Introduction of drying room types and drying process
(1) Types of drying room
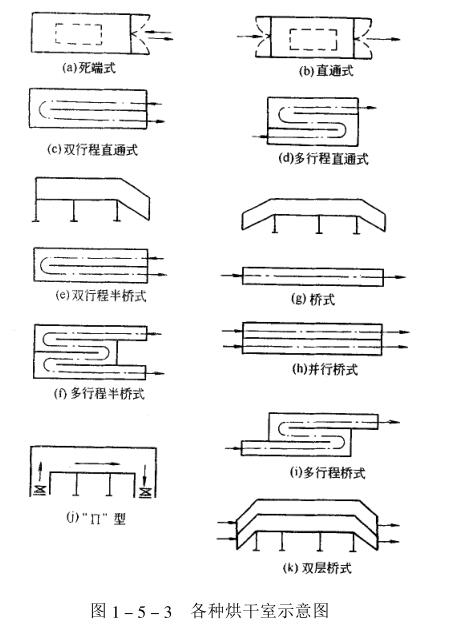
According to its shape, the drying chamber has two types: dead-end type and pass-through type. The dead-end type is used in the intermittent production mode, and the pass-through type is used in the assembly line production mode, and there are differences between single-stroke and multi-stroke. The pass-through type can be divided into straight-through type, bridge type and "II" shape according to the shape. Generally, the through-type drying room has a large heat spillover, but the equipment is relatively short; the bridge-type drying room is longer and has a higher space. . But the heat spillover is smaller. The II” type drying room is similar to the bridge type in other respects except that it is shorter than the bridge type. The structure of the single-stroke drying room is relatively simple, but the equipment is long and occupies a large area; the multi-stroke drying room The structure is more complex, the equipment is shorter, the floor area is reduced, and it is beneficial to the layout of the car; the parallel equipment is beneficial to improve the heat preservation and reduce the floor area; the double-layer drying room can make full use of the space height and reduce the floor area. The shapes of various drying chambers are shown in Figure 1_5_3.
(2) Drying process
The entire drying process of the coating film in the drying chamber goes through three stages of heating, heat preservation and cooling (see Figure 1_5_4).
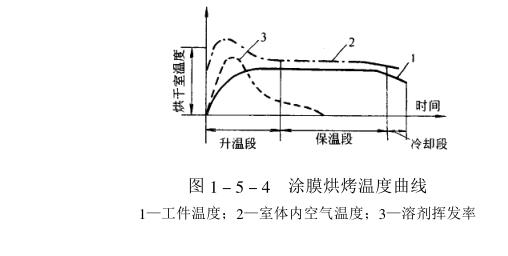
In the heating section, the coating temperature is gradually raised from room temperature to the drying process temperature, so that more than 90% of the solvent in the wet coating film is released at this stage, and the required time is about 5 to 10 minutes. The length of time is determined by the absence of appearance defects in the coating film. Generally, the heating time of high boiling point solvents can be short, and the heating rate of low boiling point solvents should be slow to avoid solvent boiling.
Since the solvent evaporates rapidly in the heating section, it is necessary to strengthen the ventilation to remove the solvent vapor and replenish fresh air. In addition, heating the workpiece consumes a lot of heat, so most of the heat is consumed in the heating section during drying.
In the heat preservation stage, the heat preservation time is determined by the curing process time required for the chemical cross-reaction of the coating film, and less heat and fresh air are needed to compensate for the exhausted solvent gas.
The cooling section adopts a forced cooling method to rapidly cool the workpiece below 40°C, so that the next process can be carried out immediately to ensure the normal operation of the assembly line. If natural cooling is adopted, it will take about 20-30 minutes to drop to 30-40°C, which can only meet the batch production method.
According to the heating method, the drying chamber is divided into convection type, heat rate rich injection type and rate rich injection convection compound type, etc.
- 1Types of drying rooms and drying process
- 2Introduction of coating curing method
- 3Summary of post-treatment of electro-coating
- 4Introduction of heat radiation drying equipment
- 5Introduction of film drying method
- 6Metal surface preparation before painting
- 7Water tank, radiator, leaf spring painting new technology
- 8Drying technology of automobile topcoat
- 9How to solve the coating defects caused by wrinkling and biting?