Natural exposure and accelerated weathering test of body coats
foreword
During the actual use of automobile body coatings, due to the influence of environmental factors (such as light, water and temperature), its physical properties and mechanical properties
It can deteriorate or even lose, and there will be phenomena such as loss of light, discoloration, cracking, pulverization, and blistering, which are called weather aging. In order to predict the weathering resistance of materials, there are two commonly used test methods: outdoor natural exposure test and artificial accelerated aging test.
The outdoor natural exposure test is carried out under typical natural environmental conditions. Although it takes a long time (generally takes 1 to 2 years), due to the real test conditions, the test results are not consistent with the aging results in the actual use process. The consistency is good, and it is an earlier and widely used method. But this puts automakers in a dilemma when applying new topcoat materials. On the one hand, the market requires new color coatings to have a "design-to-market" production cycle and a "use-to-eliminate" life cycle. On the other hand, the test cycle for the selection of new coating techniques and new materials is relatively long.
The artificial accelerated aging test simulates natural environmental conditions and uses equipment with artificial light sources to accelerate the aging process of coatings. Although the reproducibility of the test results is good, the correlation with the aging results in the actual use process (that is, the correlation with the natural exposure results) is particularly important.
Based on a large number of test data, this paper summarizes the regularity and correlation of these two types of test methods.
test part
2.1 Natural exposure test conditions
my country's Hainan Province has a subtropical and tropical climate. Due to strong sunlight, long hours of sunshine, and sufficient rainfall, it can significantly promote the aging of coatings. The location of the natural exposure test is Hainan Automobile Test Research Institute, and the climate characteristics of the location are shown in Table 1.
2.2 Artificial accelerated aging test conditions
The iCs (X old-type atmosphere lamp climate testing machine produced by ATLAS company in the United States, the irradiance (34Onm). Can be 10Zmin, test time 1000h.
2.3 Test standard
The natural exposure test standard for direct exposure to the atmosphere without backboard is GB/T9276-1996 (IDT ISO2810) "Coating Natural Weather Exposure Test Method"; the experimental conditions for artificial accelerated aging test meet GB/T1865-1997 "Paint and Varnish Artificial Weathering and Artificial Radiation Exposure"; the evaluation standard of the two tests is GB/T1766-1995 "Rating Method for Aging of Paints and Varnish Coatings".
2.4 Sample preparation
The test samples are all prepared according to the traditional three-coat structure "primer layer - middle coat - top coat (base color paint + finish paint)", the main construction process is: whiteboard - phosphating - cathodic electrophoresis - - Drying - Intermediate coating - Drying - Topcoat (base color paint - flash dry - varnish) - drying.
2.5 Test results
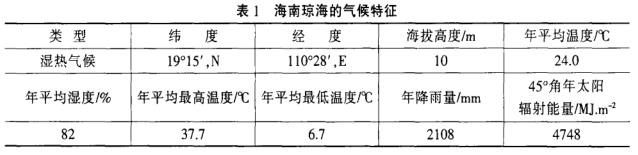
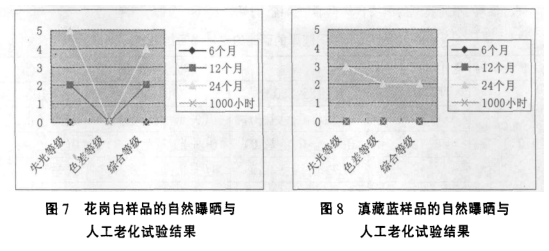
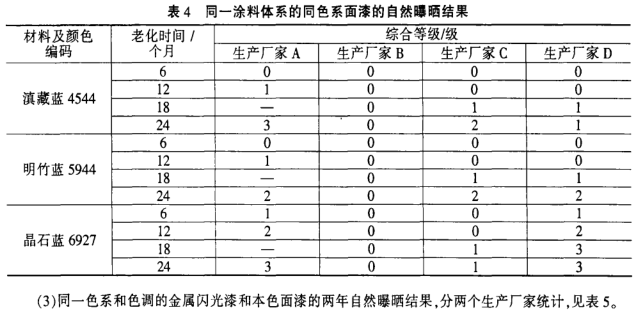
(1) The two-year natural exposure results of topcoats with different colors and different coating systems are shown in Table 2 and Figure 1-4, and the 1000h artificial accelerated aging results are shown in Table 3. Figure 8 (A, B, and C respectively represent samples provided by different paint manufacturers).
