Film performance testing summary
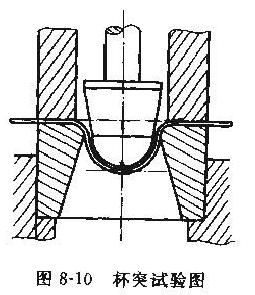
Cup experiment (GB/T9753-88)
The cupping test is to detect the ability of the layer to resist deformation and cracking, and it is a comprehensive manifestation of the plasticity of the coating film and the bonding force of the substrate. The QBJ outburst solution test machine is designed and manufactured according to the requirements of lS01520 and GB9753--88, and the pressure head is 2mm Move the pressure head at a speed of (o.2±0.l) mm/s until the coating appears delaminated, and take the corresponding indentation depth (mm) as the cupping test value (see Figure 8-10 ) (related instrument: cupping Tester)
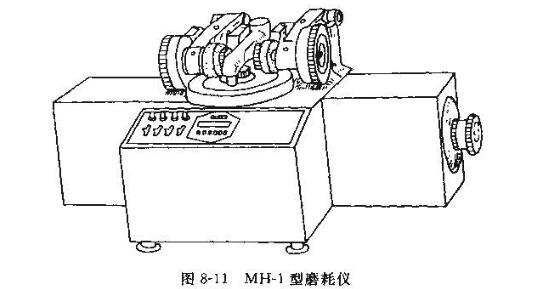
wear resistance
The wear resistance test tests the mechanical wear resistance of the coating film, which is a comprehensive reflection of the cohesive energy of the coating film and the hardness of the film. The falling sand method and the sandblasting method are used to simulate the natural wear of the coating to test the natural wear of the coating on the production site. For rubber grinding wheels, a certain cutting load is applied, which is expressed by the number of grinding wears or the weight loss at a specified number of revolutions. This type of instrument is collectively called Taber abrasion Tester. The domestic MH-1 abrasion Tester is shown in Figure 8-11.
Stone chip resistance
The stone impact test is a test method that imitates the impact of sand and stones on automobile coatings during driving. It is used to show the ability of coating films to resist the impact of high-speed sand and stones. It is a special test technology developed for the requirements of automobile coatings. During the test, spray steel grit with a particle size of 4~5mm on the sample to be tested with compressed air, spray 500g of copper grit each time, and spray it on the sample with a pressure of 2MPa within (10±1)s, repeat twice, and then paste l. Pull off the loose coating film with tape, and compare the damage situation with the standard picture. Grade 0 is better, and Grade 10 is the worst. The difference between it and the spray method is that the sand grain size is large and the spray pressure is high. Abrasion resistance is expressed by the mass of abrasive required to wear per unit thickness. The purpose of the test is completely different. The test method for stone impact resistance of ASTM D3170--87 stipulates that 9.6-16mm source stone is used, and the amount of each use is 5oOm1. The pressure is 48okPa ± 20kPa.
water resistance
According to the provisions of GB/Tl733--93, the bottom plate is 120mmX25mmX(0.2~0.3) mm tinplate plate, after the coating film is edge-sealed, immerse 2/3 of the test plate in 23°C±2°C water (or waste water), self-specified Take it out after the time. Check and record whether there are any phenomena such as loss of light, discoloration, blistering, wrinkling, shedding and rust, and the correction time.
Gasoline resistance
According to the regulations of GB/T1734-93, the bottom plate is 120mmX50mmX(0.2-0.3) mm tinplate plate, 2/3 of the test plate is immersed in 120·solvent gasoline at 23℃l2℃, and taken out after the specified time, and the inspection records are as follows: No wrinkling, blistering, falling, softening, discoloration, loss of light, etc.
chemical resistance
According to GB/T1763-89, the bottom plate is 120mmX50mmX(0.45-0.55) mm thin steel plate, LY12 aluminum plate with a thickness of 1~2mm, and a bottom carbon steel rod with a length of 10~12 mm and a length of 120mm. Edge banding, painted by dip coating method on steel bar, do soaking test directly after drying
(1) Salt water resistance Immerse 2/3 of the test panel in 3% NaC1 aqueous solution at a temperature of 25°C ± 1°C, take it out after the specified time, and check for discoloration, loss of gloss, blistering, peeling, and rust.
(2) Acid and alkali resistance. Immerse 2/3 of the painted steel sample in the acid and alkali solution of specified concentration at a temperature of 25°C to 11°C. Take it out for inspection every 24 hours. Rinse it with tap water and dry it with paper for each inspection. , Observe whether there is discoloration, loss of light, vesicles, spots, and shedding.
Scrub resistance
This is an important property of architectural coatings, and it is also applicable if other Facon has this regulation. The test uses a QFS type paint scrubbing Tester, the test plate is 430mm x 150mn, X3mm glass plate, after washing, first measure a piece of iron Red alkyd primer, after drying, apply the white latex paint to be tested (if the material to be tested is a dark paint, use the primer method of white alkyd matt enamel paint), so that the dry film thickness of the latex paint is 45µm±5µm. The board is fixed in the test tank of the instrument, and the brush soaked in 0.5% soapy water is placed on the coating film for reciprocating scrubbing, and at the same time, 0.5% soapy water is continuously added until the bottom of the 100mm long area in the middle of the test board appears. , Record the number of times of washing and use it as the washing resistance effect.
