Discussion on Light spectrum characteristics of ZBD Whiteness meter
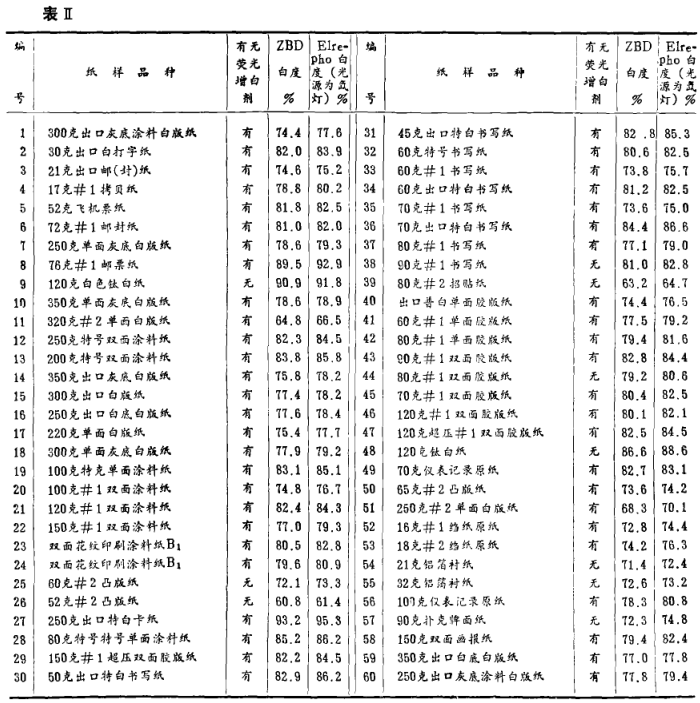
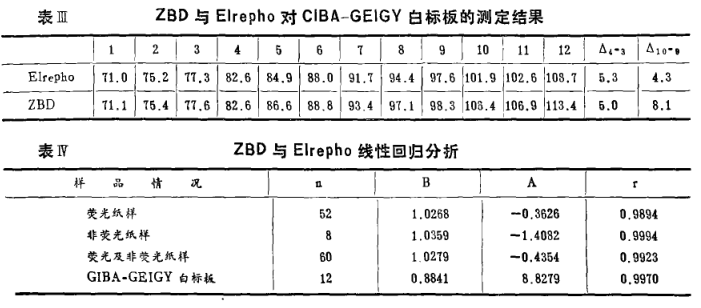
Experiments have confirmed that the ZBD Whiteness Meter and the Elrepho Whiteness Meter illuminated by the filter float lamp are very close to the whiteness measurement results of non-fluorescent materials and fluorescent materials, and the correlation coefficient is greater than 0.98. The accurate measurement of the degree shows that it has unique spectral characteristics, that is, the weighting factor for the fluorescence emission of the sample is greater than the weighting factor for the visible light reflection of the sample. It has been demonstrated that further investigation into the choice of fluorescence emission weighting factors is needed to professionalize the performance of an intensity meter illuminated by filtered tungsten lamps.
One, citedWord
As a quality index of white or near-white paper and paperboard, whiteness has always been valued by people in the paper industry. They are expressed by the blue light diffuse reflectance factor of the sample under test. The calculation formula is:
W=B(1)
(1) In the formula, W is the whiteness of papermaking, and B is the blue color in the three-dimensional excitation value of the color.
The ISO/2469 and ISO/2470 standards promulgated by the ISO organization in 1979 have unified regulations on the spectral characteristics of the Whiteness Meter: the effective wavelength is 457nm±0.5nni, the half-wave width is 44nm, and the Elrepho Whiteness Meter is set as International standard reference instrument.
Since the application of fluorescent whitening agents in the paper industry, the measurement of the fluorescent whiteness of paper has attracted widespread attention. In fact, the whiteness of paper can be regarded as composed of two parts, one is the diffuse reflection factor of the non-fluorescent material in the paper to the visible light in the light source radiation; the other is the absorption of the radiation by the fluorescent whitening material in the paper The fluorescent excitation components of mid-ultraviolet and near-ultraviolet, after STOKES shift, emit visible fluorescence, and are called fluorescent whitening agents to contribute to whiteness.
