Study on HDPE surface tension based on dyne test
Because the surface of solid polymer materials has pores, uneven defects, and complex surrounding environments such as gas adsorption, it is difficult to directly and accurately measure its surface tension[1,2]. Although scientific researchers have explored many methods of indirect calculation of solid surface tension on the basis of experiments, such as solution heat method, temperature extrapolation method, splitting work method, contact angle method and tension method, etc. [3-5]. However, in engineering applications and daily testing, these methods not only have their own shortcomings, but also are inconvenient to use.
According to the information [6], the DY-L series dyne pen can conveniently and accurately test whether the surface tension of the plastic reaches the value of the test pen. In this experiment, in order to study the surface properties of high-density polyethylene hollow spheres with different fluorination degrees in No. The shrinkage of the beads can be used to determine the surface tension of the microspheres.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Materials and instruments
Non-fluorinated HDPE hollow spheres (0#), fluorinated HDPE hollow spheres (1#, 2#, 3#, see Table 1 for surface fluorination content), Shanghai Jinfei Petrochemical Co., Ltd.; No. 3 jet fuel and No. 75 Aviation gasoline, produced in Daqing Oilfield; absolute ethanol, 99.9%, commercially available; 32, 38, 44, 56mN/m4 dyne pens, produced by Italian Melan company.

1.2 Test method steps and surface tension evaluation criteria
Test method: Make the DY-L dyne pen always point to the center of the HDPE hollow ball, apply appropriate pressure, and gently draw a line on the surface of the ball. Usually 3 dyne pens with adjacent dyne numbers are needed.
Test procedure: divided into 3 test groups according to different test conditions. Before the test, wash the microspheres with absolute ethanol, and then treat the microspheres under different conditions, and then wash the treated microspheres with absolute ethanol. After drying, coat the surface of the microsphere with a dyne pen and record the test phenomenon.
The surface tension evaluation criteria are shown in Table 2.
1.3 Results and discussion
Table 3 is obtained by comparing the dyne test phenomena of unsoaked microspheres with different fluorine contents.
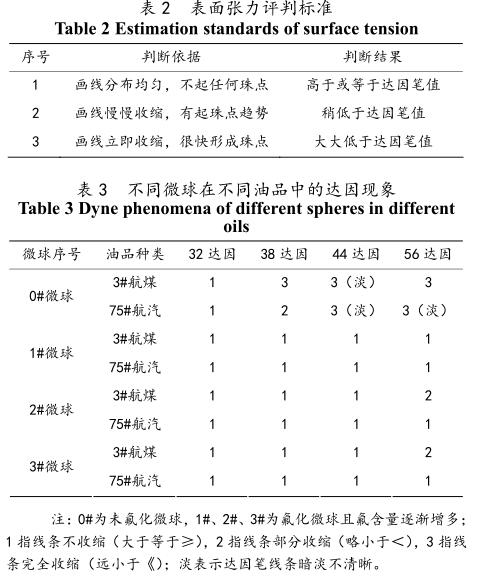
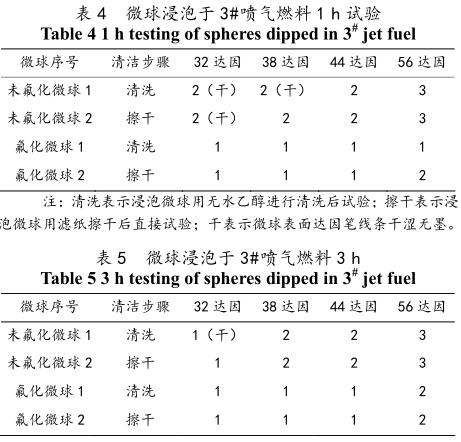
According to the analysis of test phenomena, it is concluded that the dyne value of non-fluorinated microspheres is between 32 and 38, and the dyne value of fluorinated microspheres is between 44 and 56, indicating that the surface tension of non-fluorinated microspheres is much lower than that of fluorinated microspheres. The surface tension of the microspheres increases with the increase of the fluorine content on the surface of the microspheres. Therefore, with the increase of the fluorine content on the surface of the microspheres, its oil-repellent performance is also better. Comparing the dyne test phenomena of the microspheres soaked in 3# jet fuel for 1h and 3h, the experimental phenomena are shown in Table 4 and 5. Analysis of the test phenomenon: the dyne value of the soaked microspheres decreases, indicating that soaking in oil reduces the surface tension of the microspheres. At the same time, the non-fluorinated microspheres become dry compared to the surface of the fluorinated microspheres after soaking, and the lines on the dyne strokes appear dim, while the lines on the fluorinated microspheres cannot be removed with general detergent, and absolute alcohol must be used forcibly Wiping shows that the soaked fluorinated microspheres have strong adhesion and high surface energy, and also show that the oleophobic property of fluorinated microspheres is better than that of non-fluorinated microspheres.
The reason why the oleophobic performance of fluorinated microspheres is better than that of non-fluorinated microspheres is that the fluorine segment in the surface fluorinated layer reduces the surface tension of the microspheres, increases the contact angle, and improves the oleophobic performance. In addition, the oleophobic performance of fluorinated microspheres does not increase indefinitely with the increase of fluorine content. When the fluorine content reaches a certain value, the fluorine atoms spread on the surface of the film to form a fluorinated layer, making it wrap the carbon chain skeleton, Increasing the fluorine content does not significantly change the spread of fluorine atoms on the surface of the film, the change of the contact angle is no longer obvious, and the oil repellency is no longer improved.
2 Conclusion
Dyne tests were performed on fluorinated and non-fluorinated microspheres to compare their surface tension. From the observation of the lines they appear in the experiment, it can be seen that the lines on the surface of the non-fluorinated microspheres appear the darkest, indicating that the surface tension of the non-fluorinated microspheres is the smallest, and the measured surface tension of the microspheres increases with the increase of the fluorine content. , indicating that fluorinated microspheres have better oleophobic properties than non-fluorinated microspheres, and the higher the fluorine content, the better the oleophobic properties. At the same time, the lines on the surface of the non-fluorinated microspheres are dry and inkless compared to the surface of the fluorinated microspheres, while the lines on the fluorinated microspheres cannot be removed with general detergent, and must be wiped with absolute ethanol to clean them. Fluorinated microspheres have strong adhesion and large surface energy, which also shows that the oil repellency of fluorinated microspheres is better than that of non-fluorinated microspheres.
-
-
Fengzhiyue 30 Dyne pen$ 83.00
- 1Application of Dyne pen in surface tension measurement
- 2Dyne pen in film printing
- 3Dyne pen test method
- 4How to Use a Dyne Pen to Determine Surface Energy
- 5How to Ensure the Accuracy of the Dyne Pen Test
- 6Dyne Pen Controls Surface Tension of Printed Coatings
- 7Four simple steps to use the dyne pen correctly
- 8Dyne pens and test fluid -- how do they work?
- 9What is dyne level?







