Introduction to the working principle of ConductivityMeter
The conductivity meter is an instrument commonly used in laboratories to measure the conductivity of solutions, and it is also commonly used in the field of chemical analysis. For example, by measuring the conductivity of water, the degree of contamination of water by impurities and the amount of salt or other ions contained in the solution can be known. By measuring the conductance change of a certain liquid phase reaction, the degree of chemical reaction can be observed, the reaction rate constant can be calculated, and the reaction mechanism can be studied.
The degree of electrolysis exists in the form of charged ions in aqueous solution, so the solution is similar to a conductor and also has the ability to conduct electricity. The strength of its conductivity is called conductivity, referred to as conductance, expressed in G. The conductivity of the electrolyte in solution is the reciprocal of the resistance, that is,

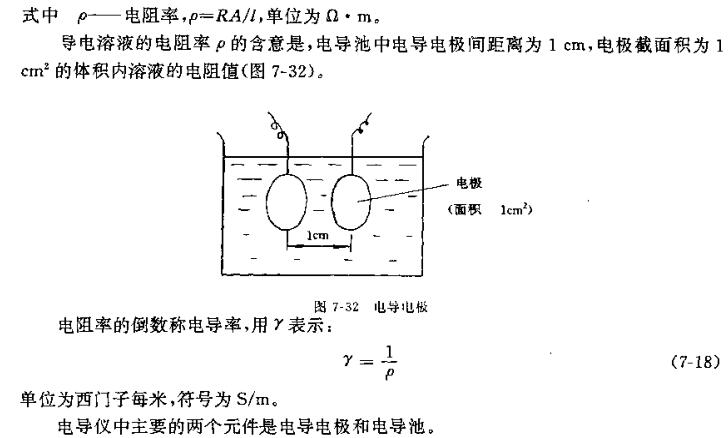
The working principle of conductivity meter
At present, the DDS-11 conductivity meter is widely used in CHINA. This kind of instrument is direct-reading, has a wide measurement range and is easy to operate. If the automatic electronic potentiometer is used in conjunction with it, the conductivity of the solution can be measured. For continuous measurement records. When making accurate conductivity measurements, the conductivity cell can be operated in a thermostat.
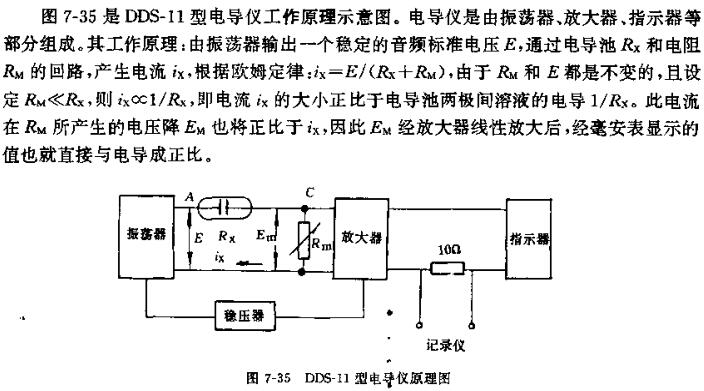
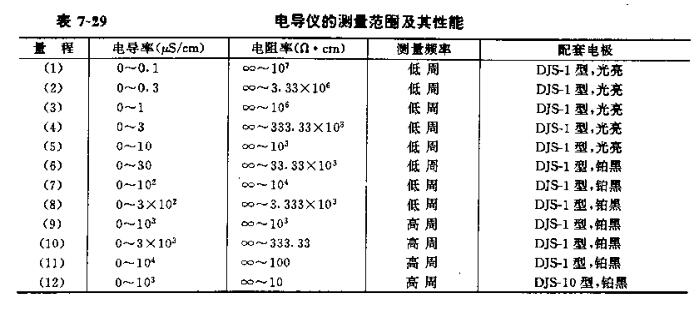
The principle of the DD-11A conductivity meter is basically the same as that of the DDS-11 conductivity meter. It adopts a full-transistor circuit and is equipped with an electrode constant adjustment device. Conversion. In addition to measuring the conductivity of common solutions, it can also measure the conductivity of high-purity water and be used for conductometric titration. Table 7-29 lists the measurement ranges and supporting electrodes of each range in the DDS-11 conductivity meter.
- 1The Working Principle of Gel Conductivity Meter Has Been Detailed
- 2Detection Principle and Application Analysis of Conductivity Meter
- 3Principle of Conductivity Analyzer
- 4Several common electrode types for Conductivity Meters
- 5Differences between three STIP-scans: pH Meter, Conductivity Meter, and Dissolved Oxygen Meter
- 6Conductivity Meter and Ion Meter specific differences
- 7Common types and application differences of STIP-scan
- 8How to detect the conductivity of lithium battery coating slurry?
- 9How to choose a high-precision conductivity meter?