Application of Dyne pen in surface tension measurement
A dyne pen, also known as a surface Tension Tester, corona pen, or printer pen, is a tool used to measure the surface tension of materials. It determines the surface energy of a material by coating a test solution with known surface tension on the surface to be measured and observing its wetting. It is widely used in industrial production lines, especially in the fields of coatings, printing and plastic processing, to ensure the quality of material surface treatment and optimize product performance.
Test principle
Surface tension is the contractile force exhibited by the surface of a liquid due to the gravitational pull between molecules, which affects the contact behavior between the liquid and the solid surface. In the dyne pen test, the definition of surface tension helps to understand the hydrophilic or hydrophobic nature of the material. When the test liquid comes into contact with the material to be measured, its degree of wetting reflects the surface tension value of the material.
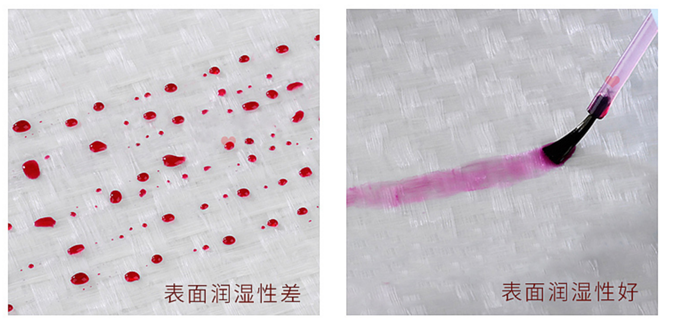
The test principle is to determine the surface tension of a material by using test liquids with different surface tensions, marking a line on the surface to be measured and observing the behavior of the liquid. If the liquid quickly forms water droplets on the surface and does not diffuse, the surface tension of the material is low; Conversely, the rapid diffusion and uniform distribution of the liquid indicates a high surface tension. This method is simple and effective, and accurate surface tension data can be obtained quickly.

Test Method:
In the Dyne pen test, choosing the median value as a starting point is an effective method. This is because the surface tension value of the material to be measured may be uncertain in practice, so choosing a medium value (e.g., 40 mN/m) as a starting point can help the Tester quickly determine the surface tension range of the material. At the heart of this process is the gradual adjustment of the surface tension value of the Tester to find an accurate value that matches the material to be measured.
At the beginning of the testing process, place the dyne pen perpendicular to the surface of the material to be measured and apply the appropriate pressure to draw a line on the surface. The surface tension value of the test pen should be selected as the middle value, and then the infiltration of the liquid after the scribing should be observed. If the liquid quickly wets the surface and forms water droplets within two seconds, the surface tension of the material is higher than that. If the liquid does not diffuse significantly or beads form, the surface tension of the material is below this value.
The test results are determined based on the wetting of the liquid. If the liquid spreads rapidly on the surface and does not form beads, the surface tension of the material to be measured is equal to or higher than the value indicated on the dyne pen. If the liquid gradually shrinks, indicating that the surface tension of the material is lower than the selected value, it will be necessary to test again with a lower surface Tension Tester. If the liquid immediately forms water beads and shrinks rapidly, the material surface tension is much lower than the selected value, and the value of the test pen needs to be adjusted to find the exact surface tension.
data analysis
There is an inverse relationship between the surface tension and the water drop angle. When the droplet angle is small, the surface tension of the liquid is higher, which is manifested as the droplet expands better on the surface. Conversely, when the droplet angle is larger, the surface tension is lower, and the droplets are more likely to form spherical on the surface.
| Drop angle | Surface Tension (dyne/cm) |
| 10° | 60 |
| 20° | 57 |
| 30° | 53 |
| 40° | 50 |
| 50° | 46 |
| 80° | 35 |
| 90° | 31 |
| 100° | 28 |
| 110° | 25 |
| 120° | 21 |
By testing the wetting of the liquid, the surface tension of the material can be determined. Depending on the behavior of the water droplets on the surface of the material, the results can be interpreted as follows:
1. The liquid spreads rapidly, and there are no beads
Indicates that the surface tension of the material is equal to or higher than the value indicated on the test pen. This means that the material is hydrophilic and the liquid wets and expands quickly.