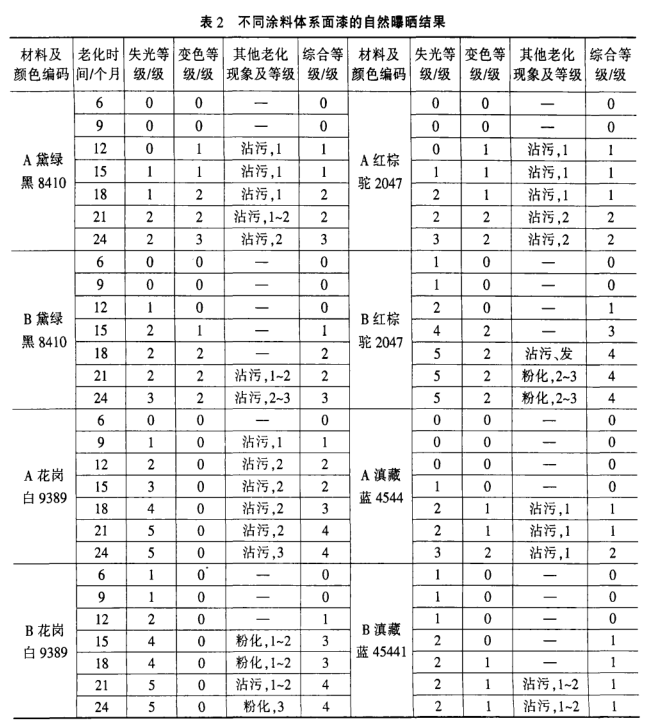
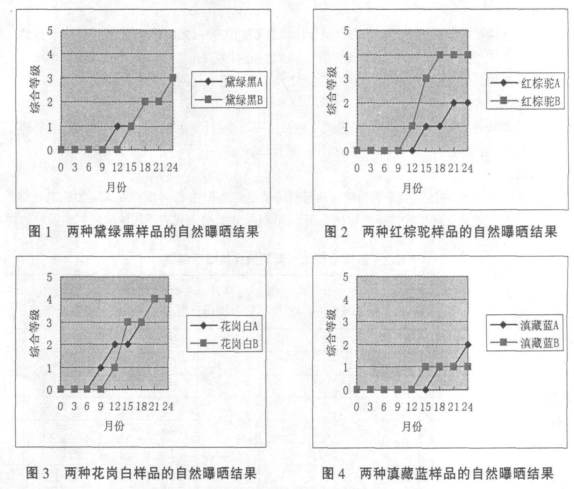
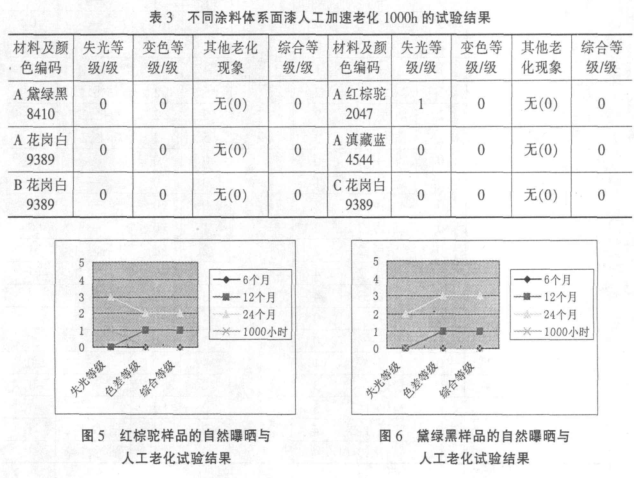
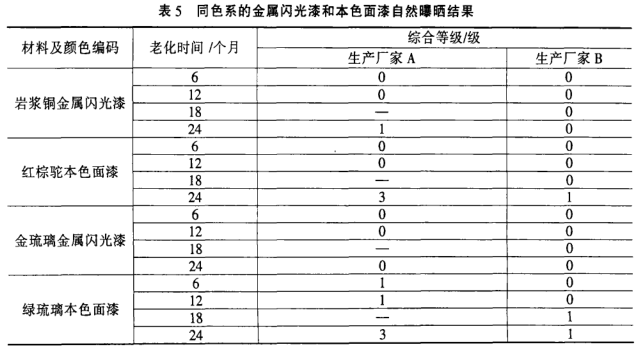
(2) The two-year natural exposure results of the same paint system with the same blue color topcoat are divided into 4 manufacturers, see Table 4.
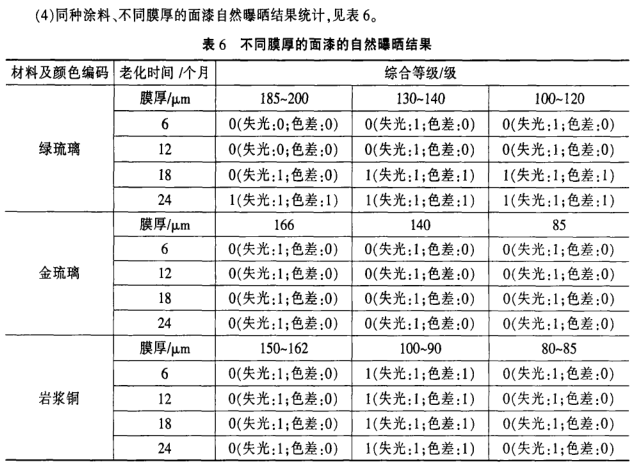
2.6 Result Analysis
(1) The natural exposure test can accurately evaluate the lightfastness and durability of various paints and coatings, and is the basis of the artificial accelerated test. From the data of testing every 3 months listed in Table 2, it can be seen that the aging grade of the samples will gradually increase, and generally the aging grade will change suddenly after 12 to 18 months. Therefore, the natural exposure test period of one to one and a half years is a critical period for various aging phenomena of materials, such as loss of light, sudden increase in color difference, and other aging phenomena such as staining, whitening, and chalking. The test cycle for decorative coatings should be set at 2 years, and the test frequency should be set at once every 3 months.
