Coated steel coatings adhesion performance
Abstract : Through the research, a test method for quickly predicting the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated board coating was found, and the systematic analysis of the experiment showed that the resin structure of the coating, the roughness of the substrate, the type of substrate and the pre-treatment process of the color-coated board all affect the color-coated board coating. The adhesion and aging properties of the coating have a great influence, and a way to improve the adhesion and aging properties of the color-coated plate coating is proposed.
Coating adhesion is an important technical index for evaluating the quality of color-coated panels. At present, the T-bend test is generally used at home and abroad to characterize the adhesion of the color-coated plate coating. However, the use experience of color-coated plates shows that some color-coated plates will experience rapid deterioration of coating adhesion as the storage time increases, which affects the normal use of color-coated plates.
The most direct manifestation of the coating adhesion and aging performance of color-coated plates is that the T-bend test results of color-coated plates decrease rapidly with the prolongation of storage time. The main factor causing the continuous decline of T-bend performance is nothing more than the influence of water, oxygen and ions in the natural environment where the color-coated board is stored [1]. This effect is a slow process, so it takes a certain amount of time for this effect to occur and can be shown by the T-bend test. This will cause the color-coated sheet to show poor adhesion after reaching the user's hands, which will have a negative impact on both the color-coated sheet production unit and the user.
In this paper, by accelerating the simulation of the influence of the natural environment on the coating adhesion, a detection method that can quickly and accurately predict the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated plate coating is obtained. Through the test, the change law of the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated plate coating of different coating systems was obtained, and various factors affecting the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated plate coating were studied and analyzed. performance path.
1 Experimental method
1.1 Determination of the adhesion and aging properties of the color-coated plate coating
T-bend test will be carried out on the off-line color-coated sheet according to the "Test Method for Color-coated Steel Sheet and Steel Strip". Then the sample is stored in the laboratory environment for 6 months and taken out, and the T-bend test is also carried out to obtain the aging performance of the coating adhesion of the sample for half a year.
1.2 Prediction of coating adhesion and aging performance of color-coated plate
T-bend test will be carried out on the off-line color-coated sheet according to the "Test Method for Color-coated Steel Sheet and Steel Strip". Then put the sample into a constant temperature and humidity Chamber for 24 h accelerated aging test, the test temperature is 70 °C, and the test relative humidity is 95%. Take out the sample and do the same T-bend test, then you can accurately predict the aging performance of the coating adhesion of the sample for half a year. Figure 1 shows that this prediction method can quickly and accurately predict the coating adhesion and aging performance of color-coated panels within 24 hours for half a year.
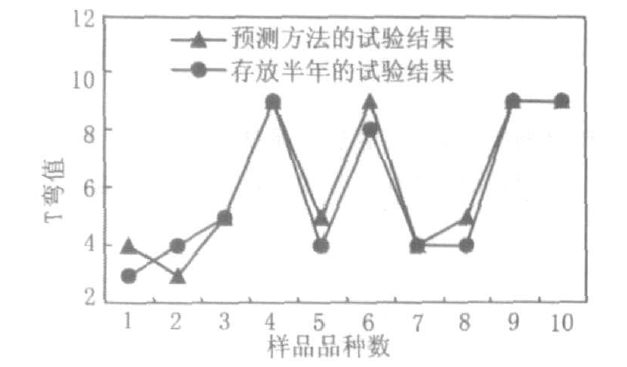
Fig.1 The comparison between the prediction method and the actual test results of the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated plate coating
1.3 Infrared spectroscopy experiment
The infrared spectroscopy experiment used a Nico-let 6700 infrared spectrometer from American Thermoelectric Company. The Ominic sampler is used to directly collect the infrared spectrum data of the color-coated plate coating.
1.4 Salt spray experiment
The salt spray test uses the CCT-1100 salt spray Test Chamber of Q-Panel Company of the United States. The salt spray test is carried out in accordance with ASTM B117 "Salt Spray Test Standard", and the test period is 1000 h.
