Effect of Ground Conditions on Dispersion of UV Ink-jet Printing ink
UV inkjet inks have high requirements on dispersibility, and grinding conditions have a great influence on the dispersibility of inks. In order to obtain UV inkjet ink with good dispersion, under the condition of fixed ink formulation, by changing the size of the grinding beads during grinding, and mixing the grinding ink with different sizes of grinding beads in a certain proportion, the ink particles obtained at different grinding times were tested. The size distribution of the grinding beads was used to investigate the effect of the size of the grinding beads and the grinding time on the ink dispersibility.
The experimental results show that: the smaller the grinding beads, the better the grinding effect, 95% of the ink obtained by grinding the grinding beads with a diameter of 1.0 ~ 1.2mm is below 0.972μm; only when the grinding time is very good can the dispersion be obtained Good ink, and the best grinding time of different sizes of grinding beads is different. The grinding time of grinding beads with diameters of 2.0-2.2mm, 1.6-1.8mm, and 1.0-1.2mm is 105min, 105min, and 90min respectively. ; The ink obtained by grinding the medium and small beads with a mixing ratio of 1:1 has the best dispersibility, and 90% of the particle size of the ink is below 0.656 μm.
With the wide application of digital technology in printing and printing industry, inkjet technology has developed rapidly. The coloring materials (inkjet inks) used in inkjet printing include water-based inks, solvent-based inks and UV inks. UV inkjet ink has the advantages of high printing quality, energy saving, environmental protection, instant drying, wide range of substrates, no nozzle blockage due to drying before curing, and stable ink composition. It has huge development prospects and market potential. UV inkjet ink is composed of pigments, prepolymers, monomers and various additives. The size of pigment particles and the dispersion state in the ink system directly determine whether UV inkjet ink can be ejected smoothly from the nozzle, and the dispersion of pigments has a great influence on The coloring power, transparency and other properties of the ink have a great influence. Therefore, determining the technical conditions of the pigment dispersion process is a technical problem to be solved in the development and preparation of UV inkjet inks.
Generally speaking, UV inkjet inks are low-viscosity inks, which are usually produced by grinding and dispersing. During the grinding and dispersing process, the size and amount of grinding medium (zirconium beads or glass beads), grinding time, and grinding method determine the dispersibility of pigments in the ink system. In other words, the grinding and dispersion process conditions directly affect the performance of UV inkjet inks.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Experimental raw materials
Zirconium beads (Zhejiang Tiantai Jinggong Xili Glass Bead Co., Ltd.): the diameters are 2.0-2.2mm, 1.6-1.8mm, and 1.0-1.2mm. Prepolymer: polyester acrylate (Viajet100, Cytec). Monomer: 2-Ethoxyethyl Acrylate (EOEOEA, Tianjin Tianjiao Company), 1, 6-Hexanediol Diacrylate (HDDA, Tianjin Tianjiao Company), Trimethylolpropane Triacrylate (TMPTA, Tianjin Tianjiao Company) ).
Pigment: carbon black (R250, Cabot Corporation).
1.2 Instruments and equipment
Grinding equipment: GJ-2S high-speed grinding machine (Qingdao Haitongda Company).
Testing instrument: Microtrac's S3500 laser particle size analyzer (microtrac, USA).
1.3 Experimental method
The preparation of UV inkjet ink is carried out in two steps: at room temperature, according to the established formula, the pigment, prepolymer, part of the monomer and dispersant are mixed and stirred for 15 minutes, poured into the GJ-2S high-speed Grinder, and added A specific type of zirconium beads is ground at a speed of 2000r/min, so that the pigment is fully wetted and dispersed in the binder, and a better color paste can be taken out at a good grinding time. Then, the color paste is mixed with film-forming prepolymer, monomer and initiator to prepare ink. In the two-step process, the dispersion performance of the color paste basically determines the dispersion performance of the ink. Therefore, the dispersibility of the color paste is very important. After grinding, the ink particle size test is carried out on the laser particle size analyzer, and the particle size and distribution of the ink can be obtained from the particle size distribution diagram of the test.