2. The liquid gradually shrinks
Indicates that the surface tension of the material is lower than the value indicated on the test pen. This situation indicates that the material is less hydrophilic to liquids and has limited wettability of liquids.
3. The liquid immediately forms beads and shrinks
Explain that the surface tension of the material is much lower than the value indicated on the test pen. This means that the surface of the material is very difficult to wet, and the liquid quickly aggregates into beads.
Application examples
Coatings industry – In the production of coatings, the adhesion of coatings to different substrates is ensured by the dyne pen test. If the surface tension of the material is too low, the coating may not cover evenly, affecting the quality of the coating.
Packaging materials – In packaging material production, testing the surface tension of a material helps to select the right adhesive or printing ink. The correct surface tension value ensures good adhesion of the ink to the packaging surface and the printing quality.
Plastics manufacturing – In plastics processing, dyne pen tests are used to verify the effectiveness of plastic surface treatments. For example, after corona treatment on a plastic surface, a dyne pen can be used to measure the surface tension to ensure that the desired hydrophilicity is achieved to improve the subsequent processing performance of the plastic.
Selection form
| material | Initial Tension (dyne/cm) | Tester Selection (Surface Tension) |
| Polydimethyl siloxane | 22-24 | To be tested |
| Natural rubber | 24 | To be tested |
| Paraffin | 23-25 | To be tested |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 29-31 | 36, 38, 40, 42, 44 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 30-31 | 36, 38, 40, 42, 44 |
| Nylon-11 | 33 | 38, 40, 48, 52, 56 |
| Polystyrene (PS, low ionomer) | 33-35 | To be tested |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC, plasticized) | 33-38 | 38, 40, 48, 52, 56 |
| Polystyrene (PS, high ionomer) | 37-38 | To be tested |
| Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) | 38 | To be tested |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC, rigid) | 39 | 38, 40, 48, 52, 56 |
| Plexiglass (Polymethylmethacrylate, PMMA) | 41 | To be tested |
| Nylon-6 | 42 | To be tested |
| Polyester (Polyethylene terephthalate, PET) | 41-44 | 38, 40, 48, 52, 56 |
| Cellulose (regenerated) | 44 | To be tested |
| Copper | 44 | 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44 |
| Aluminum | 45 | 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44 |
| Iron | 46 | 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44 |
| Nylon 6/6 | 46 | To be tested |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 46 | To be tested |
| Glass (Glass, soda lime) | 47 | To be tested |
The selection table provides the initial surface tension values for the different materials and their corresponding dyne pen test selections. A variety of commonly used materials such as silicone rubber, natural rubber, polypropylene, etc., are listed in the table, and corresponding test pens are recommended according to their surface tension range. By selecting the appropriate test pen, the surface tension of the material can be accurately measured, thus ensuring the quality of material handling and application.
Dyne pens play a vital role in production line testing, as they are able to quickly and accurately measure the surface tension of materials, which is essential to ensure the quality of materials during production. By using dyne pens on the production line, companies can monitor the surface treatment of materials in real time, ensuring good adhesion of coatings, adhesives or printing inks to a wide range of substrates. This not only improves production efficiency, but also reduces rework and scrap due to material surface issues, resulting in cost savings and improved product consistency.
When it comes to measuring the surface energy of materials, the importance of the dyne pen is no less significant. It provides a simple and effective way to assess the hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity of materials, which is essential for a variety of applications, such as the coating properties of coatings, the adhesion of packaging materials, and the surface treatment of plastics. By accurately measuring the surface tension of a material, producers can optimize the processing of the material and ensure that the final product performs as expected, thereby increasing the product's competitiveness in the market.
- 1Dyne pen in film printing
- 2Dyne pen test method
- 3How to Use a Dyne Pen to Determine Surface Energy
- 4How to Ensure the Accuracy of the Dyne Pen Test
- 5Dyne Pen Controls Surface Tension of Printed Coatings
- 6Four simple steps to use the dyne pen correctly
- 7Dyne pens and test fluid -- how do they work?
- 8What is dyne level?
- 9What is dyne (surface tension)?














