How Digital Viscometers Work
The digital viscometer produced by Shanghai Nirun Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. can adjust different speeds. Its biggest advantage is that it uses a stepping motor instead of gear transmission. It makes the digital viscometer rotate more smoothly, and the speed can be continuously variable .
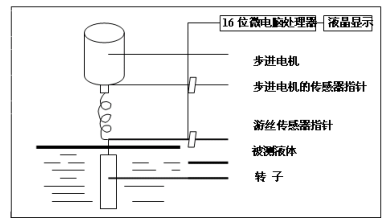
As shown in the figure, the stepper motor is driven with high resolution to drive the pointer of the sensor, and the rotor is driven to rotate through the hairspring and the rotating shaft. If the rotor is not resisted by the liquid, the hairspring sensor pointer is in the same position as the stepper motor sensor pointer. On the contrary, if the rotor is subjected to the viscous resistance of the liquid, the torque sensor will generate torque to compete with the viscous resistance, and finally reach a balance. At this time, the output signal of the photoelectric sensor is sent to the 16-bit microcomputer processor for data processing, and finally the viscosity value (mPa·s) of the liquid is displayed on the LCD screen with night vision function.
Viscosity, viscous force, and flow resistance (related to the tightness of the torque sensor) are related to the speed of the rotor and the shape of the rotor. When the speed increases or the rotor increases, the viscous force will increase. Therefore, when the speed increases or the rotor becomes larger, it can be read by the deviation of the torque sensor. The smallest range of viscosities can be measured with the largest surface area spindle at the highest speed; and the largest range of viscosities can be measured with the smallest surface area and slowest speed. The rheological properties of the fluid can be measured with the same rotor at different speeds.
- 1Professional technology teaches you how to choose a digital viscometer?
- 2Determination of viscosity of redispersible latex powder by digital viscometer
裴勇兵 - 《《丙烯酸酯可再分散乳胶粉的制备及再分散稳定机理与应用研究》》
- 3Fangrui DV-1T/2T digital viscometer installation and operation video tutorial
- 4Fangrui NDJ-5S digital viscometer installation video tutorial
- 5Digital viscometer maintenance learn these ten tips!
- 6How does Nirun DV-79 digital viscometer time measurement work?
- 7Nirun DV-79 Digital Viscometer How to measure unknown viscosity samples correctly?
- 8How to install Shanghai Nirun DV-79 digital viscometer correctly?
- 9Digital Viscometer Tips [Must Read Dry Goods]