The measurement of paper whiteness was originally illuminated by tungsten lamps. Through the function of optical filters, the irradiation can be in good agreement with the standard illuminant De5 light source in the visible light range, as shown in Figure (1). Show. However, due to the application of fluorescent whitening agents, some problems have been caused to the original method. The reason is that the higher the irradiation power in the wavelength range of fluorescence excitation, the lower the irradiation power in the fluorescence emission range, and the lower the fluorescence contrast whiteness. contribution becomes more important. Therefore, the power distribution of irradiation should not only conform to the standard illuminant in the visible light range, but also need to conform to the standard illuminant in the entire near-ultraviolet and visible short-wave regions that cause fluorescence excitation. It can be seen from Figure (1) that the power distribution of the filtered tungsten lamp and the D85 light source in the fluorescence excitation area are very different. The results of measuring the whiteness of the same fluorescent sample with different instruments are inconsistent, which mainly ignores the dependence of the radiance factor of the sample on the irradiance power distribution in the fluorescence excitation and fluorescence emission bands. The domestic ZBD Whiteness Meter measures the whiteness of the sample containing fluorescent whitening agent under the illumination of the filtered lb filament lamp. The result is quite close to that of the Elrepho Whiteness Meter simulated by the De5 light source and xenon lamp illumination, and the correlation coefficient between the two is greater than 0.98. The reason is that the design of the optical filter and its position in the light source constitute the unique spectral characteristics of the ZBD Whiteness Meter. The optical filter plays two roles here: one is that the optical filter and other optical The combination of components makes the spectral characteristics of the instrument close to the DeB light source in the visible light range. The second is that the weighting factor of the filter on the fluorescence emission of the sample is greater than the weighting factor of the visible light reflection of the sample, which makes up for the shortage of near-ultraviolet components in the filtered tungsten light source.
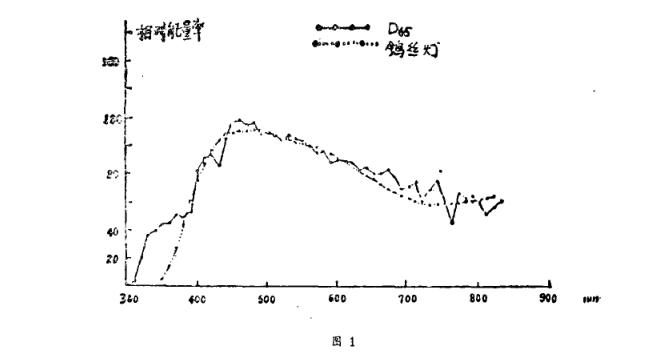
2. Spectral characteristics of ZBD Whiteness Meter
What are the spectral characteristics of the Whiteness Meter? ISO/2469 states: "The spectral characteristics of the instrument are mainly determined by the filter inserted into the beam." "The characteristics of the receiver, spherical lining and other parts of the equipment also change the spectrum of the instrument. Characteristics.” We believe that the spectral characteristics of the Whiteness Meter can be defined as follows: the spectral characteristics of the instrument are composed of the light source, the receiver and the optical components between them.
Figure (2) is a schematic diagram of the optical path of the ZBD Whiteness Meter, and the optical path is 4570. It can be seen from the figure that the spectral characteristics of the ZBD Whiteness Meter are composed of the light source-tungsten lamp, the blue filter between the light source and the sample, the amber filter between the sample and the receiver, and the receiver. A selenium photocell is composed • The mathematical expression of the spectral characteristic of the ZBD Whiteness Meter is.
