Optical inspection of ultraviolet curing coatings for PET film - Lv Jianbo
Lv Jianbo
(Beijing Yingli Technology Development Co., Ltd., Beijing 100084)
Summary:
In this paper, a transparent hard coating material for PET optical film was prepared by using modified polyurethane acrylate as the main body. The effects of photocurable resin, active diluent, photoinitiator and other factors on the properties of hardness, wear resistance and adhesion of hardened PET optical film were discussed, and the experimental results were analyzed and discussed from the aspect of reaction mechanism. After testing: the hardness of the coating prepared in the experiment is 5H, and the adhesion is 100%. After the RCA paper tape abrasion test (500g, 1000cycles), the visible light transmittance of the PET film has no loss, and it has low surface tension and good flexibility. and good chemical resistance.
Key words: PET optical film; hardening; wear-resistant coating; UV curing
Article ID: 1674-0475 (2011) 06-0449-07
CLC number: O64; TQ57
Document identification code: A
Ultraviolet curing technology is a new green technology that came out in the 1960s. It refers to the process of forming a solid polymer through crosslinking and polymerization of liquid substances with chemical reactivity under the action of ultraviolet light. Compared with the existing thermal curing technology, it has the advantages of fast curing speed, low production energy consumption, less pollution, and superior coating performance. It is a new generation of green chemical products. At present, UV-curable coatings have been widely used in photosensitive materials, electronic communications, optical devices, packaging and decoration and other fields. In recent years, various optical parts based on polyester film (PET) have been widely used due to the development of raw materials and processing technology. PET materials have excellent properties, such as good mechanical properties, heat resistance and high transparency. However, due to the low surface hardness and poor wear resistance of PET materials, it is necessary to apply a wear-resistant protective coating to improve its service life. In this paper, taking PET optical film as the coating target, the effects of photocurable resin, reactive diluent, photoinitiator and other factors on the coating performance were studied, and a UV curable hard coating material applied to PET optical film was prepared.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Reagents and instruments
Reagent:
Modified polyurethane acrylate (PUA), Japan Synthetic Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.; hexyl ester acrylate derivatives (DPCA), Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; dipentaerythritol pentaacrylate (DPHA), Changxing Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.; 2- Hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenylacetone (1173), Beijing Yingli Technology Development Co., Ltd.; 1-hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone (184), Beijing Yingli Technology Development Co., Ltd.; leveling agent, BYK Company; butyl acetate, Tianjin No. 1 Chemical Reagent Factory; PET optical film, Japan Higashiyama Film Company.
instrument:
F300S electrodeless ultraviolet lamp (output power: 120W/cm; spectral output: 200-450nm), American Fusion UV company; LC-6B desktop transmission UV curing system, American Fusion UV company; LT-HW-012 infrared flux Flat machine, Baoding Special Light Source Electric Factory; DYL type dyne pen, Beijing Landmaker Technology Development Co., Ltd.; RDS type wire rod coater, American RDS Company ; PPH-Ⅰ type pencil Hardness Tester, Shanghai Modern Environmental Engineering Technology Co., Ltd.; QFH cross-cut device, Shanghai Modern Environmental Engineering Technology Co., Ltd.; 7-IBB RCA paper tape abrasion Tester, American Normal Tool Company; WGW haze meter, Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.; EIT UV Illuminance meter, American EIT company; SFS-S 400 laboratory high-speed dispersing machine, Shanghai Shihe Electromechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1.2 Preparation of wear-resistant coating and PET hard coating
1.2.1 Preparation of wear-resistant coating
Add photocurable resin and active monomer into high-speed dispersion kettle according to the ratio, stir at 60°C for 30 minutes at high speed, add metered photoinitiator and leveling aid, disperse at high speed for 10 minutes and filter The basic formula is shown in Table 1.

1.2.2 Preparation of PET hard coating The prepared wear-resistant coating sample is uniformly coated on the PET substrate by RDS-type wire Bar Coater, and the infrared leveling at the temperature of 60°C is carried out for a certain period of time. , Then, UV curing was carried out on a UV curing machine, the thickness of the coating was 3μm-4μm, and a PET hard film was obtained.
