Properties of hyperbranched polymer modified alkyd resin
Hyperbranched polymers are macromolecules with a three-dimensional structure, and many branched structures with approximate relative molecular mass and narrow relative molecular mass distribution extend from the core to the surrounding. Its compact structure endows special physical and chemical properties, such as high solubility, low viscosity, high rheology, etc., so this kind of macromolecules is constantly attracting people's attention. In addition, hyperbranched polymers with high functional end groups are easy to modify and crosslink. It is widely used in film-forming resins of various coatings, such as powder coatings, high solid content coatings, refractory coatings and insulating coatings. In the field of coatings, the most widely studied hyperbranched polymers are currently commercialized hyperbranched aliphatic polyester Boltorne and hyperbranched polyesteramine Hybarnee. Hyperbranched polymers used in UV curing systems are generally end-capped with methacrylate or acrylate. Resins based on hyperbranched polymers have lower viscosities and higher cure rates than those of linearly unsaturated resins. The use of hyperbranched polyacetate acrylic acid copolymers in UV-curable coatings without any photosensitizer can reduce the cost of coatings by 10% to 40%, which makes the research on hyperbranched polyesters and their modified copolymers very popular. Hyperbranched polymers have been made into photocurable types and can be used in coatings. The application of hyperbranched polymers in UV light-curing powder coatings mainly utilizes the characteristic of low softening temperature due to its low viscosity. The aliphatic polyester BolotmTMHZO containing 16 terminal groups introduces long chains with different degrees of polymerization through caprolactone ring-opening, and is drunk-capped with methacrylic acid to prepare UV-curable powder coatings with a melting point of 50 °C. In this study, the alkyd resin was modified by using a hyperbranched polymer whose terminal group is a warp group instead of the polyol in the alkyd resin, and the paint film properties of the modified alkyd resin were investigated.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Experimental raw materials
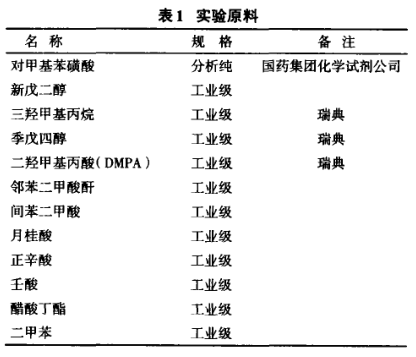
The main raw materials used in the experiment are shown in Table 1 .
1.2 Experimental Instruments
BYK Gardner Pendulum Hardness Tester, BYK Gardner, Germany; QuaNix1500 Metal Coating Thickness Gauge, Nix, Germany; DFZ-II Paint Film Adhesion Tester, Tianjin Material Testing Machine Factory; QCJ Paint Film Impactor, Tianjin Material Testing Machinery Factory; wGG60-E Gloss Meter, Keshijia Photoconductive Instrument Research Institute; QTX Paint Film Elasticity Tester, Tianjin Zhonghuan Test Instrument Factory.
1.3 Synthesis of hyperbranched polymer and modification of drunken acid resin
Synthetic principles in the synthesis of hyperbranched polymers. Firstly, polyhydric alcohol, dimethylpropionic acid, and catalyst p-toluenesulfonic acid are added to the four-port reactor according to the designed ratio, and xylene is added as the reflux solvent at the same time. Then the reactor is heated in an Oil Bath at a predetermined temperature, and after a certain period of reaction, the solvent and water are distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a hyperbranched polymer.
In the alkyd resin synthesis process, hyperbranched polymers are used instead of polyols, fatty acids, benzene and other monomers are put into the reactor according to a certain ratio, and then the temperature is gradually raised to 200 ℃, and xylene is refluxed for a certain period of time. , measure the acid value of the reaction mixture, when the acid value reaches a certain value, lower the temperature, dilute the resin with a solvent, and finally discharge.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Basic properties of resin
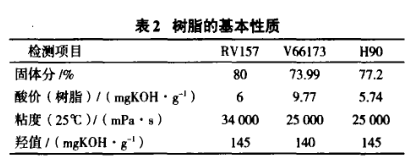
Table 2 lists the properties of several resins, among which Rv57 is a commercial fatty acid resin, V66173 is a fatty acid modified alkyd resin, and H90 is a hyperbranched polymer modified alkyd resin.
