How to control the conductivity of Electrophoresis primer painting?
The electrical conductivity has a direct impact on the stability of the electrophoretic coating, the coating quality and the throwing power of the coating. The conductivity of the electrophoretic coating increases, the deposition amount increases, and the deposition speed accelerates, but the throwing power of the coating decreases. If the conductivity is too high, due to the intensification of electrolysis, there will be defects such as pinholes in the coating film, the quality of the coating film will decline, and it will even be difficult to form a complete coating film. Therefore, the importance of controlling the conductivity of the bath solution within the normal process range is needless to say.

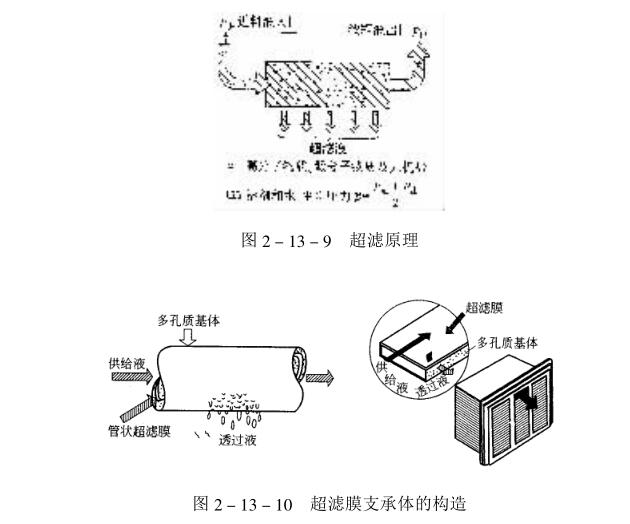
Ultrafiltration (also known as UF) is to pass the bath solution under a certain pressure (0.3~0.5MPa) through a semipermeable membrane (or ultrafiltration membrane) with a specific pore size, so that low molecular weight substances in the coating solution, such as high impurities Substances, small molecular amines or residual acids are highly concentrated with high molecular weight substances such as resins and pigments, so that the bath solution is kept within the normal parameter range (see Figure 2_13_9). Ultrafiltration is one of the membrane separation methods, which is mainly based on the selection of pores. Under the applied pressure, the solvent and solutes with low molecular weight pass through the ultrafiltration membrane, while macromolecules and colloids are intercepted by the membrane. The size of particles intercepted by ultrafiltration is in the range of 1~20μm. The structure of the ultrafiltration membrane support is shown in Figure 2_13_10.
The concentrated coating solution after ultrafiltration directly enters the electrophoresis tank, and the mixture of small molecules, solvents and additives is called ultrafiltered water. If the conductivity is too high, it can be adjusted by regularly discharging a part of ultra-filtered water, adding fresh, solvent and additives.
To sum up, the ultrafiltration device mainly plays three roles in electrophoretic coating.
(1) Stabilize the tank solution, improve the quality of the coating film, and prolong the service life of the coating solution.
(2) Recycling paint. Practice has proved that the paint attached to the electrophoretic coating film or left in the groove of the workpiece and taken out of the groove can reach 10%~15% of the used amount. If it is discharged into the sewer together with the flushing water, it will not only waste a lot of paint and There is a large amount of flushing water, and the environmental water quality is polluted. The ultrafiltration device is used to make the flushing water enter the ultrafilter, recycle the paint and purify the discharge water, forming a "closed loop" and zero discharge.
(3) Provide ultra-filtered water to save a lot of flushing water. Rinse the workpiece with ultra-filtered water to wash away most of the paint from the surface of the workpiece, and then return the washed ultra-filtered water to the electrophoresis tank. Since the ultrafiltration water itself is part of the electrophoresis bath, washing with ultrafiltration water and returning to the electrophoresis bath will not affect the composition of the electrophoresis bath.
- 1The Working Principle of Gel Conductivity Meter Has Been Detailed
- 2Detection Principle and Application Analysis of Conductivity Meter
- 3Principle of Conductivity Analyzer
- 4Several common electrode types for Conductivity Meters
- 5Differences between three STIP-scans: pH Meter, Conductivity Meter, and Dissolved Oxygen Meter
- 6Conductivity Meter and Ion Meter specific differences
- 7Common types and application differences of STIP-scan
- 8How to detect the conductivity of lithium battery coating slurry?
- 9How to choose a high-precision conductivity meter?