Analysis of Dynamic Tensile Test Method for Concrete
Based on the test of this paper and other work researches, the applicability of the three tensile testing methods of axial tension, bending tension and splitting is discussed and analyzed according to the testing equipment conditions to be applied to the concrete dynamic tensile test. It can provide reference for operators in related industries.

1. Tensile stability analysis of concrete
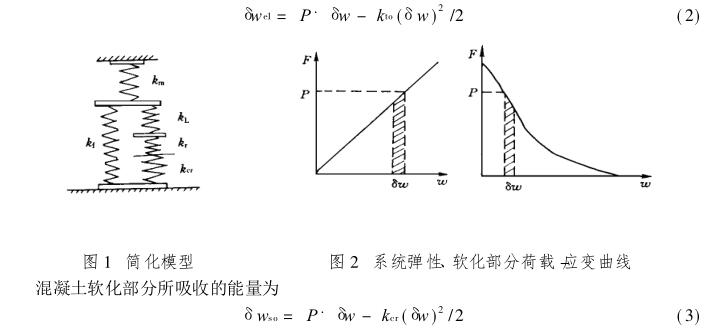
According to the analysis of the tensile deformation characteristics of concrete, it can be seen that the process of tensile strain softening of concrete is also the process of strain localization, that is, the process of gradual cracking. Therefore, in order to measure the descending section of the tensile stress-deformation curve of the concrete specimen, it is necessary to make the cracking process of the specimen a stable process.
The experimental setup is simplified to the physical model shown in Figure 1. Wherein: km is the stiffness of the testing machine itself, which depends on the stiffness of the column, beam, piston, etc., kL is the stiffness of the force measuring rod, kf is the stiffness of the additional frame, kr is the elastic stiffness of the non-cracking zone of the specimen, and kcr is the maximum (absolute) stiffness of the load-cracking width curve of the specimen. The stiffness of the experimental equipment and the elastic part of the specimen in series is
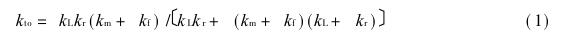
For arbitrarily small virtual cracking δW, the elastic energy released by the entire test system, including the elastic part of the specimen, is (see Fig. 2)

2. Requirements for instruments and equipment for dynamic tensile test
In the previous chapter, the necessary conditions for stable cracking of specimens have been described. It was concluded that the stiffness of the testing machine system needed to be sufficient; The cross-sectional area of the specimen should not be too large, and the length of the specimen should not be too long. When the stiffness of the testing machine is insufficient, it can be used to absorb the elastic energy released by the testing machine by adding rigid auxiliary components such as tie rods and springs to the testing system (related instruments: Tensile Testing Machine)
When using an ordinary hydraulic testing machine, only the full curve of axial tensile stress deformation under static load can be measured. Due to the inability to control the rate after the peak of overstress, the strain rate of the descending section of the curve generally fluctuates greatly, which is often recorded by the ordinary analog X-Y Recorder, that is, the whole descending section process cannot be shorter than a few tenths of a second. Therefore, when considering the influence of loading rate, it is not appropriate to use ordinary testing machine for axial tension test; Servo-hydraulic testing machine is more suitable. In addition to the force, the loading control mode can be used as the actuator stroke (displacement) control, and the deformation of the specimen or the strain control of a certain point can be used, which is very useful for obtaining a stable whole process of destruction; In addition, the loading rate can be accurately controlled, generally 0~50Hz, that is, it can include creep, static load, and seismic loading rate range.
Since the electro-hydraulic servo-testing machine is controlled by a displacement sensor installed in the machine (LVDT differential variable is generally usedPressurized displacement sensors) to accurately measure the stroke of the piston rod and thus to measure the stiffness of the testing machine system. The method is to make the actuator directly pressed to the lower pressure head of the machine base (if the stroke is not enough, there can be a large cross-sectional area of the body between the upper and lower pressure heads; Its stiffness can be regarded as infinity, or its stiffness value can be accurately calculated), and the force is applied step by step, so that the force-stroke relationship can be measured. The stiffness of the testing machine can be calculated:
Km=F/(Δla-Δlb)(11)
where: Km is the stiffness of the testing machine system; F is the applied force; Δla is the actuator stroke value; Δlb is the compression value of the cushion block, which can be measured or calculated according to the force, cross-sectional area of the cushion block, length and elastic modulus.