2.2 Compatibility of H90 and cured Jing
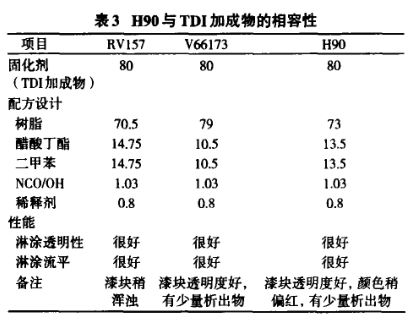
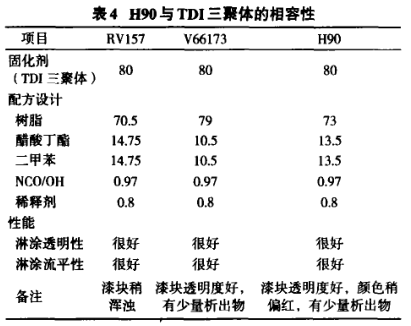
The compatibility research results of the modified alkyd resin and the adduct and trimer of the curing agent TDI are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. It can be seen from the results in the table that the modified alkyd resin It is not only compatible with the adducts and trimers of the curing agent TDI, but also has better transparency after finishing the paint than the commercial resin RV157. The redness of the paint block may be related to the fact that the catalyst added during the resin synthesis process has not been separated.
2.3 Compatibility of H90 and acrylic resin
The compatibility test results of the modified alkyd resin and acrylic resin are shown in Table 5.

From the results in Table 5, it can be seen that the modified alkyd resin is substantially incompatible with the acrylic resin. The reason may be that the modified alkyd resin has a dendritic structure, and its hydroxyl groups are located at the end of the chain, and these hydroxyl groups are primary hydroxyl groups with strong polarity, and these hydroxyl groups are hydrogen bond acceptors. , and at the same time are hydrogen bond donors, so they are easy to form internal hydrogen bonds inside the resin. The hydroxyl group of the hydroxyl group belongs to the secondary hydroxyl group, and the hydroxyl group is located on the main chain, and the polarity is relatively weak. According to the principle of similar compatibility, the formation of internal hydrogen bonds has caused the modified alkyd resin to be compatible with the hydroxyl group. Sex is poor.
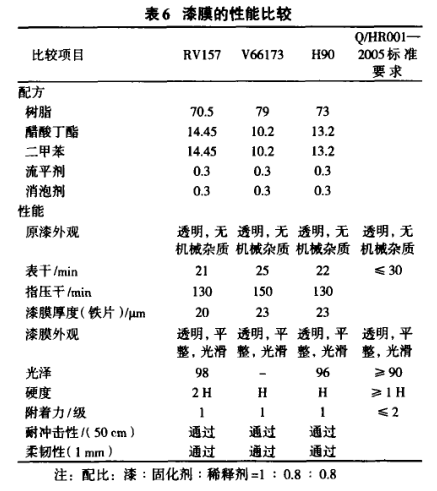
2.4 Comparison of physical properties of paint film
The physical properties of the paint film are shown in Table 6. From the data in the table, it can be seen that the physical properties of the alkyd resin paint modified by the hyperbranched polymer meet the requirements of the Q/HR001-2005 standard. Except that the pencil hardness is lower than that of the commercial resin RV157, other properties are the same as those of the commercial resin RV157. It is worth noting that the pendulum hardness of the H90 resin paint film during the drying process is greater than that of the RV157 resin paint film, which can be reflected in Figure 1.
2.5 Hardness changes of the paint film during the drying process
The changes in the hardness of the pendulum during the drying process of the paint film are shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from the figure that the pendulum hardness of the paint films made of the two resins has basically the same change trend during the drying process, but the pendulum hardness of the alkyd resin paint film modified by the hyperbranched polymer is higher than that of the commercial resin RV157. The hardness is high. The reason may be that the crosslinking density of the modified alkyd resin is large on the one hand, and on the other hand, it may be caused by its paint film leveling (on the board surface) better than RV157.

3 Epilogue
Alkyd resins modified by hyperbranched polymers have good compatibility with curing agent TDE adducts and trimers, but poor compatibility with acrylic resins. Although there is a small amount of precipitates after reacting with the curing agent for two days, the transparency of the paint block is better than that of RV157, and the drying rate is comparable to that of Rv157. The physical performance parameters of the paint film meet the requirements of the Q/HR001-2005 standard. Other special properties of the modified alkyd resin need to be further studied.
-
Qnix 5500 Coating Thickness Gauge$ 1044.00
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 1Acrylic resin: performance inspection and Application
- 2Two Methods and Instruments of Film Flexibility Test
- 3Key performance and specific detection methods of resilience Coatings
- 4Key performance of powder coatings and their testing instruments
- 5How are architectural coatings flexibility tested?
- 6Acrylic resin and its performance testing subjects and methods
- 7ASTM D5019 Single-layer roofing film reinforced CSM board (chlorosulfonated polyethylene (PE)) standard interpretation
- 8Analysis of Conical Mandrel Test of ASTM D522 Film
- 9Three methods for determining the flexibility of putty coatings








