Determination of Viscosity of Liquid Coatings - Outflow Method
 简单实用的测定方法是将一根木棍(或玻璃棒)放入涂料中并加以搅动,感觉受到的阻力大小。阻力越大说明黏度越大,反之黏度越小。而且涂料各处受到的阻力应基本一致,否则说明涂料性能是不均匀的。但这种方法一般只用于测定厚浆状的原漆,而且不可能定量估算它的黏度。本文主要介绍流出法来测定粘度。
简单实用的测定方法是将一根木棍(或玻璃棒)放入涂料中并加以搅动,感觉受到的阻力大小。阻力越大说明黏度越大,反之黏度越小。而且涂料各处受到的阻力应基本一致,否则说明涂料性能是不均匀的。但这种方法一般只用于测定厚浆状的原漆,而且不可能定量估算它的黏度。本文主要介绍流出法来测定粘度。
流出法是通过测定液体涂料在一定温度条件下从一定容积的容器内流出所需时间,求出涂料黏度的方法。使用的仪器有毛细管和流量杯两种黏度计。
(1)毛细管黏度计
毛细管黏度计的结构如图1-5所示。用毛细管法测定涂料黏度是最古老和经典的方法。它较适合测定透明的清漆和低黏度的色漆等牛顿型涂料的黏度。不同研制者设计的毛细管黏度计外观有一定差别,常以研制者的名字命名,如奥氏黏度计(Ostwaldvisc0me-ter)、赛式黏度计(Sayb0ltvisc0meter)、坎氏黏度计(Cannan-Feuskevisc0meter)、乌氏黏度计(Ubbe10hdevisc0meter)等。各种黏度计按毛细管内径尺寸的不同规格,分别适用于对不同范围的黏度进行测量。其缺点是玻璃制品容易损坏,而且操作和清洗都比较麻烦,不太适用于工业生产。
(2)流量杯法
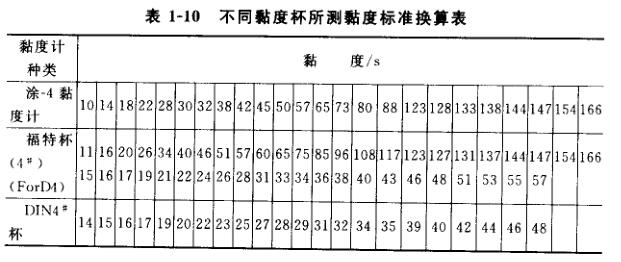
①流量杯黏度计的类型。流量杯法实际上是毛细管黏度计的工业化应用。世界各国使用的流量杯黏度计(简称流量杯)形状大致相同,但结构尺寸略有差别,故名称有所不同,并都按流出孔径大小分成不同型号。如我国通用涂一1黏度计和涂一4黏度计(GB/T1723-93),同时等效采用IS0流量杯(GB/T6753,4-86),有3#、4#、6#三种型号。德国和欧洲各国采用的是DIN黏度杯,有2#、3#、4#、6#、8#五种型号。每种型号的黏度杯都有其很好的的测定范围,如我国的涂一1黏度计适用于测定流出时间小于20s的涂料,涂一4黏度计适宜测定流出时问在20~100s的涂料,Is0及福特杯则适合测定流出时间在30~90s的涂料,若低于或高于此流出时间范围,则所测得的数值准确度变差。测定的流出时间(单位s)都可換算成以mm2/s为单位的运动黏度,但不同种类黏度杯的換算公式不同,而用不同种类黏度杯测定的流出时间也可以相互換算(见表1-10)。所以用流出法测定的是在流动过程中黏度保持不变的牛顿型流体的黏度。
②流量杯黏度计的构造和使用。从结构上看,流量杯黏度计是把毛细管黏度计起止线之问的容积放大并把细长的毛细管部分改成粗短的小孔,由于测量容积加大,流出孔变粗短,操作、清洗均比毛细管黏度计方便,而且适用于不透明色漆,因此在工业上应用较广。但应注意,这种黏度计较适用于低黏度的清漆和色漆,而不适用于测定非牛顿型流体的涂料和高稠度、高颜料分的涂料。
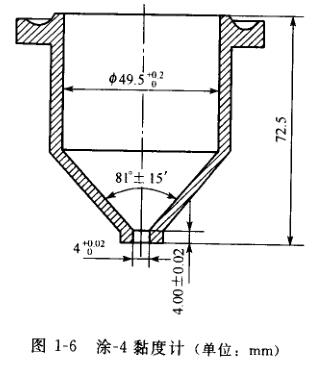
涂一4黏度计是上部为圆柱形、下部为圆锥形的金属容器。内壁粗糙度为Ra0.4µm。锥形底部有一漏嘴。在容器上部有一圈凹46

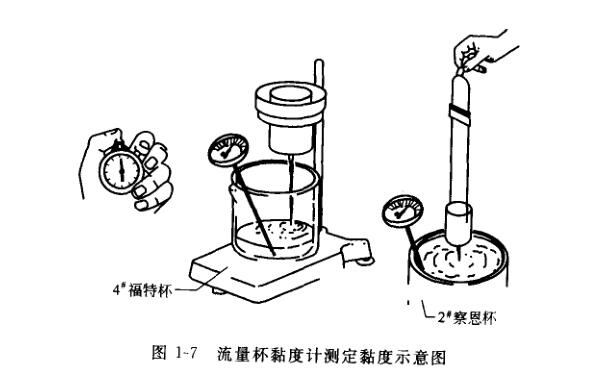
Before measurement, dip the solvent with gauze, wipe the viscometer clean, and dry it; then stir the paint sample evenly, and filter it with a metal sieve with a pore size of 246 µm if necessary. If there is no special requirement, the temperature of the sample should be kept at (23 ± 1) °C or (25 ± 1) °C; adjust the level screw to make the viscometer in a horizontal position, and place a 150ml enamel used for contacting liquid under the viscometer cup. During the measurement, block the leak with your finger, fill the viscometer with the sample, scrape the air bubbles and excess sample into the groove with a glass plate, quickly remove the finger, start the stopwatch at the same time, and stop the watch immediately after the sample flows out. After completion, repeat the test once according to the above formula, and the difference between the two measured values should not be greater than 3% of the average value. Figure 1-7 is a schematic diagram of measuring viscosity with a Flow Cup viscometer.