2 Experimental results and analysis
2.1 Effect of grinding time on dispersibility of UV inkjet ink
Fix the formula of the UV inkjet ink color paste, the color base ratio of the color paste is 3:1, use different sizes of grinding beads to grind the color paste, the total amount of grinding beads is 75mL, and the total amount of ground color paste is 100g. Use a laser particle size analyzer to test the particle size of the color paste obtained at different grinding times, and use the particle size of 95% of the ink for comparison, as shown in Figure 1.
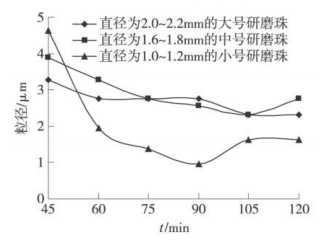
Figure 1 Effect of milling time on the dispersibility of UV inkjet ink
It can be seen from Figure 1 that each bead has a different particle size at different grinding times, and as the grinding time increases, the particle size of the obtained ink generally first decreases and then gradually increases. In the initial stage of grinding, under the action of grinding beads, the pigment particles are gradually dispersed, and the gaps between the pigment particles are gradually filled by the prepolymer. Ink The particle size of the pigment particles in the ink system gradually decreases with the increase of time. However, as the grinding time increases, the particle size of the pigment obtained after pre-grinding is smaller, and its specific surface energy is larger, and aggregation will occur between the pigment particles and the pigment particles, so that the particle size of the ink gradually increases. Therefore, there is a problem of a good grinding time during grinding, that is, the particle size of the ink obtained by grinding under this time is the smallest. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the three kinds of grinding beads with diameters of 2.0-2.2mm, 1.6-1.8mm, and 1.0-1.2mm correspond to good grinding times of 105min, 105min, and 90min, respectively. This is due to the large specific surface area of the small beads, that is, the large area of interaction with the pigment and high efficiency, so that the particle size of the ink drops rapidly in a short period of time, and quickly reaches a good grinding state.
2.2 Effect of grinding bead size on dispersibility of UV inkjet ink
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the particle sizes of the inks obtained by the three kinds of beads with different particle sizes at different grinding times are not the same. Use a laser particle size analyzer to test the ink particle size distribution obtained by these three kinds of grinding beads at a good grinding time, as shown in Figure 2.
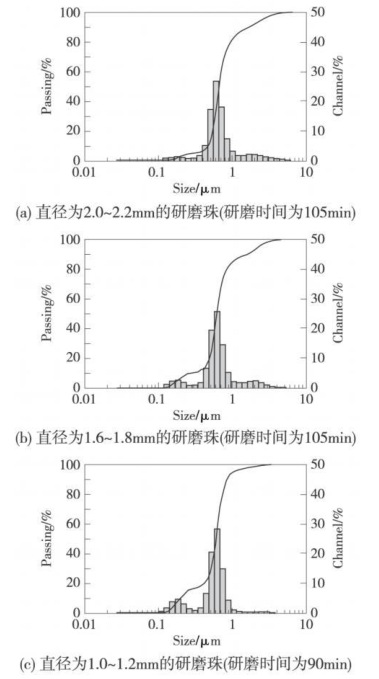
Figure 2 The particle size distribution of inks ground by grinding beads of different sizes
It can be seen from Figure 2 that the particle size distribution and particle size of the ink corresponding to the three kinds of beads with different particle sizes are different under a good grinding time. The particle size distribution corresponding to the medium-sized beads with a diameter of 1.6-1.8mm and the large-sized beads with a diameter of 2.0-2.2mm is better than that of the small-sized beads with a diameter of 1.0-1.2mm. The particle size distribution corresponding to the grinding time of 90min should be wide.
