Precautions for the use of laboratory high temperature furnaces
High temperature furnace
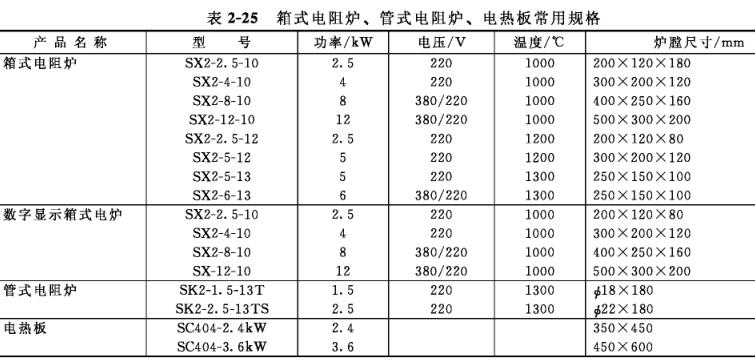
The high-temperature furnaces used in the laboratory include: box-type resistance furnace (muffle furnace), tube-type resistance furnace (tube-type combustion furnace) and high-frequency induction heating furnace. According to the different forms of heat source, it can be divided into resistance wire type, silicon carbide rod type and high frequency induction type. The commonly used specifications of box-type and tube-type resistance furnaces and Electric Heating Plates are shown in Table 2-25.
(1) Box-type resistance furnace (muffle furnace) is often used in mass analysis for precipitation burning, ash determination and carbonization of organic substances. When in use, it is matched with the corresponding thermocouple and temperature console, and can automatically measure and control the temperature within the rated temperature range.
For an electric furnace with a working temperature of 950°C, the heating element is iron-chromium-aluminum wire, which is wound around the furnace. For an electric furnace with a working temperature of 1300°C, the heating element is a silicon carbide rod, which is installed on the upper part of the furnace.
The muffle furnace with electrothermal structure has a maximum operating temperature of 950°C, and its furnace chamber is made of high temperature resistant silicon oxide combination. There are electric heating wires around the furnace, and the whole furnace is heated evenly after power on. The periphery of the furnace is covered with refractory soil, refractory bricks, asbestos boards, etc. to reduce heat loss. The shell is wrapped with the frame and iron sheet of angle iron, and the furnace door is made of refractory bricks. A small hole is opened in the middle, and a transparent mica sheet is embedded to observe the temperature rise in the furnace. When the hearth is dark red, it is about 600°C, when it reaches dark pink, it is about 800°C, and when it is light red, it is 950°C. For safe operation, some electric furnaces are equipped with limit switches on the furnace door. When the furnace door is opened, the electric furnace will automatically cut off the power, so it can only be heated when the furnace 1-] is closed. Furnace must be temperature controlled. The temperature controller consists of a millivolt meter and a relay, connected to a matched thermocouple for temperature control. The thermocouple is installed in a high temperature resistant porcelain tube and extends into the hearth from the small hole at the rear of the high temperature furnace. The temperature of the furnace is different, and the thermocouple produces different potentials, and the magnitude of the potential is directly displayed on the controller meter by the value of the temperature. When the pointer indicating the temperature slowly rises to meet the previously adjusted control temperature pointer, the relay immediately cuts off the circuit and stops heating. When the temperature drops and the upper and lower pointers separate, the relay reconnects the circuit and the electric furnace continues to heat. Repeatedly, the purpose of automatic temperature control can be achieved. Usually before the temperature is raised, the temperature control pointer is set to the predetermined temperature position, and the burning time is calculated from the time when the predetermined temperature is reached.
The muffle furnace commonly used in the laboratory is usually equipped with a nickel-chromium-nickel-silicon thermocouple, and the temperature measurement range is 0~1300°C.
The production units are: Wuhan Wuchang Experimental Instrument Factory; Shanghai Experimental Instrument Factory; Jiaxing Electric Heating Instrument Factory, Changsha Kesheng Industrial Co., Ltd., etc.
The following points should be paid attention to when using the box-type resistance furnace (muffle furnace)
①The muffle furnace needs to be placed on a solid cement platform or a special iron frame, and no chemical reagents and flammable and explosive items should be stored around it. The thermocouple rod is inserted into the furnace from the small hole at the back of the high temperature furnace, and the special wire of the thermocouple is connected to the connection column of the temperature controller. Be careful not to connect the positive and negative poles incorrectly, so as not to damage the temperature pointer due to reverse direction.
