Viscosity of oils and fats
1. Definition and content
Viscosity is one of the main physical and chemical properties of a liquid or colloidal system. Its physical meaning is the ability of a liquid to interact with molecules under the action of external forces (pressure, gravity, shear force) to hinder the relative movement of its molecules. resistance to fluid flow
2. Measurement method
(1) Use the standard GB 1660-1982 Determination of Viscosity of Plasticizers by the Pinnacle Method.
(2) Experimental principle Viscosity is the internal frictional resistance generated by the fluid in the flow, and its numerical meaning is the ratio of shear stress to shear rate.
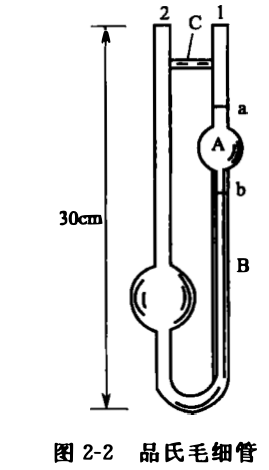
(3) Operation Adjust the viscometer to a vertical state. Adjust the thermostat to the specified temperature, and immerse the viscometer with the sample installed in the constant temperature liquid. Use the rubber tube covered by the tube body to suck the sample into the expansion part, so that the liquid level is slightly higher than the marking line a in Figure 2-2, and be careful not to cause air bubbles or cracks in the liquid in the capillary and the expansion part. Start the stopwatch when the liquid level just reaches the marking line a, and stop the stopwatch when the liquid surface just flows through the marking line b in Figure 2-2, and record the flow time.
(4) Instrument Pinner capillary viscometer, constant temperature Water Bath, automatic stirring, etc.
- 1Analysis of factors affecting viscosity
- 2The relationship between viscosity and shear rate
- 3Viscosity and surface tension
- 4How to measure the viscosity of glue
- 5The relationship between viscosity and rheology
- 6Effect of viscosity on inks wettability
- 7How to effectively control ink viscosity?
- 8Differences and advantages and disadvantages of viscometer and viscosity cup testing
- 9Paint rheology and its function