1.5 Roughness measurement
The roughness experiment uses the Tokyo Precision SURFCOM 130A roughness meter to measure the average roughness Ra of the color-coated substrate.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Adhesion drop is the initial macroscopic manifestation of metal corrosion under the coating
By comparing the test results of the adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated board with the results of the salt spray test, it can be found that the color-coated board with poor adhesion and aging performance has a higher probability of 3-4 blistering in the salt spray test. It is much higher than the color-coated plate with good aging performance, which shows that the aging performance of coating adhesion is directly proportional to the corrosion resistance of the coating. (Cyclic corrosion test) and other aspects of the surface are better than color-coated plates with poor aging performance. That is to say, the degradation of the T-bend performance of the color-coated sheet is the initial manifestation of metal corrosion under the coating. At this time, the color-coated sheet is only observed from the surface, and there is no coating blistering, peeling off, etc., but the decline of the T-bend performance has already shown that Corrosion of the metal beneath the coating begins to occur.
This is because even if the coating has no defects such as internal density unevenness, micropores, cracks and gaps, there are still transmission channels for the infiltration of external media in the environmental medium, and water molecules on the surface of the coating can reach Coating the metal-substrate interface until the coating/metal-substrate bonding interface is destroyed[2]. The initial macroscopic manifestation of this interface damage may be the decrease of coating adhesion, which is manifested as poor aging performance of coating adhesion, and its further macroscopic manifestations are coating blistering and peeling. Therefore, the corrosion resistance performance of the color-coated plate can be predicted through the test results of the coating adhesion and aging performance of the color-coated plate, which has a good early warning effect on improving the quality of the color-coated plate product.
2.2 Variation law of adhesion and aging properties of color-coated panels with different coating systems
Through the accumulation of test data on the natural performance of the adhesion and aging properties of the color-coated panels of the two main coating systems, the following rules can be obtained: the color-coated panels with polyester topcoat and epoxy primer will, over time, Significant decline in coating adhesion occurs, showing that the aging performance of coating adhesion is poor; the coating adhesion aging performance of the color-coated board with polyester topcoat and polyurethane primer is good, and the coating adhesion does not appear See Figure 2 for a clear decrease over time.
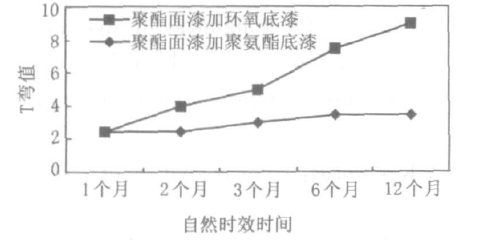
Fig. 2 Comparison of natural aging properties of coating adhesion of prepainted panels with different coating systems
And other paint system color-coated panels, such as fluorocarbon topcoat plus polyurethane primer, silicon-modified polyester topcoat plus polyurethane primer, high-performance polyester topcoat plus polyurethane primer, etc., have been found through tests that the coating Adhesion will not decrease significantly over time.
When the color-coated plate is stored in the natural environment, oxygen, water and corrosive ions in the environment will penetrate through the coating to reach the interface between the coating and the metal substrate, forming a continuous or discontinuous water phase, resulting in continuous coating adhesion. Lower [3]. Therefore, when the types of primer resins are different, the cohesion of the topcoat coating itself, that is, the coating's ability to resist oxygen, water and corrosive ion penetration directly affects the aging performance of the color-coated coating adhesion. When the topcoat is silicon-modified polyester resin (SMP), high-performance polyester resin (HDP) and polyvinylidene fluoride resin (PVDF), the electronegativity of these resins is high due to the large atomic weight of silicon and fluorine. The introduction of strong atoms increases the density of the polymer [4] and enhances the corrosion-resistant medium penetration ability of the topcoat, so that the color-coated plate shows better coating adhesion and aging performance.