②The muffle furnace should use a special switch to control the power supply, and cannot be controlled by a direct plug-in plug. It is necessary to find out whether the power supply voltage, configuration power, fuse and switch required by the muffle furnace are suitable, and connect the ground wire to avoid danger. A piece of thick rubber can be laid on the ground in front of the furnace, which is safer during operation.
③Because the electric furnace may be damp during storage and transportation, it needs to be dried in the oven before use to prevent the furnace from cracking due to rapid temperature changes. Oven time:
The working temperature of the electric furnace is 950°C, room temperature ~200°C, 4h; 200~600°C, 4h.
The working temperature of the electric furnace is 1300°C, room temperature ~200°C, lh; 200~500°C, 2h; 500~800°C, 3h; 800~1200°C, 2h.
④ In order to maintain the service life of the electric furnace, do not exceed the limit temperature during use. When loading and unloading the sample, care must be taken to prevent damage to the silicon carbide rod.
⑤ When melting or burning in the muffle furnace, it is necessary to strictly control the operating conditions, heating rate and maximum temperature to prevent samples from splashing, corroding and sticking to the furnace. Such as burning organic matter, filter paper, etc., need to be carbonized in advance. Keep the furnace clean and flat to prevent the crucible from sticking to the furnace. For this reason, the oxides in the furnace should be removed frequently, and refractory sheets should be placed in the furnace to prevent accidental splashes from damaging the furnace and make it easy to replace.
⑥ When the muffle furnace is in use, someone should always take care of it to prevent the self-control from malfunctioning and causing accidents. Never use the muffle furnace at night when no one is around.
⑦ The thermocouple should not be inserted or pulled out suddenly at high temperature to avoid bursting. Care should be taken when inserting or removing to prevent breaking.
⑧When the burning is completed, the electric llllJ should be opened first to cut off the power supply. The furnace door should not be opened immediately to prevent the furnace from being suddenly cold and shattered. Usually open a small slit first to let it cool down faster. When the temperature drops to 200°C, open the furnace door and take out the sample with long-handled crucible pliers.
(2) Tube-type resistance furnace (tube-type combustion furnace) tube-type combustion furnace is usually used for the analysis of gas components in minerals, metals or alloys.
Its heat source is electrically heated by two silicon carbide rods of the same specification, usually equipped with a voltage regulator and power distribution device (including ammeter, voltmeter, thermocouple, temperature measuring millivolt meter), and a set of gas scrubber .
Pay attention to the following points when using
①The heating and cooling needs to be carried out slowly. The temperature in normal use should not exceed 1350°C, and the current should not exceed 15A.
② Check whether the power supply voltage, power, and switch fuse are suitable. Connect the ground wire to ensure safe operation.
③ After the gas is washed, it must pass through the drying device before it can enter the furnace to prevent the furnace from breaking.
④ During use, sparks often occur due to poor contact between the wire and the silicon carbide rod joint. At this time, make sure that the contact is good before continuing to use it.
⑤ Always check the electrical wiring, especially the high-temperature head of the thermocouple is often inaccurate due to poor contact.
⑥ After the silicon carbide rod is broken, it needs to be replaced with a new rod of the same specification.
(3) The high-frequency induction heating furnace, also known as the high-frequency furnace, uses the self-excited oscillation of the electron tube to generate a high-frequency magnetic field and the eddy current generated by the metal under the action of the high-frequency magnetic field to generate heat, causing the metal sample to melt. After the oxygen is passed through, gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide are produced for chemical analysis.
- 1Principle and application of muffle furnace
- 2Introduction of working principle and application of muffle furnace
- 3Working principle and application analysis of muffle furnace
- 4Application of muffle furnace in Determination of Tobacco Ash
- 5Box type resistance furnace - temperature magician in industry
- 6How does a muffle furnace analyze the ash content in food?
- 7How does muffle furnace affect rubber properties?
- 8How to test the different properties of rubber?
- 9Determination of Ash and Pigment Base Ratio in Electrophoretic Coatings