由图 2还可看出, 3种珠在各自的很好的研磨时间下所研磨得到的油墨粒径不同 , 大号珠在 95%的粒径大小对应的粒径为 2.312μm, 中号珠在95%的粒径大小对应的粒径为 2.31μm, 而小号珠在 95%的粒径大小下对应的粒径为 0.972μm, 要比 2.31μm小得多。这是因为在研磨过程中 ,直径为 1.0~ 1.2mm的小号珠本身直径较小 ,所以其作用面积较大 ,对颜料的作用力大, 使得油墨粒径整体迅速下降 , 最后得到的粒径也较小 ;而直径为1.6~ 1.8mm的中号珠和 2.0~ 2.2mm的大号珠由于其本身粒子直径较大,比表面积小 ,作用面积小,所以对颜料的作用力比较小,不能够使得油墨粒径整体下降而只能使部分油墨粒径下降, 所以 ,对应的油墨粒径的分布范围比较宽 ,得到的油墨粒径比较大。且从图 2还可看出, 研磨珠的粒径越小,对应得到的小粒径油墨越多,大粒径油墨越少 。
从图 2看 ,直径为 1.0 ~ 1.2mm的小号珠的粒径分布相对于大号珠和中号珠而言,整体向小粒径方向偏移 ,即小粒径的油墨占的比例较大。在选择研磨珠尺寸时 , 主要考虑两个方面:一是需要便于从基料中分离研磨介质 ;二是要获得更高的研磨效率。
通过比较可知, 在很好的研磨时间下, 大号珠和中号珠这两种珠的研磨效果大体相同,而小号珠的研磨效果要比它们好得多, 所需的研磨时间也短 ,且较易从基料中被分离, 操作较方便。所以, 选用直径为 1.0~ 1.2mm的小号珠研磨油墨较称心 。
2.3 混合大小研磨珠对油墨分散性的影响
将不同大小的研磨珠混合来研磨油墨 ,以考察混合大小研磨珠对油墨分散性的影响 。由于本实验所选用的大号研磨珠与中号研磨珠的研磨效果相似, 因此只将中号研磨珠与小号研磨珠以 1∶1的比例混合研磨油墨, 测试所获得的油墨的粒径,并与单纯使用中号、小号研磨珠的研磨效果相比较 ,如图 3所示。
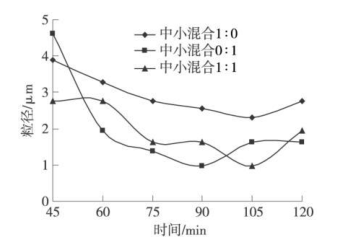
图 3 采用混合珠研磨对油墨粒径的影响
从图 3可以看出, 不同大小珠以一定比例混合与采用同样大小的珠子研磨所得到的油墨粒径大小不同。这是因为在研磨时, 研磨珠大小不同会对颜料分散的作用力不同 ,而当大小珠混合时 , 由于珠粒径不同 ,对较小和较高的颜料附聚体的作用应力也各不相同。由图 2分析可知,单纯采用粒径为1.0 ~ 1.2mm的小号珠研磨效果更好 , 所以, 下面主要对采用 1∶1的中小混合珠和单纯小号珠的研磨效果进行比较。从图 3可以看出 , 用 1∶1的中小混合珠研磨时 , 在研磨的初始阶段, 油墨粒径下降得比较缓慢, 研磨到 105min时 ,油墨的粒径才达到最小 0.972μm, 这是由于混合珠对较小和较高的颜料附聚体的作用应力各不相同 ,可在短时间内使粒径分布比较均匀且在一定的范围之内,即粒径不会陡然下降而是整体平稳下降, 这样能够使大小不同的颜料粒子粒径都得到很好的研磨 。但由于前期的研磨使得整体粒径都下降, 使得颜料粒子的比表面积较大, 后期的继续研磨会使得颜料粒子聚集比较快。从图 3还可看出,到 120min时 ,粒径从最小的 0.972μm变为 1.944μm。而采用小号珠单独研磨时, 由于珠本身的比表面积较大, 对颜料的作用面积大 ,研磨的过程中油墨的粒径下降得比较快。从图 3可看出, 在 90min时研磨的油墨粒径达到最小 0.972μm, 且在后期颜料粒子的聚集比较缓慢 ,在 105min和 120min时 ,粒径达到 1.635μm。
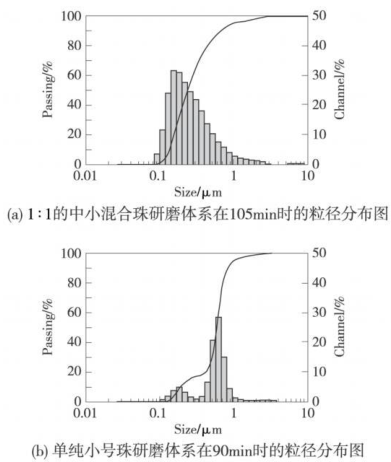
图 4 混合珠和小号珠研磨体系在很好的研磨时间下的粒径分布图
综上所述, 采用 1∶1的中小混合珠研磨体系的研磨效果也能够达到单纯采用小号珠研磨体系的研磨效果,但所需的时间较长为了更好地比较 1∶1的中小混合珠研磨体系和单纯小号珠研磨体系的研磨效果, 我们对二者在很好的研磨时间下的粒径分布图进行比较 , 如图 4所示。
从图 4可以看出, 在各自的很好的研磨时间下,1∶1的中小混合珠研磨体系相对于单纯小号珠的研磨体系研磨得到的油墨粒径明显地整体偏向于小粒径分布 ,这是因为它是由小珠和中珠混合而成的 ,是混合体系, 对较小和较高的颜料附聚体的作用力不同, 研磨时能够使得油墨粒径整体得到下降 ,所以 , 最后得到的更小粒径的油墨相对较多。
因此,由图 4可知 ,采用 1∶1的中小混合珠研磨体系的研磨效果比采用单纯小号珠的研磨体系要好,获得的更小粒径的油墨要多一些, 研磨得到油墨90%的粒径在 0.656μm以下 , 而使用小号珠研磨得到油墨 90%的粒径在 0.815μm以下 。
3 结论
1)在 UV喷墨油墨的研磨过程中,研磨时间对油墨的粒径有很大影响。随着研磨时间的增加 ,油墨的粒径呈现先减小后增加的趋势, 且不同大小的研磨珠对应的很好的研磨时间也不同 。本实验条件下 , 直径为 2.0 ~ 2.2mm、 1.6 ~ 1.8mm、 1.0 ~1.2mm的大、中、小号 3种研磨珠对应的很好的研磨时间分别为 105min、105min和 90min。
