Coating Gloss performance test summary
Gloss is the ability of a coated surface to reflect light falling on it in one direction. Different products have different requirements for coating gloss. For example, high-end cars require coating gloss as high as possible, while some optical devices, military equipment and ground camouflage facilities require flat and matte.
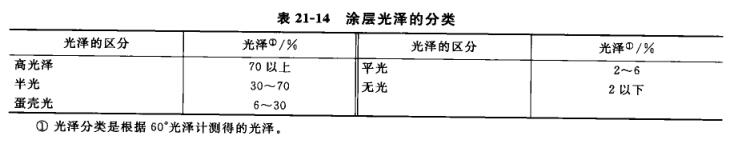
According to the level of gloss, the coating gloss can be divided into high gloss, semi-gloss or medium gloss, egg-shell gloss, flat gloss and matte, etc. The gloss range is shown in Table 21-14.
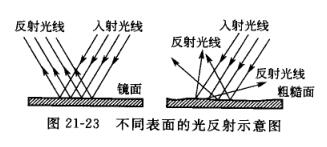 Coating gloss is not only related to the paint used, but also related to the quality of coating construction. The surface of a properly constructed coating is relatively flat and smooth, and has a high reflectivity to light, while a relatively rough coating surface with sagging, pinholes, orange lines and impurities adhered to it has a low reflectivity to light, see Figure 21 -23 shown.
Coating gloss is not only related to the paint used, but also related to the quality of coating construction. The surface of a properly constructed coating is relatively flat and smooth, and has a high reflectivity to light, while a relatively rough coating surface with sagging, pinholes, orange lines and impurities adhered to it has a low reflectivity to light, see Figure 21 -23 shown.
National standard analysis methods include; GB/T1743-79 "Determination of Paint Film Gloss", GB/T9754-2007 "Determination of 20°, 60° and 80° Specular Gloss of Paint Films of Paints and Varnishes Without Metallic Pigments ».
The practical analysis methods in the factory include: paint film gloss measurement method, the measurement of 20°, 60° and 85° specular gloss of the paint film without metallic pigments, the measurement of coating gloss is generally carried out by a gloss meter, and the results It is expressed as a percentage of the ratio of the amount of regular reflected light from the coating surface to the amount of regular reflected light from the standard surface under the same conditions. Therefore, the coating gloss generally refers to the relative comparison value with the standard plate gloss.
According to the incident angle of the light source of the Glossmeter, it can be divided into fixed angle Glossmeter (such as 45°, 60°), multi-angle Glossmeter (such as 0°, 20°, 45°, 60°) and variable angle Glossmeter (It can be measured between 20°~85°). For high-gloss coatings (60° gloss higher than 70%), a gloss meter with an incident angle of 20° should be used; for low-gloss coatings (60° gloss lower than 30%), a gloss meter with an incident angle of 5° should be used. to make the test results more accurate.
Coating gloss testing is generally divided into two processes: calibration and testing. Taking the GZ-1 spot gloss meter as an example, the testing process is as follows.
Turn on the power, press the power switch of the instrument, and after warming up for 10 minutes, press the 140% range selection button. Pull the template clip, insert the black standard board into the gap and clamp it. Slowly turn the standard knob to make the pointer indicate the gloss number calibrated by the standard plate. .Take out the standard board and insert the tested sample board. When the gloss of the coating is lower than 70%, press the 70% range selection button to measure at three different positions of the sample, and the reading is accurate to 1%.
The difference between the readings of each measuring point and the average value should not be greater than 5% of the average value, and the result is the arithmetic average of the readings at three points. If it is not a glass substrate, make 6 measurements on different areas or different directions on the surface, record the average value and limit value, if the error between the limit values is not greater than 10 units or greater than 20% of the average value, discard the test panel , otherwise record the average value and limit value, after every five samples are measured, check with the standard plate once. The standard board should be wiped with lens paper or flannelette. When the standard board is not in use, it should be stored in an airtight container and kept clean to prevent scratches or damage to its surface and dust falling on it. It is absolutely not allowed to place the standard face down. May be dirty or have worn surface. Hold the edge of the standard every time you use it to prevent oil stains from staining the standard surface. To clean the standard plate, use warm water and a light detergent solution, scrub slowly with a soft nylon brush (do not use soap solution to clean the standard plate, because the soap may leave a film on the surface), and use running hot water (≤ 60°C) to remove the detergent solution, followed by a final rinse with distilled water, and then dry in an oven at an appropriate temperature.
- 1Sag problems and their solutions
- 2what is the coating Leveling and Sag resistance
- 3How to assess the sag resistance of paints and varnishes according to ISO 16862
- 4Why does the coating have orange peel defects? How to solve sagging and leakage?
- 5Wetting, coalescing and hanging of paint rheological phenomena
- 6The difference between ink fluidity and fluidity
- 7Common paint film defects and solutions of container coatings
- 8Determination of leveling and sagging of coatings
- 9Leveling and sag resistance of coatings