(2) It can be seen from the table that the decorative three-coat system generally appears loss of light and color difference first, accompanied by staining and pulverization, and aging phenomena such as blistering, mildew and rust appear less.
(3) It can be seen from Table 2 that generally, the results of 12 months of natural exposure are excellent and good, and the aging results of 24 months are likely to reach the intermediate level.
(4) It can be seen from Table 2 that the exposure results of products of the same color and different coating systems will vary greatly; there is no reference between the exposure results of products of different colors in the same coating system.
(5) From Figures 5 to 8, it can be seen that the artificial aging 1000h test results of high-grade decorative topcoats are in good agreement with the atmospheric exposure for 6 months, and the artificial aging 1000h test cannot reflect staining, blistering, whitening and Chalking and other aging phenomena.
(6) It can be seen from Table 4 that the exposure results of the topcoats of the same color system and different shades of the same paint system will have large differences, and the test results cannot be replaced by each other, but the timing of aging phenomena and the law of acceleration can be used for reference; System, the same color system and tone, only the topcoat with different lightness, the exposure effect has reference value. In order to shorten the test period, artificial accelerated aging test can be carried out at the same time as natural exposure test to predict the final result.
(7) It can be seen from Table 5 that compared with the exposure results of the metallic flash paint and the natural color top paint of the same color and tone, the metallic flash paint is better than the natural color top paint.
(8) As can be seen from Table 6, comparing the two-year atmospheric exposure results of topcoats with different film thicknesses of the same paint, it is found that the large difference in film thickness will lead to a large difference in the measured color difference value, which interferes with the color difference value of each test . Although the increase of film thickness is beneficial to the evaluation of light loss rate and color difference at the initial stage of exposure, it will not improve the final result. Therefore, in order to pursue good weather resistance results, it is not advisable for some manufacturers to blindly increase the film thickness when making panels. The samples submitted for air exposure test should be in accordance with the requirements of the material construction process, with uniform film thickness, flat and smooth, and no paint film defects.
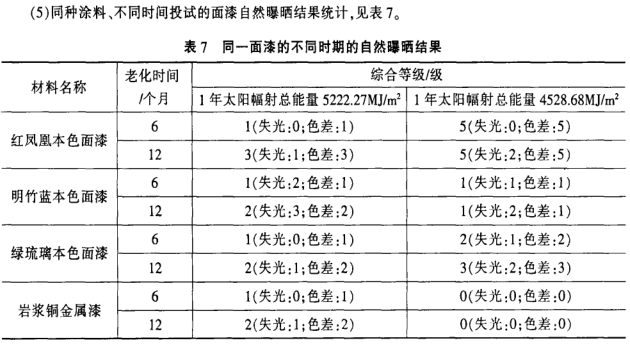
(9) It can be seen from Table 7 that the atmospheric exposure test under natural climate conditions is not controllable by humans, because the light in the environment
, water, and temperature will change at any time, so it is difficult to obtain consistent results from experiments started at different times. Only when the board is strictly made and the samples are put into the same period can they be comparable, and the results of the comparative test can be used as the basis for evaluating the weather resistance of the samples.
(10) It is recommended to use the following two methods for expressing the results of the artificial accelerated aging comparative test: reaching the test period and comparing the expression of the sample evaluation grade. For example: 1(XX)h, the comprehensive rating of sample 1 is grade 0; the comprehensive rating of sample 2 is grade 1. When the sample reaches a certain aging level, the comparative expression of the test cycle. For example: l000h, the comprehensive grade of sample 1 is grade 0; 2000h, the comprehensive grade of sample 2 is grade O.
in conclusion
The natural exposure test is consistent with the operating conditions of automobiles, and can accurately evaluate the corrosion resistance and durability of coatings and coating products, and is the basis of artificial accelerated tests.
Although the test conditions of the artificial accelerated aging test are controllable, because there are many factors that cause coating aging, the interaction between the environment and the material is very complicated, and it only simulates and strengthens the main factors that affect material aging in nature, such as solar radiation, It is unscientific to try to find a generally applicable method or formula to calculate the acceleration factor.
The artificial accelerated aging test is beneficial to the comparative test of samples with the same properties and the same properties, which can shorten the development and selection cycle of new color coatings, predict problematic coatings, and reduce the loss of automobile manufacturers.
- 1The relationship between natural aging and accelerated aging
- 2Artificial climate accelerated weathering test and natural aging conversion
- 3Application of accelerated weathering Test Chamber in respirator
- 4UV accelerated weathering Test Chamber for weathering resistance of epoxy resin
- 5Application analysis of ultraviolet accelerated weathering Test Chamber in PEVA film
- 6Application and test method of UV accelerated weathering Test Chamber in automotive Glass film
- 7Application of xenon arc aging Test Chamber in outdoor Coating
- 8Application of xenon arc aging Test Chamber in water-based paints industry
- 9Application of xenon arc aging Test Chamber in paints industry