当面漆为聚酯树脂时, 由于其抗渗透能力弱于上述几种树脂, 因此环氧树脂和聚氨酯树脂作为彩涂板的底漆常用的树脂, 它们所体现出的涂层附着力时效性能差异较大, 普通环氧底漆的彩涂板涂层附着力时效性能远远差于聚氨酯底漆的彩涂板。纯环氧树脂分子结构中含有许多羟基和醚键, 这些基团的极性较大, 与金属基材之间有强的极性结合力, 而且由于纯环氧树脂中无酯键, 因此即使金属基材发生腐蚀而呈碱性, 也不会发生皂化反应而破坏树脂结构[ 5] , 而聚氨酯底漆中主链上含有氨酯键, 因此从理论上来说, 纯环氧底漆的彩涂板涂层附着力时效性能至少不应该比聚氨酯底漆的彩涂板差。由此可以判断, 普通环氧底漆中应该除了环氧树脂外, 还有其它含有酯键的树脂。由下面的环氧底漆红外谱图可以证明酯键(1 712 .9γ(C =0))的存在。由于环氧树脂的结构决定了其涂层柔韧性较差, 所以一般在环氧树脂中会加入一些别的树脂(如聚氨酯、聚酯树脂等)以改善其柔韧性, 而这些树脂的加入可能会造成涂层附着力时效性能的下降。因此, 要提高彩涂板的涂层附着力时效性能, 除了使用抗渗透性能好的面漆, 使用树脂组成更合理的底漆也是关键之一。
2 .3 基板粗糙度对于涂层附着力时效性能的影响
通过对部分彩涂板进行涂层附着力加速时效试验, 可以发现, 涂层附着力时效性能与基板的表面粗糙度之间呈明显的正比关系, 即粗糙度越高, T 弯值下降越少。这是因为基板表面的粗糙度越高, 其表面积越大, 这样涂层与基板之间的结合面积也越大, 它们之间的机械结合力也就越大, 因此适当提高基板的表面粗糙度可以改善彩涂板涂层附着力的时效性能。
2 .4 基板种类对于涂层附着力时效性能的影响
试验证明, 即使是附着力时效性能最差的涂料组合, 如果基板为镀铝锌基材时, 彩涂板的涂层附着力时效性能也较好。造成这种情况的主要原因是镀铝锌基板的特殊表面结构。镀铝锌基材表面主要有2 种金相组织:1 种是在凝固初期形成的树枝状结构的富铝区;另1 种是枝晶间网络状的富锌区。当彩涂板的涂层抗渗透性能较差时, 水、氧气和腐蚀性离子渗透到镀铝锌基材表面, 枝晶间网络中的富锌区先被腐蚀, 氧化产物会填充在枝晶间的空隙中, 从而降低了腐蚀速度, 因此这种基板的彩涂板涂层附着力时效性能表现更好。
2 .5 彩涂预处理工艺对于涂层附着力时效性能的影响
涂层与基材之间的结合力直接影响着彩涂板的涂层附着力, 因此基材表面的化学处理状态也直接影响着涂层与基材的结合程度, 好的预处理工艺可以在基材表面生产稳定的转化膜, 不但可以提高基材的耐腐蚀性能, 还可以提高基材与涂层之间的结合力。
试验表明, 不同的预处理工艺对于彩涂板涂层附着力时效性能是有明显影响的。不同预处理供应商的配方和工艺参数均不相同, 因此对于基材表面油脂的清洁程度、基材被清洗剂的腐蚀程度、转化膜本身的韧性、转化膜中起防腐蚀作用的元素等均会对涂层附着力时效性能有很大影响,本文未作进一步研究。
3 结 语
采用试验室加速模拟自然时效的方法, 可以准确快速预测彩涂板涂层附着力时效性能。
试验和分析表明, 彩涂板的涂层附着力时效性能受到涂层性能、涂层下基材的性能以及涂层与基材之间化学转化膜的性能的影响。其中主要影响因素是涂料体系和基板的预处理状态。通过以下途径可改善彩涂板的涂层附着力时效性能:
(1)使用耐腐蚀性介质渗透能力强和树脂构成更合理的涂料体系;
(2)改善基板的表面粗糙度;
(3)使用防腐蚀性能更优的镀铝锌基板;(4)改善基板的预处理状态。
【参考文献】
[1] 刘 彬, 李 瑛.防腐蚀涂层失效行为研究进展[ J] .腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2001 , (5):305.
[2] Lin Haichao, Li Moucheng. Corrosion process of metal under coating [J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2002, (3): 180.
[3] Wu Yuehuan. The relationship between steel corrosion and coating wet adhesion [J]. Aging and Application of Synthetic Materials, 2002, (1): 28.
[4] Xiao Youguo, Fu Jun. Pre-coated metal coils and coatings [ M ]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003.
[5] Zhang Hongde. Aluminum-zinc-coated steel sheets for construction [J]. Steel Structure, 2003, (68):49.
- 1Purpose, method, principle and operation points of coating adhesion test
- 2Coating adhesion test
- 3Adhesion Factors of Paints and Coatings & Test Methods
specialchem
- 4How good is the relationship between coating adhesion and coating cohesion? To what extent?
- 5What is coating adhesion?
- 6What is the cause of poor coating adhesion?
- 7Coating structure and adhesion principle
- 8Standards for quality inspection of color-coated boards
- 9Color coated board back paint