Heat resistance
For painted products used in humid tropical regions, the damp heat test is also a method to evaluate the protective performance of the coating film. According to the provisions of GB/T1740-89, the test panel of the method is vertically measured in a damp heat chamber, and the experimental condition is that the temperature is 47°C ±1°C, relative humidity 96%±2%, no condensation should appear on the surface of the test panel during the test, check once every 49 hours for the first two times, and check once every 72 hours thereafter, after each inspection, the position of the test panel should be changed , until the end of the test within the specified time, and finally grade according to Table 8-6. When rating, use a 150mmX70mmX(0.5-2) mm plexiglass plate to divide it into 9 equal parts, and use it to measure the foaming area.

GB/T138-93, IS06270 and ASTM D4585--92 adopt the continuous cooling method, the temperature of the Water Bath is 42C±2C, and the space of 2S mm below the test plate is The temperature is 37°C±2°C, so that the surface of the method is continuously in a condensed state, which is conducive to water infiltration. The lake humidity test has been developed to a composite cycle test of immersion, drying, and heat and humidity.
Salt tolerance test
In the coastal area, because the atmosphere is full of salt spray, it has a strong corrosion effect on metal products, and also puts forward strict requirements for the protection measures in the coastal area. However, in the salt spray test process, due to the influence of various factors such as salt concentration, spray pressure, spray particle size, salt spray settlement, etc., the results obtained in different types of test equipment are different. It is relatively large and there are some controversies, but it is still widely used. The salt spray test is divided into neutral salt spray test (SS) and acetic acid salt spray test (Ass). Set, the concentration of sodium chloride aqueous solution is bOg/L±10g/1, pH6.5~7.2, temperature is 35°C±2°C, the size of the test plate is 150mm X7omm, the cross is 15ohmXl0omm, and the scratches are away from either side The distance between them should be greater than 20 mm. The test panel is inclined at 25°±5°, and placed in the salt spray chamber with the tested side facing upwards for continuous testing. Check once every 24 hours, and each check should not exceed 60 minutes. And the surface of the test plate is not allowed to be in a dry state. Take it out after a certain period of time, and check the records for swelling, rust, adhesion and corrosion at the scratches. Other standards with more neutral salts include 1S07253, ASTM B117 etc.
The acetic acid salt spray test is to improve the effect of the corrosion test (GB1o125-88). The pH of the salt spray is 3.1-3.3. There is also a modified acetate chamber test (CASS) by adding copper chloride to the acetic brine to further speed up the corrosion process. Corrosion contact test speed.
The salt spray test is also combined with the dry and wet test, and is used as a cyclic corrosion test assessment for automotive coatings, for example: at 35 ℃, 5% NaC1 solution spray 4h-60 ℃, RH < 35%, dry for 2 hours, 50 ℃, RH > 95%, humidity test 2h, repeat this cycle.
Atmospheric aging test
Atmospheric aging test is used to evaluate the durability of the coating to the atmospheric environment. The result is a comprehensive reflection of the various properties of the coating, which also determines the service life of the coating. Following the provisions of GB/T1767--89, the exposure site should be selected Establish in a place that can represent the harshest climate or under environmental conditions similar to practical applications, such as coastal areas, industrial areas, etc. The exposure field should be surrounded by open spaces, the site should be flat, and the local natural vegetation state should be maintained, away from obstacles. The distance height is at least three times the height of the obstacle. (aging Test Chamber)
The exposure site in the coastal area should be set up in a representative place by the sea, and the exposure site in industrial climate should be set up in the factory area. The exposure site should be selected so that the samples can be fully affected by various atmospheric factors. Meteorological observation stations should be set up in the exposure field, especially to record the amount of ultraviolet radiation, the type and content of corrosive gas or the content of passivation chloride, etc.
The exposure test plate is 15omm><250mmX(0.8~1.5) mm cold-rolled steel plate, 1~2mm thick Ly12 aluminum alloy plate, MB8 Jun alloy plate or other actually used plates (such as plastic plates, wood plates, etc.), for comparison The standard sample size of the test is 70mmX150mml. The exposure test panel faces the south, and is placed at the local latitude angle with the horizontal plane. For the exposure rack with adjustable angle, take (25°) as the hottest angle in spring and multiple seasons, and the hottest angle in autumn. , winter (0.893p + 24°) is the hottest angle


- 1Coating film adhesion and its relationship with metal protection
高瑾 米琪 - 《《防腐蚀涂料与涂装》》
- 2Circular adhesion Tester How to measure film Adhesion
- 3Cross-Cut Tester for film Adhesion
- 4Film Adhesion Test Method and Test Instrument
刘振作 - 《天津市建筑仪器试验机公司》
- 5Hardness testing for hard film applications
Carestream Tollcoating
- 6Effect of surface tension on emulsion paint and film performance
高海伟 - 《涂料工业》
- 7Method and review of film Hardness determination by pendulum method
虞莹莹 - 《涂料技术与文摘》
- 8What are the important factors that determine the protective properties of a film?
- 9Film Pencil Hardness Measurement


