Film Conditioning Test
The chemical reaction in which the main chain of a polymer is broken without changing its chemical composition and its molecular weight is reduced is called polymer degradation. During the use of the coating film, it undergoes a series of chemical and physical changes under the action of various factors, making it lose its use value, which is called the aging of the coating film. The degradation of polymer is the main cause of coating film aging. The outdoor durability of coatings refers to the performance of coatings exposed to outdoors and resisting various changes in the outside world. Outdoor durability is also called weather resistance.
Aromatic polyurethane (Ar-NH-C00R) and bisphenol A epoxy resin absorb ultraviolet rays with a wavelength less than 290nm in sunlight, and generate free radicals through direct photocleavage, causing oxidative degradation of polymers. Coatings made from aromatic isocyanates tend to yellow severely after a short period of exposure. Coatings made of bisphenol A epoxy resin will chalk quickly after exposure to sunlight. Because ketones absorb UV light, ketone solvents should be avoided. When acrylic acid is polymerized in a ketone solvent (such as methyl amyl ketone), the ketone group enters the resin through chain transfer. Therefore, it is better to use esters or toluene as a solvent for acrylic acid polymerization to avoid the introduction of ketone groups into the resin. .
Highly chlorinated resins such as vinyl chloride copolymers, vinylidene chloride copolymers, and chlorinated rubbers are degraded by autocatalysis and dehydrochlorination in the environment of heat or ultraviolet radiation. Such coatings should be formulated with stabilizers.
The degradation of other polymers is carried out by the absorption of ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of less than 290nm in sunlight by the peroxide and ketone groups formed in the polymer. The degradation of these polymers is a chain reaction process. After absorbing ultraviolet rays, the polymers are in a high-energy excited state, and chemical bonds are broken to generate free radicals. Free radicals and 02 undergo automatic oxidation to produce peroxide radicals (POO ), on the one hand, POO captures hydrogen atoms in the polymer to form new free radicals or hydrogen peroxide (POOH) and peroxide (POOP), Entering the chain transfer stage, on the other hand, POO·cracks into ketones and polymer radicals with lower molecular weight, which degrades the polymer. Hydrogen peroxide (POOH) and peroxide (POOP) are unstable, and they dissociate under the conditions of light irradiation and moderate heating to generate alkoxy radicals (PO·) and differential radicals (HO·) radicals, so the degradation reaction It is done under autocatalysis. These free radicals are very active, and it is very easy to capture hydrogen atoms to generate new polymer free radicals, which enter the chain transfer stage of polymer degradation. Polymethylsiloxane resins and fluororesins lack hydrogen atoms that are easily taken away. Therefore, polymethylsiloxane and silicone-modified resins are stable to photooxidation, and their stability is generally proportional to the content of silicone. Fluorine resin has excellent outdoor durability.
The mechanism of action of the UV absorber is that it has a strong absorption in the wavelength range that the polymer absorbs. Commonly used UV absorbers are substituted 2-tetraphenone, 2-(2-tetraphenyl)-2H-benzotriazole, 2-(2-tetraphenyl)-4,6-phenyl 1,3,5-triazine, benzylidene malonate and N,,N'-diphenyloxalamide, etc. These UV absorbers convert UV energy into thermal energy through intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer or cis-trans isomerization.
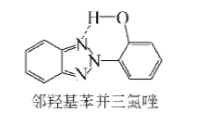
The ultraviolet absorber needs to be dissolved in the paint film, and different types and specifications of stabilizers can have different substitutions on the aromatic ring to meet the solubility requirements of different polymer systems. Stabilizers are usually added to the topcoat of composite coatings, but due to the effect of migration, the stabilizers are often distributed throughout the coating, thereby reducing the concentration in the topcoat, this phenomenon is particularly significant in baking paint . Long-lasting stability of the UV absorber in the paint film is required. The vapor pressure of phenyltriazine is very low, so it can remain in the paint film for a long time. The use of light stabilizers in the oligomeric form as well as polymer-bound stabilizers results in longer-term physical stability of the paint film.
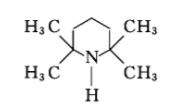
Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) are amines with two methyl groups on two α-carbon atoms, most of which are derivatives of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine. The four methyl groups prevent oxidation of the ring carbon structure attached to the nitrogen atom.
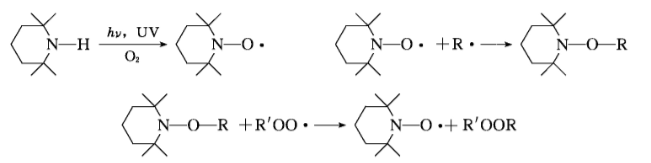
The hindered amine light stabilizer derivatives are converted into nitroxyl (R2NO·) after photooxidation. Nitroxyl (R2NO·) reacts with free radicals to generate amines or ligands. The differential amine and 1 ether react with the peroxy group to regenerate the nitroxyl group. Therefore, the hindered amine light stabilizer derivatives interfere with the chain transfer reaction of free radicals. In the paint exposed outdoors, the derivatives of hindered amine light stabilizers need to undergo rapid photooxidation to form nitroxyl groups before they can effectively function. In the paint film, nitroxyl only accounts for a small part (about 1%), and the main components are the corresponding general amine (R2NOH) and 1 ether (R2NOP). To maintain continuous stability, the presence of nitroxyl is still required. Once the nitroxyl group disappears, the degradation of the polymer will occur immediately.
UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers can produce a synergistic effect together. The agent can effectively remove free radicals on the surface of the paint film.
Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) are more effective in stabilizing acrylic polyurethane coatings than acrylic melamine coatings. Both polyurethane and melamine coatings undergo oxidative degradation. The content of hydrogen peroxide in melamine was significantly lower than that of polyurethane cross-linked coatings, and the formation of free radicals was slower, so the stabilization effect of HALS on melamine was not obvious. This result was related to the ability of melamine to decompose peroxide.
Carbon black is both a strong UV absorber and an antioxidant. Coatings added with carbon black have excellent weather resistance. Transparent iron oxide colored coatings absorb almost all radiation at a wavelength of 420nm. This coating is especially suitable for wood staining to prevent photodegradation of the paint film.
- 1Artificial climate accelerated weathering test and natural aging conversion
- 2What types of metals can be tested for aging?
- 3What factors should be considered for good paint-based weather resistance?
- 4Interpretation of UV Conditioning Test in IEC 61215 Standard
- 5What is the Conditioning Test?
- 6What is a conditioning test and reliability test and what is the difference?
- 7Natural exposure and accelerated weathering test of body coats
王纳新;周胜蓝;廖大政 - 《吉林省科学技术学术年会》
- 8A minute to tell you the development of the Conditioning Test Chamber
- 9Modern environment LUV series accelerated weathering test box Instructions for use



