Determination of Varnish permeability performance by standard methods
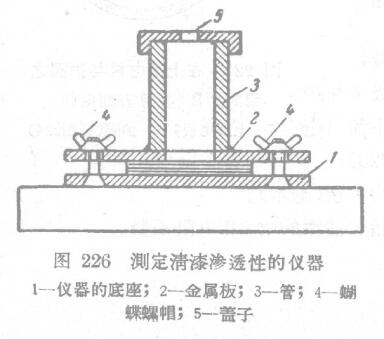 Varnish permeability can be measured by means of the apparatus shown in Figure 226. This instrument consists of a metal base 1 and an upper part of the instrument (consisting of a metal plate 2 and a pipe 3 supplying the injection varnish). The upper part of the instrument is tightly pressed on the lower part by the butterfly nut 4. On the tube 3 (110 mm high, 35 mm internal diameter) a cap 5 with three small through-holes is screwed on.
Varnish permeability can be measured by means of the apparatus shown in Figure 226. This instrument consists of a metal base 1 and an upper part of the instrument (consisting of a metal plate 2 and a pipe 3 supplying the injection varnish). The upper part of the instrument is tightly pressed on the lower part by the butterfly nut 4. On the tube 3 (110 mm high, 35 mm internal diameter) a cap 5 with three small through-holes is screwed on.
Place one; beam (50 layers) NO288 standard white linen on the base of the instrument, the size of which is 100x100 mm. After the upper part of the instrument is tightly pressed against the bottom, the varnish to be tested is poured into the tube 3 at a temperature of 20°C (±5°C) until it is lower than the marking line 10 mm above the tube (the height of the varnish column is 100 mm). Care should be taken not to allow the lacquer to get on the top of the white linen. After 15 minutes, the varnish was poured off and the instrument was disassembled. (Related instruments: constant temperature and humidity Test Chamber)
The number of layers of calico penetrated by the varnish is a measure (indicator) of the permeability of the material. Even if traces of varnish are visible from one side of the white linen, it can be considered that the layer of white linen has been penetrated. If during the test there is condensation of the film-forming substance and its precipitation on the first layer, this phenomenon shall be recorded in the record.
- 1What are the main differences between Varnish and Paints?
- 2What is varnish? (for packaging and printing)
- 3Natural resin paint
- 4Coatings performance requirements for concrete surface protection (corrosion protection)
- 5What is enamel?
- 6What is varnish?
- 7Classification of Coatings: Classification Principles and Introduction to Basic Products
- 8Paint Film Appearance and Optical Properties inspection method--Paint Film Color Determination Method
- 9How to determine the lacquer acid value for Paints and varnishes?







