Pigment generality
Pigments enable paint to have basic functions such as coloring, covering, and protection. The coloring of the paint film by the pigment is to give the paint film the desired color. Covering is the ability of the paint film to cover the substrate, so that the substrate does not show the original color, and it is realized by the hiding power of the pigment. This section first discusses the concept of hiding power, and then discusses the concepts of tinting strength, oil absorption, and the basic properties of pigment particle size, shape and particle size distribution used in the formulation design of paint.
(1) Hiding power
The hiding power of the pigment is the ability of the pigment in the paint film to cover the substrate without revealing the original color of the substrate. Apply the paint on the substrate with black and white stripes, and the mass (g) of the pigment required to cover the surface area of 1m2 of the substrate represents the covering power of the pigment, g/m2. The hiding power of the colored paint made after adding pigments to the surface is called the hiding power of the colored paint. Hiding power is an important indicator for evaluating the performance of paints. Selecting pigments with strong hiding power can reduce the amount of pigments in the paint and meet the requirements of covering the substrate.
The hiding power is due to the difference between the refractive index of the pigment and the refractive index of its surrounding medium (polymer resin in the paint film). When the difference between the two is zero, that is, when the refractive index of the pigment is equal to that of the polymer resin in the paint film, the paint film is transparent; the greater the difference between the two, the stronger the hiding power. Hiding power is the result of light scattering and absorption by pigments, and its level is determined by the composition of the paint.
Calcium carbonate is applied to the wall in a wet state. Since its refractive index is not much different from that of water, it seems that the covering power is poor. However, after drying, the air replaces water, and the difference in refractive index increases. Increase. The hiding power is also related to the size and distribution of the pigment particles, the pigment particles are small and the hiding power is strong. For most pigments, the effective particle size is half of the visible light transition length, that is, o.2~o.4µm. During the drying process of the paint film, the distance between the pigment particles decreases, and the effect of the size of the gap between the pigment particles on the hiding power is:
S=(0.75/PVC)1/3-1.0
HP=KS/(S+1)
In the formula, HP is the hiding power; S is the diameter of the void between the pigment particles; K is the proportionality constant.
The PVC of a paint is 4.5%, the average distance between pigment particles is 1.54µm, HP=0.61K, after forming a dry paint film, PVC=15%, the distance is 0.70µm, HP=0.41K. After the paint film dries, the pigment concentration increases and the hiding power decreases.
At present, there are three methods for measuring the hiding power of paints.
①Use the mass per unit area method to determine the minimum amount of paint required to cover a unit area, and use g/m2 to express the hiding power. Usually black and white grid glass is used, and standard black and white grid paper can also be used. my country's national standard GB1726-79 (88) "Determination of Coating Hiding Power" stipulates the use of black and white grid panels, and there are two methods: brushing and spraying.
② The minimum paint film thickness method uses the minimum wet film thickness required to cover the bottom surface to measure the hiding power of the paint, and the results are expressed in µm. The measuring instrument is a
It is covered with a transparent glass top plate with a certain height at one end, thus forming a wedge-shaped space. When measuring, pour a small amount of sample on the bottom plate and move the top plate back and forth until the black and white dividing line on the bottom plate cannot be seen through the top plate and the paint layer. , write down the reading from the dividing line to the front end of the top plate, since the angle of the wedge-shaped space is known, the minimum wet film thickness can be obtained, or the amount of paint per unit area can be converted through the conversion table attached to the instrument. This method uses less paint, and the test speed is fast, but it is still a visual test, and there are problems with the accuracy of the test results.
③Reflectance comparison method In order to overcome the difficulty of visually measuring the end point, Is0 and national standards all recommend using a reflectance meter to evaluate the hiding power more accurately, but this method is mainly suitable for white and light-colored paints. Coat the sample with different thicknesses on the transparent polyester film, place it on the black and white glass plates after drying, measure the reflectance with a reflectance meter, RB is the reflectance on the black plate, Rw is the reflectance on the white plate , According to CR=RB/Rw, thus draw the contrast ratio CR.
When the contrast ratio is equal to 0.98, it is considered to be fully covered, and the hiding power can be obtained according to the thickness of the paint film. This method is more accurate in judging the end point and can overcome the shortcomings of the above two methods, but the operation is more complicated. my country has equivalently adopted the ISO standard, and formulated the national standard GB9270-88 "Determination of the Contrast Ratio of Light-Colored Paint by Polyester Film Method". This method can also be used to measure the contrast ratio at different spreading rates (m2/L), that is, the corresponding hiding power.
(2) Tinting power
Tinting strength is the ability of a color pigment to present its own color strength after being mixed with a reference pigment. White pigments are usually used as a benchmark to measure the coloring power of colored or black pigments to white pigments.
(3) Size, shape and particle size distribution of pigment particles
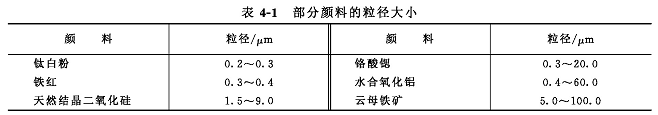
The average particle size of most pigments is 0.01~1.0µm, but the particle size of extender pigments and a small amount of other pigments is larger (as listed in Table 4-1). The smaller the particle size of the pigment, the greater the degree of dispersion, the greater the hiding power, and the greater the tinting power. Narrow particle size distribution, pure color, good performance.
Pigments mainly exist in three shapes: tumor-like, approximately spherical, such as titanium dioxide and lithopone; needle-like, such as asbestos, certain zinc white, which have a reinforcing effect and can improve the mechanical properties of coatings; flat, such as The buoyant aluminum powder paste and micaceous iron oxide also have a strengthening effect on the coating, and some flat pigments also have an orientation effect, which are arranged in parallel in the paint film, can block the penetration of gas and water, and have good corrosion resistance and special appearance .
The particle size of the pigment has a certain distribution range, and the frequency of particle appearance is plotted against the particle size, showing a non-normal distribution, that is, a distribution skewed to the left. This shows that the probability of occurrence of small particle size particles is greater than that of large particle size particles. A peak appears on the distribution graph, that is, the probability of particles appearing under a certain particle size is the greatest. We hope that the faster the decline of the curve on both sides of the peak, the better, which means that the probability of particle size is concentrated, the particle uniformity is good, and the color of the pigment at this time is pure and the performance is good.
(4) Oil absorption
The oil absorption is determined by the following method: add linseed oil drop by drop to 1oog of pigment, and mix it with a spatula at any time. When adding oil at the beginning, the pigment remains loose, but in the end all the pigment can be bonded together to form a ball. If you continue to refuel, the system will become thinner. The minimum amount of oil used to bond all pigments together is the oil absorption (OA) of the pigment.
Oil absorption (OA) = linseed oil / 100g pigment
When the oil absorption is reached, the surface of the pigment is full of oil, and the gaps between the particles are also full of oil. If oil is added, the viscosity will decrease.
- 1Summary of determination methods for hiding power of coatings
- 2Pigment hiding power
- 3Determination of Coating hiding power
- 4GB/T 23981.2-2023: Paints and varnishes - Determination of hiding power - Part 2: Checkerboard method - Interpretation
- 5Importance and determination method of paraffin resistance of pigments
- 6Concept, influencing factors and determination method of Coating hiding power
- 7Mayer Rods: The right-hand man for hiding power tests
- 8Coating performance testing: ensuring the efficiency and mass of the painting process
- 9Coating hiding power measurement