With the stiffness value of the testing machine, it can be used to estimate whether the specimen has stable failure and whether it is necessary to add rigid auxiliary components to ensure the stable failure of the specimen.
Another key problem with dynamic testing is that the sampling rate of the data acquisition system needs to be fast enough to record rapidly changing force and deformation data. The sampling rate of the computer-controlled data acquisition system depends on the response rate of the sensor, the digital-to-analog conversion rate, the channel switching rate and the rate of the computer. The general sampling rate is 103~104 times/s, and the special one can reach 106 times/s. For other recording instruments, the high-speed multi-trace memory oscilloscope is more satisfactory, and the time resolution of its recording can be as high as 0.1μs. The Tektronix 511A four-trace memory oscilloscope, which was used in the test, is one such instrument. The disadvantage is that it is necessary to calibrate the relationship between the displayed value (voltage value) and the true value of the physical quantity (force, displacement, etc.) in advance; The resolution of its physical quantity can reach about 2%, which is not as accurate as computer acquisition. The X-Y Recorder used for static load test is not suitable for rapid dynamic test because its recording needs to convert the analog voltage into a recording pen tip motion drawing line through a mechanical transmission device, and its line drawing speed is generally completed within 1 to a few seconds.
Sensing elements for measuring force and deformation, such as force sensors, strain gauges, clip-on extensometers and other resistive sensors, have a response rate of more than 104Hz, which is sufficient for fast loading tests. However, resistance displacement meter, electronic dial gauge, etc., because their displacement measurement needs to be realized by the movement of the slide bar in the machine, at high rate, there is mechanical hysteresis, so it is not suitable for dynamic testing.
3. The applicability of the three tensile test methods to the dynamic tensile testThere are currently three static test methods for concrete tensile test, axial tensile test, split tensile test and flexural tensile (also known as flexural) test. The axial tensile test is the most basic test method, and the core of the method is to perform uniform axial tension on the concrete prismatic test piece. In the standards of various concrete test methods in CHINA, the test methods for hydraulic concrete SD10582 specify the axial tensile test methods in detail [8]. The axial tensile test can directly and accurately measure the axial tensile strength of concrete without conversion. The disadvantages are: it is difficult to align the specimen, and once the eccentricity occurs, the measured strength error is large; It is difficult to install and clamp the specimen, so it is necessary to embed stiffeners at the end of the specimen or make a local large head. Although the test is difficult, it is possible to obtain the stress-deformation relationshipOK method. Splitting tensile test is an alternative method of axial tensile test, most of the current specifications stipulate that the splitting method is the standard test method, and stipulate that the strength measured by the splitting method should be multiplied by the conversion factor of 0.9. According to elastic mechanics, the stress distribution on the splitting surface is shown in Figure 3, so it is difficult to determine where the stress-strain represents the stress-strain relationship of the specimen. Furthermore, due to the plywood cushion and the arc-shaped splitting strip on the upper and lower pads of the splitting surface, when the specimen cracks to reach the load peak, the load does not drop immediately due to the friction and the action of the bridge on both sides of the cushion, and there is an obvious lag phenomenon. Fig. 4 shows the load-strain relationship in the middle of the specimen measured by the splitting method [7].It is evident that the load drop lag caused by the above reasons is obvious. The flexural tensile strength measured by the flexural tensile test is applicable to cement concrete pavement and airport pavement. A large number of studies have shown that when concrete is bent, the stress distribution on its section appears to be softened and can be simplified into trapezoidal or rectangular distribution. Therefore, there is a conversion relationship between tensile strength and flexural tensile strength.
