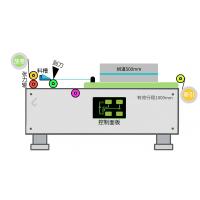
Analysis of Advantages and Disadvantages of Coil Film Applicator and Sheet Flat Film Applicator
A flat coater is a type of equipment used to coat rigid or fixed substrates (e.g., glass, silicon wafers), and is usually suitable for low-volume, high-precision production scenarios. It reduces mechanical vibration by keeping the substrate in a stationary or linear motion, thus ensuring stability during the coating process.The roll coater is a kind of equipment used to coat flexible and continuous substrates (such as film, paper, etc.), which is suitable for high-volume, continuous production scenarios. It utilizes a tension control system to maintain stable transmission and efficient production through high-speed coating technology.
The stability and accuracy of flat coaters and coil coaters depend on the specific application, equipment design, and process requirements. So what's the difference between the two?
1. Operational stability
Flat coater
【Advantages】
It is typically used for single sheets or fixed substrates (e.g. glass, silicon wafers, plates) that remain stationary or linear during the coating process with low mechanical vibration.
It is suitable for high-precision, small-batch production, with high requirements for the flatness of the substrate and easy control of stability.
【Limitations】
Intermittent production is less efficient, and frequent starts and stops can affect long-term stability.

Coil coater
【Advantages】
Continuous production, suitable for large quantities (such as thin films, flexible circuits, lithium battery pole pieces), high operation efficiency.
The tension control system of modern coiling machines is mature (such as servo motor + deviation correction device), which can maintain stable transmission.
【Limitations】
Flexibility and tension control of the substrate are extremely demanding, and slight jitter or stretching of the web can affect the coating uniformity.

Concentrate:Flat coaters are suitable for single sheets or fixed substrates (e.g., glass, silicon wafers) and are stable in low-volume, high-precision production, but are inefficient and can affect long-term stability due to frequent start-stops. Coil coaters, on the other hand, are suitable for high-volume, continuous production of flexible materials, which operate efficiently but require strict substrate flexibility and tension control. Therefore, the coil coater is more stable when producing in large quantities of continuous production; And in high-precision small batch or one-piece production, flat coaters are even more advantageous.
2. Coating accuracy
Flat coater
High coating thickness uniformity (within ±1 μm), especially suitable for nanoscale coatings (e.g. optical coatings, semiconductors).
The substrate is fixed, and it can be matched with high-precision nozzles or scrapers to reduce dynamic errors.
Coil coater
Accuracy is limited by substrate velocity, tension fluctuations, and the dynamic response of the applicator head (e.g. slit extrusion applicator).
High-end models can reach ±2 μm, but accuracy may be reduced at high speeds.
Concentrate:In terms of coating accuracy, the flat coater can achieve high uniformity within ±1 μm due to its substrate fixation characteristics, and is suitable for nanoscale coatings such as optical coatings and semiconductor manufacturing. In contrast, the coil coater is affected by factors such as substrate speed and tension fluctuations, and although the high-end model can achieve an accuracy of ±2μm, it may decrease when running at high speeds. Therefore, the flat coater should be selected for ultra-high precision requirements, while the coil coater with closed-loop control system can be used for high-speed production under conventional precision to maintain stability.
3. Other influencing factors
Substrate type
Rigid/brittle materials (e.g. glass) can only be used with a flat coater; Flexible materials, such as PET film, are suitable for coil coaters.
Process complexity
Multi-layer coating or patterned coating (e.g., photovoltaic cells) may be preferred over a flat coater.
In coating technology, flat coaters and coil coaters have their own application scenarios and advantages and disadvantages. The flat coater is suitable for high-precision small batches of rigid substrates (such as glass, silicon wafers), which can achieve uniformity of ±1μm, and is suitable for nano-scale coatings such as optical coating and semiconductor manufacturing; The coil coater, on the other hand, is designed for high-efficiency and high-volume flexible materials, with high-end equipment up to ±2μm, but the accuracy may be affected when running at high speeds. Therefore, the selection of coating equipment should be based on specific needs: high-precision small-batch selection of flat plates, high-speed large-batch selection of coils.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Rxf-10/600pupro Automatic Film Applicator$ 50192.00