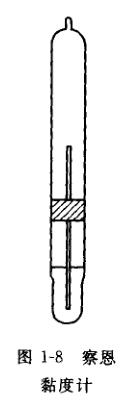
Another outflow viscometer suitable for construction sites is called Zahn (Zahn) viscometer, as shown in Figure 1-8.
It is a portable Viscosity Cup with a cylindrical and spherical bottom and a long handle; its volume is about 44cm3, and it is divided into 5 models according to the size of the small hole at the bottom, and they are combined into a set. The radii of each model hole are 1,00mm (1#), 1.37mm (2#), 1.88mm (3#), 2.13mm (4 books), 2.64mm (5#). A good measurement range is the outflow time of 30~90s. Different models can be used to measure products with different viscosities. The 2-D Zahn cup is commonly used to measure the viscosity of coatings. This kind of viscometer is characterized by simple structure, convenient operation and suitable for field use. The specific measurement method is shown in Figure 1-7. When measuring, first immerse the Zion viscometer into the coating to be tested. When starting the measurement, use the handle key ring to lift the Zion viscometer vertically out of the coating. When the coating starts to flow out from the small hole at the bottom, press the stopwatch to start timing. ,
Stop timing when the flow of liquid flowing down from the opening is interrupted (indicating that air has passed through the opening).
- 1Application of Rotational Viscometer in surface Coating viscosity measurement
- 2Application of Rotational viscometer in Coating Viscosity Detection
- 34 factors that affect paint viscosity
- 4Coating viscosity determination and viscosity influencing factors
- 5Effect of Carbon Black Pigment Characteristics on Coating Process
- 6Study on calibrating method of Coating viscometer
张蔚滨 - 《沈阳计量测试院》
- 7Four Types of Determination Methods for Coating Viscosity
郑顺兴 - 《涂料与涂装科学技术基础》
- 8Coating viscosity concept and measurement method Baike
- 9Viscosity of paint