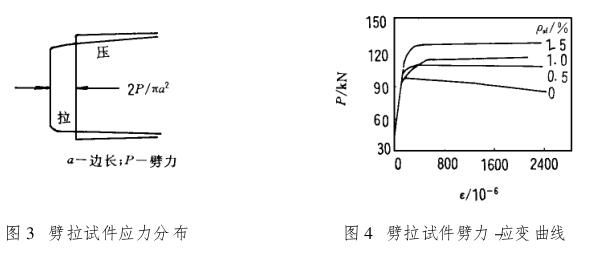
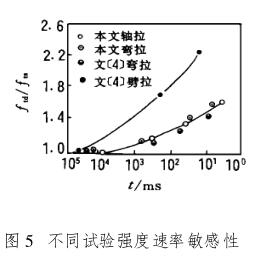
For the dynamic tensile test, according to the comparison of the test results in this paper and the test results in literature [5] (Fig. 5), the rate sensitivity of the three test results is not the same. The effect of the loading rate obtained by the splitting method is much higher than that of the other two methods. The reason for this is mainly due to the influence of mechanical hysteresis effect. Therefore, the splitting method is not suitable for dynamic testing, not to mention that the stress-deformation characteristics of concrete under tension cannot be studied by the splitting method. Although the axial tension method is difficult to implement, it is particularly suitable for dynamic testing. Not only because the stress-deformation relationship in the test is clear and easy to measure, but also because the loading rate relationship is also clear and easy to control. In addition, loadedThere are no errors caused by other mechanical reasons such as friction in the process. Flexural tensile test formulaFor concrete structures based on flexural tensile (flexural) strength, it is still a good dynamic test method to study the sensitivity of different test strength rates in Figure 5, or to study the effects of different specimen sizes and aggregate particle sizes on rate sensitivity. The reason is that the test operation is simple, the specimen is easy to make, and it can be suitable for various cross-section sizes. At the same time, there is a good correlation between flexural tensile strength and axial tensile strength. The results of this project show that the rate sensitivity of axial tensile modulus, ultimate strength and slope of softening curve is basically the same, and the flexural tensile (flexural) strength is related to the integral of the stress distribution curve on the cross-section, so the rate sensitivity of flexural tensile strength is closely related to the rate sensitivity of axial tensile strength and is relatively close. However, one point should be paid special attention to the fact that in the flexural tensile test, the two bearings and two loading points used for three-point loading should be rolled movable hinge bearings, that is, the turning angle and horizontal displacement are unconstrained as much as possible, so that the frictional resistance is as small as possible. Otherwise, it will cause a larger error than the static load.
4 Conclusion
(1) In order to obtain the softening section of the full tensile curve of concrete, in addition to the sufficient stiffness of the testing machine system, it is also necessary to ensure that the energy consumed by the local softening zone of the specimen is greater than the elastic energy released by the non-softening zone of the specimen, so that the length of the tensile specimen should not be greater than 2 times of the minimum cross-sectional width of the specimen. When the stiffness of the testing machine is insufficient, measures to increase the unloading stiffness of the test system can be increased, such as rigid auxiliary steel rods can be added on the four sides of the test piece to ensure that the test piece produces a stable cracking process.
(2) The dynamic tensile test of concrete should be carried out by electro-hydraulic servo-type structural testing machine, and displacement control should be used. loadThe rate control can be operated by the computer numerical control system or the function instruction generator in the molded control system.
(3) The data measurement of the dynamic test can use high-speed dynamic data acquisition devices, such as computer acquisition systems or memory oscilloscopesetc. The sampling rate should ensure that the sampling interval between the rising and descending sections of the test curve is not greater than 2% of the load amplitude.
(4) The dynamic tensile strength and deformation properties of concrete are tested, and a good method is the axial test. When the study loads at a speedWhen the rate affects the strength, the flexural test method can also be used. The splitting test is not suitable for the dynamic tensile test of concrete.
- 1What are the common tensile test applications and standards?
- 2How to calculate elongation in tensile test?
- 3What are the commonly used tensile test standards?
- 4What are the common tensile testing applications?
- 53 basic types of material destructive testing
- 6Destructiveness gluing tensile test
- 7Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in tensile testing
丁富连;王承忠;陈卓人;方健 - 《宝钢技术》
- 8Discuss the influence of the flexibility of the analytical testing machine on the results of the tensile test
余立; 李荣锋; 凃应宏 - 《试验机柔度对拉伸试验结果的影响》
- 9Introduction to the clamping principle of tensile testing