1.3 Test method
Hardness: pencil measurement method, determined according to GB/T 6739-2006;
Wear resistance: use RCA paper tape wear Tester, load 500g, rub 1000cycles, and then measure the transmittance;
Flexibility: Measured according to GB/T1731-1993;
Adhesion: Test according to GB 9286-1998;
Surface tension: measured with a dyne pen.
2 Results and discussion
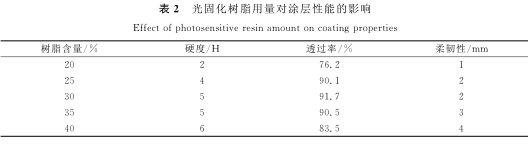
2.1 The effect of the amount of photocurable resin on the coating performance
The effect of the content of modified polyurethane acrylate on the properties of the coating film is shown in Table 2. It can be seen from the table that as the amount of photocurable resin increases, the hardness of the coating increases, while the adhesion decreases, and the wear resistance is better. When the amount is 25%-30%, the performance of the coating is better.
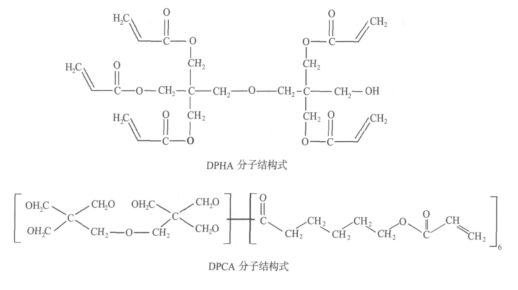
Analysis of the reason is mainly affected by the molecular structure. The resin has unique molecular structure characteristics. It has a soft chain segment composed of polyester or polyether and a rigid chain segment prepared by the reaction of isocyanate and alcohol compounds. This kind of group between them is very easy to form hydrogen bonds, and the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds can constitute a large number of effective physical cross-linking points, so a dense star-shaped space structure is formed between the two through hydrogen bonds; this special The structure of the ester group makes the ester group very stable, able to withstand the impact of the external medium as much as possible, while maintaining its own sufficient rigidity and mechanical strength. At the same time, because it does not contain benzene rings, it will not turn yellow under UV irradiation, so it has good weather resistance and mechanical properties. In the structure, because there are a large number of unsaturated double bonds (CC), they can activate the adjacent double bonds, so when a certain amount of energy is absorbed, the molecules will be excited. In the excited state, the double bond in the molecule is cleaved, and the generated free radicals can further initiate the cross-linking polymerization reaction. If the amount added in the system is too high or too low, the polymerization reaction rate and double bond conversion rate will decrease, the crosslink density of the product will be reduced, and the wear resistance of the coating will be affected.
2.2 The effect of the amount and ratio of reactive diluent on the coating performance
In terms of chemical structure, reactive diluents are generally small molecules containing polymerizable functional groups, so they are also called monomers customarily. According to the number of reactive groups contained in each molecule, it can be divided into monofunctional reactive diluents and multifunctional reactive diluents. In the UV curing system, in addition to adjusting the viscosity of the system, the reactive diluent can also affect the curing kinetics, the degree of polymerization, and the physical properties of the polymer produced; therefore, choosing a suitable reactive diluent is the key to UV wear resistance An important part of coating formulation design. Keeping the amount of reactive diluent at 60% of the system, the effects of different reactive
diluents and their amount on the coating performance are shown in Table 3.
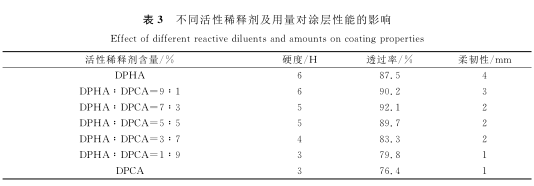
由表3可知,两种活性稀释剂对涂层性能的影响表现出不同行为,分析其原因主要是由其分子结构引起的,DPHA和DPCA的分子结构式如下所示.DPHA为高交联密度的稀释剂,和树脂交联固化时固化速度快,导致涂层残留单体多,涂层收缩率增大,涂层硬度提高,但脆性增大,附着力下降,涂层受到磨损时产生较大片状脱落,使得耐磨性下降;DPCA活性单体改善了DPHA的脆性,交联固化时具有适宜的交联密度,尽管可提高涂层的附着力和柔韧性,但是硬度较低,固化速度稍慢.将两种活性稀释剂复配使用,可发挥两者的协同效应,既可提高涂膜的硬度和固化速度,又可增强其附着力和耐磨性.由表3可见,当DPHA∶DPCA=7∶3时,涂层的综合性能更好.
