Cataphoretic coatings - Determination of main performance
1) Swimming power
Throwing power is an important indicator of electrophoretic coatings, generally measured by steel pipe method, as shown in Figure 5-29.

Immerse a ∅20mmx1300mm steel pipe (or plastic pipe) into a round paint tube (∅230mmx250mm) containing the paint solution, and insert a 20mmx300mm stainless steel sheet into the steel pipe or plastic pipe (when the paint penetration is small, use a plastic pipe) ), electrophoresis for 2 to 3 minutes according to the specified construction conditions, take out the steel sheet, rinse with water, and dry. The steel sheet can be divided into three sections A, B, and C according to the quality of the coating. Section A is the normal deposition area, section B is the transition area, and section C is no deposition. (A+B)/2 is called the infiltration height of the coating film under this condition. The inner diameter of the steel pipe is different, and the infiltration height of the electrodeposition coating film is different, and the relationship between the west and the west is inversely proportional. The diameter of the tube is selected based on the principle that the penetration height of the coating film is half the length of the immersion tube during the electrodeposition of the coating with the highest throwing power.
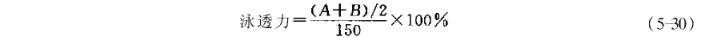
The pipe is inserted 150mm into the coating solution. The steel pipe method is more effective for measuring coatings with higher throwing power.
In addition, there are parallel plate method and v-shaped method. The parallel plate method utilizes multilayer plate electrodes, where all the plates are parallel. Five 150mmlx150mm steel plates can be used in the experiment, the gap between the samples is 1mm, the whole group of samples is parallel to the capture electrode, and the central sample is 30mm away from the high cathode, as shown in Figure 5-30. Turn on the power, take it out after electrophoresis for 3min, and weigh it after drying. Calculate the average deposition percentage of each plate according to formula (5-31).

 The throwing power is evaluated by the similarity of the average deposition percentage of 5 plates. The closer they are, the higher the throwing power is, and the farther the average deposition percentage is, the lower the throwing power will be.
The throwing power is evaluated by the similarity of the average deposition percentage of 5 plates. The closer they are, the higher the throwing power is, and the farther the average deposition percentage is, the lower the throwing power will be.
The v-shaped method is to use the west plate to form a narrow v-shaped piece, the lower part of which is connected together, and the upper part maintains a certain height. After the film is formed by electrophoresis, check the area coated with the film on the inner surface, as shown in Figure 531.
The smaller the unpainted area shown in the graph, the better the throwing power. But this method can only explain the problem qualitatively rather than quantitatively.
2) Determination of color-base ratio
Sintering method: Weigh 1~2g of coating liquid into a known amount of increasing crucible, bake at high temperature in the baking process to constant weight, and then sinter to constant weight. Calculate according to formula (532):

In the formula
A - mass of crucible, g;
H--(increasing crucible + coating liquid) mass after drying, g;
c--(increasing crucible + coating liquid) mass after sintering, g.
High heart method: Take a certain amount of coating liquid, use the high heart method to separate water and solids, wash the precipitate with acid (ammonia) and distilled water, then take it out and dry it, and measure the pigment content; then take out the same coating liquid, measure the solid content, Perform conversion to get the Yan-base ratio.

- 1Determination of pH value of electrophoretic paint - PH meter is easy to do
- 2Electro-coatings Determination of ash content and color-to-base ratio
- 3Maintenance and management of electro-coating ultrafilter
- 4Management summary of electro-coating
- 5Summary of post-treatment of electro-coating
- 6What are the factors that affect the electro-coating process?
- 7Cataphoretic coatings - Determination of main performance
- 8Summary of post-treatment of electro-coating
- 9How to control the conductivity of Electrophoresis primer painting?