Calculation method of chilling down water consumption of Air Compressor
(1) Cooling effect
Cooling of the Air Compressor cylinder and cylinder head jacket: in order to remove the frictional heat between the cylinder wall and the plug cleaning ring in time during the compression process, to prevent thermal deformation of the material, and to reduce the variable index value of air compression, so that the compression process tends to be an isothermal process. Thereby reducing the compression exhaust temperature and reducing the consumption of shaft power, so the cylinder and the cylinder head central sleeve should be cooled by cooling water. But the temperature of the cooling water should not be too low, otherwise, the moisture in the air will be condensed and condensed, and the water mist will increase the friction force of the relatively moving parts in the cylinder (such as the adjusting plate, plug cleaning ring, cylinder head, etc.) and reduce the service life , The temperature of the cooling water used in the central sleeve of the cylinder should be 8°C higher than the air dew point temperature. Generally, the secondary water or the cooling water used by the compressor intercooler is used.
Cooling of the primary exhaust: install a water cooler between the first and second cylinders of the Air Compressor to cool the exhaust gas of the first stage and cool the moisture in the condensed air (the air-cooled type adopts an air cooler). It is to improve the volumetric efficiency of the secondary cylinder (because reducing the gas temperature entering the secondary cylinder can reduce the gas specific volume) and reduce the starting temperature of the gas compression in the secondary cylinder to reduce the exhaust temperature of the secondary cylinder and save the secondary compression shaft In terms of power consumption, the water temperature used for the intercooler should be lower, so fresh cooling water (or primary water) is often used.
Cooling of the secondary exhaust: After the secondary compression (before sending it to the user), a water cooler (often called an aftercooler) is installed, the purpose of which is to finally cool the compressed air and cool the water vapor in the compressed air to increase the pressure. The rate of oil-water separation of junction air in the oil-water separator and stage air tank. The supporting equipment of the manufacturer is usually not equipped with an aftercooler. If necessary, it should be specified in the order.
Cooling of circulating lubricating oil: The lubrication method of small short-term Air Compressors is often splashed, and the cooling system of circulating oil is naturally dissipated through the outer wall of the lower part of the body, so no oil cooler is required. Large and medium long-term working systems The pump-slip method of the transmission parts of the Air Compressor often adopts the pressure type, and the gear oil is used to force the circulation of the hole, and the oil cooler is set to cool with water to remove the frictional heat of the transmission parts carried by the circulating oil. The cooling water temperature is not subject to special requirements.
Combined with the water temperature requirements of each water point, it is recommended to use the following cooling water flow scheme:
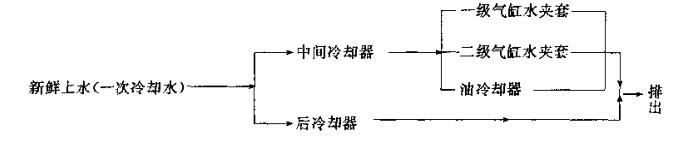
(2) Cooling water quality requirements and water temperature requirements
The cooling water should be neutral, that is, the pH range is 6.5~7.5, the temporary hardness is generally not more than 12° (German degree); the turbidity is generally not more than 100mg/L; the oil content is generally not more than 5mg/L; the organic content is generally not More than 25, mg/L. For water with high temporary hardness, when the water temperature exceeds 40°C, the precipitation of salts in the water will intensify, and the surface of the cooler will be scaled, resulting in poor heat transfer performance. Therefore, it is generally required that the cooling water supply temperature is not higher than 30°C, and the drainage temperature is not higher than 40°C. In individual hot climate areas or when the temporary hardness of water is low, the water supply and drainage temperature can be slightly higher.
The cooling water inlet pressure is generally 0.15~0.3MPa.
(3) Cooling water consumption
The amount of cooling water required by the Air Compressor (including all levels of cylinder liners and intercoolers) should basically be based on the data in the product manual provided by the manufacturer. When the data in the product catalog or manual is missing or incomplete, use Calculated by one of the following two methods.
① Calculated per m3 of inhaled air (inhaled state volume)


- 1Basic Principle and Application of Permanent Magnet Air Compressor
- 2Five steps to choosing the right Air Compressor
- 3What kind of Air Compressor do you generally choose for air Spray Gun spraying?
- 4Air Compressor selection of Fusheng
- 5Air Compressor application industry one table
- 6Iwata Air Compressor model selection method
- 7Iwata Air Compressor series standard configuration characteristics diagram
- 8Iwata teaches you how to use Air Compressor comfortably and efficiently?
- 9Common faults and treatment methods of compressors