由图1可以看出,光聚合涂层的耐磨性随功能单体加入量的增加而上升,在达到56%之后,耐磨性出现下降. 出现这种现象的原因可能是:功能单体含有可聚合的官能团,体系中单体浓度较低时,不能产生足够的交联点,导致交联密度低,影响材料的耐磨性;随着其加入量的增加,会加速聚合反应的速率,增加材料的交联度,有利于耐磨性提高.然而,如果过量,会导致涂层因收缩率太高而出现对基材的附着力下降,同时降低了双键的最终转化率,致使聚合物涂层中含有大量的单体残留,引起涂层片状脱落;并且涂层内的组分没有充分的时间调整,分子排列较为松散,使聚合材料的密度减小,进而降低其耐磨性.
出现这种现象的原因可能是:功能单体含有可聚合的官能团,体系中单体浓度较低时,不能产生足够的交联点,导致交联密度低,影响材料的耐磨性;随着其加入量的增加,会加速聚合反应的速率,增加材料的交联度,有利于耐磨性提高.然而,如果过量,会导致涂层因收缩率太高而出现对基材的附着力下降,同时降低了双键的最终转化率,致使聚合物涂层中含有大量的单体残留,引起涂层片状脱落;并且涂层内的组分没有充分的时间调整,分子排列较为松散,使聚合材料的密度减小,进而降低其耐磨性.
2.3 光引发剂用量及配比对涂层性能的影响
光引发剂是UV固化体系的重要组份,它是一类易吸收紫外光能量生成有效引发聚合反应活性中心的化合物,其作用是在吸收紫外光后产生引发固化反应的活性游离基团,如活性自由基、活性阳离子,从而使体系中的不饱和基团双键断开,发生聚合反应.本体系选择了α-羟烷基苯酮类光引发剂2-羟基-2-甲基-1-苯基丙酮(1173)和1-羟基环己基苯基甲酮(184),它是目前开发较为成功的一类商用光引发剂.这两种引发剂因为分子结构中苯甲酰基邻位没有α-H,所以有着很好的热稳定性,应用在丙烯酸酯体系中,光解时不会产生易导致黄变的取代苄基自由基结构,故基本不会导致固化涂层黄变.保持光引发剂用量为体系的5%,光引发剂种类及用量对涂膜性能的影响如表4所示.
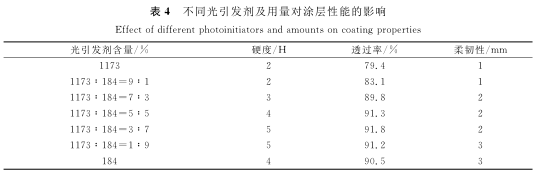
由表4可见,当1173∶184=3∶7时,涂层的综合性能更好.
如图2所示,光聚合涂层的耐磨性与光引发剂浓度呈非线形关系,在引发剂较低含量范围内 (其质量分数小于5.5%),耐磨性随光引发剂浓度增大呈上升趋势.这主要是由于光引发剂是决定光固化材料固化程度和固化速度的主要因素,在光固化过程中,体系中光引发剂浓度较低时,自由基在体系中基本是均匀形成的,它所产生的自由基部分将被涂层表面的O2所消耗,加大光引发剂浓度可增加体系中自由基的数量,充分引发自由基聚合,进而提高双键的转化率,促使聚合物交联密度升高.但当光引发剂浓度增大到一定限度后,由于涂层表层的自由基过度密集,初级游离基的耦合几率增大,以及初级游离基引起链终止的几率也增加,导致体系的交联度降低.紫外光分解光引发剂的能力已达到饱和,体系内残留自由基的量基本确定,多余的光引发剂以分子形式存在,在紫外光的照射下,残留的光引发剂分子发生分解,产生大量的自由基,引起涂层表面一定程度的老化粉化;并且随着表面聚合速率与固化层本体的交联速率之比增大,固化层内出现不同的应力,这会使固化层表面皱缩,造成耐磨性的下降.
