Introduction of covering power and tinctorial strength of emulsion paint
Hiding power
The ability of the pigment to cover the surface color of the substrate in the coating film is called hiding power. It is usually expressed in terms of the dry pigment mass required to completely cover the base color per square meter of substrate area, g/m2. Hiding power is the result of the pigment's ability to scatter, absorb and reflect light.
White pigments are mainly scattering, and the hiding power produced by scattering is mainly related to the following three factors: Lorentz (L0rentz) factor, pigment particle size and pigment concentration. The Lorentz factor reflects the relationship between the refractive index of the pigment and the film-forming material, as shown in formula (3-1).
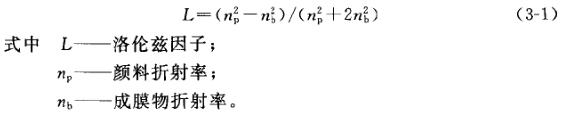
Experience has shown that hiding power is proportional to the square of f. This shows that the greater the refractive index difference between the pigment and the film former, the higher the hiding power. This is why rutile titanium dioxide has the highest hiding power.
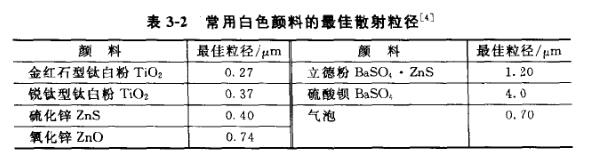
Particle size also has a large effect on scattering. When the particle size is very fine, the scattering is very small. With the increase of particle size , the scattering of rutile titanium dioxide, anatase titanium dioxide and sulfur row increases rapidly and reaches the maximum, while the scattering of zinc oxide and lithopone increases relatively slowly to the maximum. As the particle size increases further, the scattering decreases. Different pigments have different good scattering particle diameters. When the incident light is the average wavelength of visible light (λ=550nm), and Nb=1.55, the good scattering particle diameters of commonly used white pigments are listed in Table 3-2.
It can be seen from Table 3-2 that the best particle size of rutile titanium dioxide is about half of the average wavelength of visible light. This is also the reason why the particle size of commercially available rutile titanium dioxide is generally 0.2~0.4µm.
The effect of pigment volume concentration on the hiding power of the coating film is obvious. Experiments show that when the titanium dioxide is lower than 10% PVC, the hiding power increases linearly with the increase of the concentration; when the concentration exceeds 10% PVC, the hiding power increases with the increase of the concentration, but nonlinear; when the concentration exceeds 30% PVC , due to the agglomeration of titanium dioxide, the hiding power no longer increased with the increase of concentration, and even decreased slightly.
The black pigment mainly absorbs, when the frequency of the incident light is the same as the natural frequency of the pigment molecule, the absorption occurs, the larger the absorption coefficient, the better the hiding power.
For colored pigments, scattering and absorption work simultaneously.
Tinting power
Tinting strength is the ability of a certain pigment to show the strength of color after mixing with another benchmark pigment. Usually, white pigment is used as a benchmark to measure the coloring ability of various colored or black pigments to white pigments.
For the tinting strength of white pigments, it is now expressed by measuring the decolorizing power, that is, using a blue pigment to offset and determine the decolorizing power.
Tinting power is the result of the pigment's absorption and scattering of light, which mainly depends on the absorption. The greater the absorption capacity, the higher the tinting power. Tinting strength is also related to the size, shape, particle size distribution, crystal structure and dispersion of pigment particles in the coating film.
The stronger the tinting strength, the less pigment is used to prepare the same color.
- 1Summary of determination methods for hiding power of coatings
- 2Pigment hiding power
- 3Determination of Coating hiding power
- 4GB/T 23981.2-2023: Paints and varnishes - Determination of hiding power - Part 2: Checkerboard method - Interpretation
- 5Concept, influencing factors and determination method of Coating hiding power
- 6Mayer Rods: The right-hand man for hiding power tests
- 7Coating performance testing: ensuring the efficiency and mass of the painting process
- 8Coating hiding power measurement
- 9Application of paint film Applicator in hiding power test