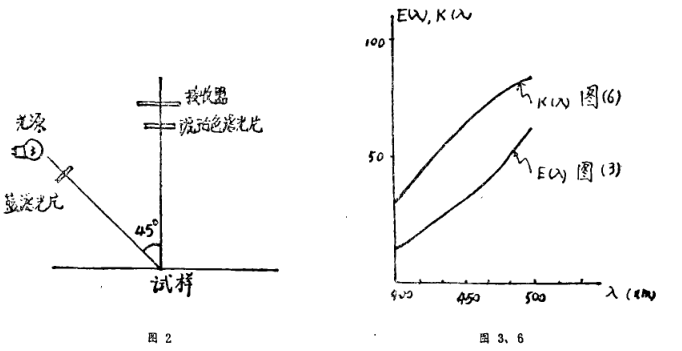
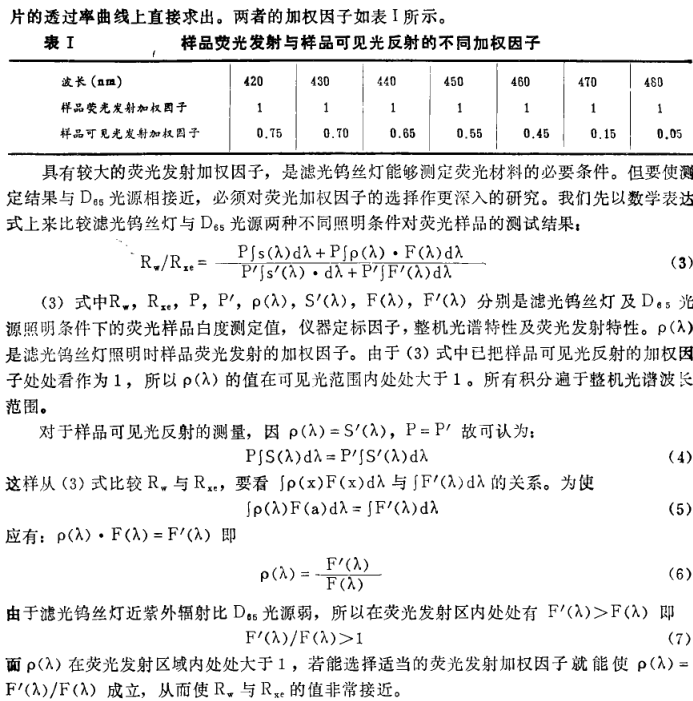
3. Discussion on the spectral characteristics of ZBD Whiteness Meter
The color filter of the Elrepho Whiteness Meter is a single blue filter with a transmittance peak at 457nm, and its position is between the sample and the receiver. The near-ultraviolet components irradiated by the light source excite the fluorescent substances in the sample, and the fluorescent emission and visible light of the sample enter the receiver after passing through the blue filter, and both have the same weighting factor. The obvious difference is that the peak value of the transmittance inserted into the optical path of the ZBD Whiteness Meter is 390The blue filter and the cut-off amber filter, the former is between the light source and the sample , and the latter is between the sample and the receiver.
For the measurement of the visible light reflection of the sample, it can be seen from the formula (2) that it has nothing to do with the position of the optical filter in the optical path. Because the spectral characteristics of the whole machine of ZBD and Elrepho are relatively close, it can be expected that the measurement of non-fluorescent whiteness is not the same. There will be significant differences.
Since the energy rate of the D85 light source simulated by the xenon lamp is significantly different from that of the filtered tungsten lamp in the fluorescence excitation region, unless the weighting factor for the fluorescence emission is greater than the weighting factor for the visible light reflection of the sample, the filtered tungsten lamp illumination for the fluorescent sample Measurements are always low. The blue filter between the light source and the sample in the ZBD Whiteness Meter has a large transmittance to near-ultraviolet light, which improves the relative proportion of near-ultraviolet components in the incident light of the sample. The transmitted near-ultraviolet light incident sample , to excite the fluorescent substance in the sample, after the fluorescent reflection of the sample is no longer passed by the blue filter, but directly enters the receiver through the amber filter.
Xiangpin’s reflection of visible light is affected by the blue filter. Compared with the two, the weight factor of sample fluorescence emission is greater than the weight factor of visible light reflection. ZBD Whiteness Meter compensates for the near-ultraviolet light in Bianqi’s tungsten light source. Insufficient ingredients. If the weighting factor for the sample fluorescence emission is regarded as 1 everywhere, then the weighting factor for the visible light reflection of the sample can be simply changed from blue filter to


- 1What are whiteness and yellowness?
- 2What is the whiteness index?
- 3How can the paper industry achieve greater whiteness?
- 4What properties should letterpress printing paper be tested for? What are the specific requirements?
- 5Opacity and Transparency Test Methods
- 6The working principle and operation method of Whiteness Meter
- 7What are the common physical properties of paper?
- 8The difference between paper whiteness, brightness and shadow
- 9Paper Brightness, Whiteness and Shadow: Definitions and Differences