(其质量分数小于5.5%),耐磨性随光引发剂浓度增大呈上升趋势.这主要是由于光引发剂是决定光固化材料固化程度和固化速度的主要因素,在光固化过程中,体系中光引发剂浓度较低时,自由基在体系中基本是均匀形成的,它所产生的自由基部分将被涂层表面的O2所消耗,加大光引发剂浓度可增加体系中自由基的数量,充分引发自由基聚合,进而提高双键的转化率,促使聚合物交联密度升高.但当光引发剂浓度增大到一定限度后,由于涂层表层的自由基过度密集,初级游离基的耦合几率增大,以及初级游离基引起链终止的几率也增加,导致体系的交联度降低.紫外光分解光引发剂的能力已达到饱和,体系内残留自由基的量基本确定,多余的光引发剂以分子形式存在,在紫外光的照射下,残留的光引发剂分子发生分解,产生大量的自由基,引起涂层表面一定程度的老化粉化;并且随着表面聚合速率与固化层本体的交联速率之比增大,固化层内出现不同的应力,这会使固化层表面皱缩,造成耐磨性的下降.
2.4 流平助剂用量对涂层性能的影响
In the surface curing system, the local part of the coating  forms , that is, the shrinkage part is a low surface tension substance; since the low surface tension substance always shows a tendency to stretch and expand, this makes it from The center begins to spread to the surroundings, but the high surface tension substances in contact with the surroundings show a tendency to shrink. Therefore, under the interaction of the two, defects such as orange peel, brush marks, fish eyes, shrinkage cavities, and pitting will appear on the coating surface. For this reason, one or several additives are usually
forms , that is, the shrinkage part is a low surface tension substance; since the low surface tension substance always shows a tendency to stretch and expand, this makes it from The center begins to spread to the surroundings, but the high surface tension substances in contact with the surroundings show a tendency to shrink. Therefore, under the interaction of the two, defects such as orange peel, brush marks, fish eyes, shrinkage cavities, and pitting will appear on the coating surface. For this reason, one or several additives are usually
added to the system to improve the surface properties of the coating. Different amounts of additives were added into the system to investigate the effect of additives on the properties of the photopolymerization coating. The experimental results are shown in Figure 3.
The results in Figure 3 show that when the amount of additives added is less than 1.6%, the wear resistance of the photopolymerized coating gradually increases. Each microscopic part of the coating system is evenly distributed, and the surface tension of the coating system is different on the vertical and plane surfaces, and Bénard Cell (Bénard Cell phenomenon) appears, resulting in poor smoothness of the coating surface, causing shrinkage cavities, edge shrinkage, needles, etc. At the same time, it is difficult to effectively reduce the surface tension of the system, increase the wettability and permeability of the substrate, and improve the adhesion between layers. However, if the additives are added in excess, some additives will gather in some parts of the substrate to form some spaces with extremely low surface tension, which will cause microbubbles on the surface of the coating and affect the rheological properties of the system. Cause recoating and loss of adhesion.
3 Conclusion
A kind of optical film coating material with excellent physical and chemical properties was prepared by using ultraviolet light curing reaction system, which solved the contradiction between surface hardness and flexibility existing in UV hardened coatings. The experimental results show that the more suitable formula is that the amount of photocurable resin is 25%-30% of the system, and the amount of reactive diluent is 55%-60% of the system.
-
-
-
Fengzhiyue 30 Dyne pen$ 84.00
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 1Application of Mayer Rods in protective coating prepative
- 2Application of Mayer Rods in 2D Single Crystal Copper Nanosheet Films
- 3Polyurethane-graphene composite prepative film
- 4Application of Mayer Rods in composite coating prepative
- 5Several Common Experimental Spreader Methods and Their Applications
- 6Application of Mayer Rods in Water-based ink Moulding
- 7Technical method and application of preparing nanometer silver wire thin films with Mayer Rods
- 8The experimental case of OSP Mayer Rods at inks Moulding [with video]
- 9Thin layer chromatography, TLC method for preparing PLA film