2) During the grinding process of UV inkjet ink, the size of the grinding beads has a great influence on the particle size of the ink. The smaller the grinding beads, the narrower the particle size distribution of the ink obtained, and the better the grinding effect, the higher the grinding efficiency, but too small grinding beads will cause inconvenience in operation. In this experiment, the grinding effect of small beads with a diameter of 1.0 ~ 1.2mm is better, and 95% of the particle size of the ink obtained by grinding is below 0.972μm.
3) Mixing beads of different sizes for grinding can improve the grinding effect. Under the experimental conditions, the grinding effect of the 1:1 small and medium-sized mixed bead grinding system is better than that of the simple small-sized bead grinding system, and more ink with smaller particle sizes can be obtained, but it is necessary to achieve a good grinding effect. The time is slightly longer, and the particle size of 90% of the ink obtained by grinding is below 0.656 μm.
references:
[1] Chen Yonglie, Yang Jianwen, Zeng Zhaohua. Radiation Curing Materials and Their Applications [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003.
[2] Xiangyang, Wang Jiexian. Printing materials and their suitability [M]. Beijing: Printing Industry Press, 2000.
[3] Hans Moritt, Arnold Gu Benmen. Emulsion, Suspension, Solid Compounding Technology and Application [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004.
[4] Zhang Wenhui, Su Li. The application of grinding media in the grinding of ink base materials [J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2007, 35(4):81-82.
[5] Ren Jun, Shen Jian, Lu Shouci, etc. Particle Dispersion Science and Technology [M]. Chemical Industry Press, 2005.
- 1What do you need to know about UV inks?
- 2Production process of ordinary emulsion paint
- 3Selection of wet dispersion in Coating formula
- 4Architectural coatings production process
- 5Production process of coating powder
- 6Coating additives addition method and addition process
- 7Key points of production and preparation of water-bomecoating
- 8Determination of organic pigment grinding dispersion process
- 9Pigment Dispersion: Dispersion Process and Dispersion System
郑顺兴 - 《涂料与涂装科学技术基础》








