower two scale marks of the falling ball viscometer, and the result is expressed in seconds (s).
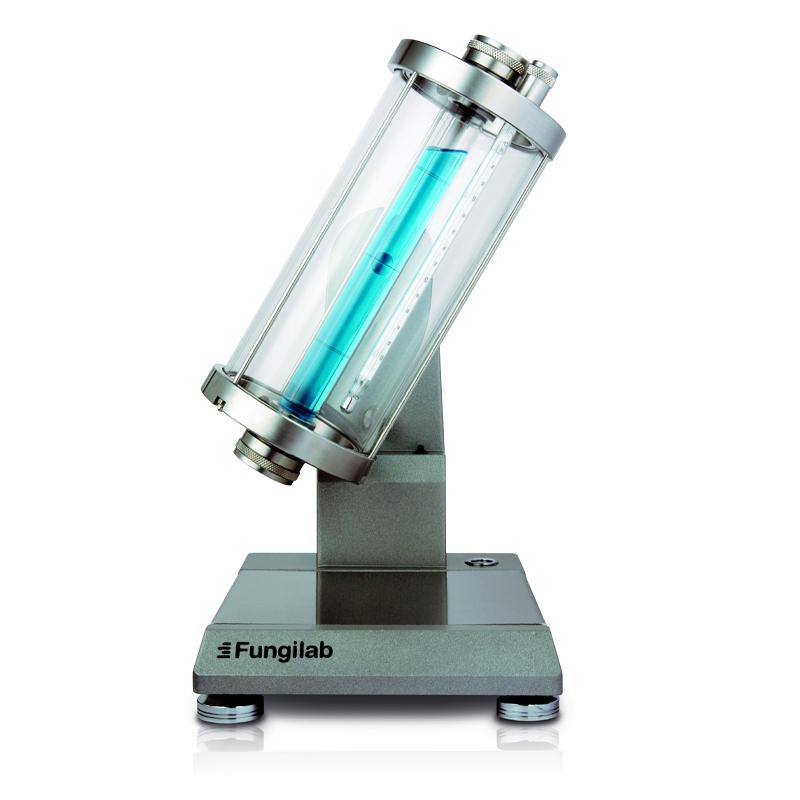

3. Bubble method
The principle of the bubble method is to determine the viscosity of a coating product by using the flow rate of air bubbles in a liquid. The specific operation is to load the sample to be tested into the tube, and leave a bubble space, quickly flip the test tube vertically 180°, the sample self-weight downflow, the bubble rises to touch the bottom of the tube, and the rising time of the bubble within the specified distance is measured, and the result is expressed in seconds (s).
4. Set the shear rate method
The principle of setting the shear rate method is to rotate a cylinder, disc or paddle in a paint specimen to produce a gyratory flow, and to measure the stress required to achieve a fixed shear rate, which is converted into viscosity. According to the provisions of GB/T 9751.1-2008 "Determination of Viscosity by Rotational Viscometer for Pigments and Varnishes", the specific operation is that the specimen is placed between two concentric circles and flows in the annular void, and the reading indicated by the pointer is multiplied by the rotor coefficient to obtain the viscosity, and the result is expressed in Pa·s.
In recent years, with the development of science and technology, viscosity measurement methods and equipment have been continuously improved. Today's viscometers can measure the viscosity of conventional coatings not only in the study of polymer materials, nanofluids, and biological fluids. The intelligent viscometer can achieve high-precision and automatic viscosity measurement through computer control and data processing, which greatly improves the measurement efficiency and accuracy.
In practical applications, viscosity measurement is widely used in petroleum, chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries. For example, in the petroleum industry, by measuring the viscosity of crude oil, its fluidity and processability can be evaluated; In the food industry, viscosity measurement helps to control the taste and quality of products; In the pharmaceutical industry, the viscosity of a pharmaceutical solution directly affects its injection performance and efficacy.
As an important indicator of liquid flow characteristics, viscosity has an important impact on the production and construction of coatings. With the correct selection and application of viscosity measurement methods, the production quality of coatings can be effectively controlled, and the performance and effectiveness of the final product can be guaranteed. With the advancement of technology, viscosity measurement will be more accurate and convenient, providing strong support for the development of various industries.
- 1Measuring method of coating viscosity
- 2Viscosity: Microscopic forces inside liquids shape macroscopic properties
- 3Thermostatic bath working principle and its application in viscosity measurement
- 4Rotational viscometer measurement of molasses viscosity
- 5Chocolate viscosity measurement with Rotational Viscometer
- 6Polymer Solution Viscosity Testing Solutions
- 7How to test the viscosity of lithium battery stirring slurry?
- 8How is the viscosity of the paste tested?
- 9How to measure the viscosity of excipient hydroxypropyl methylcellulose?