Introduction to Viscosity Testing Experiment of Resin
Viscosity is the resistance when one layer of flowing liquid moves relative to another layer of flow, reflecting the internal resistance of liquid to flow, and is an important indicator of resin flow performance. The greater the viscosity of the resin, the greater the resistance, and vice versa, the smaller the viscosity. The size of the resin viscosity affects the bonding performance and flow performance of the adhesive, and is an important indicator to measure the uniform atomization and spraying of the resin.
The viscosity of the resin is also directly related to the control of the reaction end point of the resin. If the reaction is stopped prematurely, the viscosity is small, and vice versa. In this experiment, a Tu-4 viscometer and a stopwatch with a scale of 0.2s were used to measure the viscosity of the resin. The Tu-4 viscometer is a conical container with a wide top and a narrow bottom, with a leak at the bottom, and it is placed on an iron stand with horizontal screws. Its schematic diagram is shown in the figure. The viscosity measured by the Tu-4 viscometer is the conditional viscosity, that is, the time for a certain amount of sample to flow out of a hole with a specified diameter at a certain temperature, expressed in seconds (s).
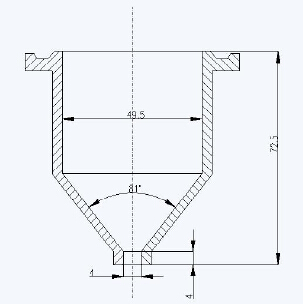
Schematic diagram of Tu-4 viscometer
The specific test steps are: before the test, clean and wipe the viscometer, especially to ensure that the leak nozzle is clean. Then stir the sample evenly, if necessary, filter it with a metal sieve with a pore size of 246 μm, and keep the temperature at 23±1°C. Place the Tu-4 cup on the iron stand, adjust the horizontal screw to make it level, place the enamel cup under the viscometer, adjust the leak switch, block the leak under the viscometer, and then fill the viscometer with the sample , use a glass rod to scrape off the excess liquid, quickly turn on the switch of the leak nozzle, and start the stopwatch at the same time, stop the stopwatch immediately when all the samples flow out, and record the flow time of the sample. Allowable difference: the arithmetic mean of the two parallel measurement results is taken as the measurement result, and the absolute difference of the two parallel measurement results is not more than 3% of the average value.
For more information, please refer to the full text of "Research on Flexible Agent in Glass Fiber Felt Binder and Optimization of Neural Network" (Sudan)
- 1How to measure the viscosity of heavy oil?
- 2Determination of paint viscosity
- 3Viscosity measurement for food and manufacturing
- 4Coating viscosity determination method and related standards
- 5How is Architectural coatings Viscosity measured?
- 6How to Measure Adhesive Viscosity?
- 7How to evaluate the viscosity index of Coating through experiments?
- 8Pressure sensitive adhesive Viscosity test and test instrument introduction
- 9Determination Principle and Detection Method of Coating Viscosity