Standard operating procedure for moisture determination
Moisture Determination Standard Operating Procedures The purpose is to establish Moisture Determination Standard Operating Procedures. Suitable for moisture determination. It is mainly the quality inspectors who implement this operating procedure, and the director of the inspection room is responsible for supervising the correct implementation of this procedure.
The standard operating procedure is as follows
The first method (Fischer's method)
A. Volumetric titration
This method is based on the principle that iodine and sulfur dioxide can react quantitatively with water in pyridine and methanol solutions to determine moisture. The instruments used should be dry and can avoid the intrusion of moisture in the air, and the measurement operation should be carried out in a dry place.
Preparation and calibration of Fischer's test solution (1) Preparation Weigh 110g of iodine (placed in a sulfuric acid dryer for more than 48 hours), put it in a dry stoppered flask, add 160ml of anhydrous pyridine, pay attention to cooling, and shake until the iodine is completely After dissolving, add 300ml of anhydrous methanol, weigh the weight, put the flask in an ice bath to cool, pass through dry sulfur dioxide until the weight increases by 72g, add anhydrous methanol to make it 1000ml, seal it tightly, shake well, and place it in a dark place 24 hours.
This solution should be shaded, sealed, and stored in a cool and dry place. Calibrate the concentration before use.
(2) Calibration Use a moisture analyzer to calibrate directly. Or take a dry stoppered glass bottle, accurately weigh about 30mg of double-distilled water, add 2-5ml of anhydrous methanol unless otherwise specified, titrate with this solution until the solution changes from light yellow to reddish brown, or use the permanent stop titration method ( Appendix VII A) indicates the end point; another blank test is performed and calculated according to the following formula.
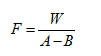
In the formula, F is equivalent to the weight of water per 1ml of Fertilizer’s test solution, mg;
W is the weight of double distilled water, mg;
A is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed for titration, ml;
B is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed by the blank, ml.
Determination method Accurately weigh an appropriate amount of the test product (about 1-5ml of Fischer's test solution consumed), unless otherwise specified, the solvent
It is methanol, measured directly with a moisture analyzer. Or put the test product in a dry stoppered glass bottle, add 2-5ml of solvent, and titrate with Fischer's test solution under constant shaking (or stirring) until the solution changes from light yellow to reddish brown, or use permanent stop Titration (Appendix VII A) indicates the end point; another blank test is calculated according to the following formula.
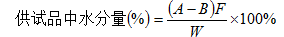
A is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed by the test product, ml;
B is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed by the blank, ml;
F is the weight equivalent to water per 1ml of Fischer's test solution, mg;
W is the weight of the test product, mg.
B.coulometric titration
This method is still based on the Karl Fischer reaction, and the permanent stop titration method (Appendix VII A) is used to determine the water content. Compared with volumetric titration, the titrant iodine in coulometric titration is not added from the burette, but is produced by electrolysis of the anolyte containing iodide ions. Once all the water has been titrated, a small excess of iodine is present in the anolyte, which is detected by the double platinum wire electrode and iodine production is stopped. According to Faraday's law, the amount of iodine produced is proportional to the current passing through, so the total amount of water can be determined by measuring the total consumption of electricity. This method is mainly used for the determination of substances with a small amount of moisture (0.0001-0.1%), especially for the determination of moisture in chemically inert substances such as hydrocarbons, alcohols and esters. The instruments used should be dry and able to avoid the intrusion of moisture in the air; the measurement operation should be carried out in a dry place.
Fischer's test solution Prepare or purchase the titration solution according to the requirements of the Karl-Fischer coulometric titrator. Because the instrument can measure electricity very accurately, there is no need to calibrate the titrant.
Determination method: remove the water in the system by pre-titration, then accurately measure the appropriate amount of the test product (water content is about 0.5 ~ 5mg), quickly transfer to the anolyte, and use the Karl Fischer coulometric titrator for direct measurement. Use the permanent stop titration method (Appendix VII A) to indicate the end point, and read the water content in the test product directly from the display screen of the instrument, of which 1 mg is equivalent to 10.72 coulombs of electricity.
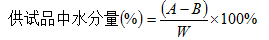
In the formula, A is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed by the test product, ml;
B is the volume of Fischer's test solution consumed by the blank, ml;
F is the weight equivalent to water per 1ml of Fischer's test solution, mg;
W is the weight of the test product, mg;
The second method (toluene method)
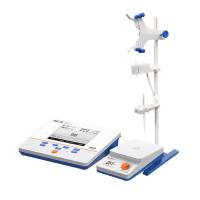
The instrument setup is shown in the figure. A is a 500ml short-neck round bottom bottle; B is a moisture measuring tube;
C is a straight condenser tube with an outer tube length of 40cm. Before use, all instruments should be cleaned and dried in an oven.
Determination method: Take an appropriate amount of the test product (about 1-4ml of water content), weigh it accurately, put it in bottle A, add about 200ml of toluene, and add a few glass beads if necessary. Add toluene to fill the narrow portion of tube B. Put bottle A in an electric heating mantle or heat it slowly by other suitable methods. When the toluene starts to boil, adjust the temperature so that 2 drops per second are distilled. When the water is completely distilled off, that is, when the water volume in the scale part of the measuring tube does not increase, first rinse the inside of the condenser tube with toluene, and then use a long brush soaked in toluene or other suitable methods to push down the toluene attached to the tube wall. Continue to distill for 5 minutes, let cool to room temperature, and disassemble the device. If water adheres to the wall of tube B, push it down with a copper wire dipped in toluene, and place it to completely separate the water from toluene (you can add a small amount of methylene blue powder, stain the water blue for easy observation). Check the water content and calculate it as the water content (%) of the test product.