Viscosity measurement methods?
Like most answers in the world of crazy measurements, the answer is "it depends". To find out what it depends on, we'll start by defining viscosity.
What is viscosity?
Viscosity is the mechanical friction between molecules in motion, and resistance to deformation due to mutual attraction of molecules. In other words, it is resistance to flow.
There are two types of viscosity:
1. Dynamic viscosity, also known as absolute viscosity, is the tangential force per unit area required to move one level at a unit velocity relative to another while maintaining a unit distance through the fluid.
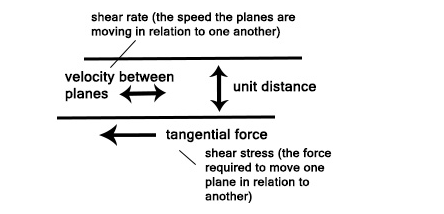
2. Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of dynamic viscosity to density.
Methods of Measuring Viscosity
Viscosity was first measured using the capillary method as early as the 1800's. Below is a brief overview of the different techniques and tools that have been developed since then and are in use.
Capillary Viscometer
Older methods of measuring viscosity were based on using capillary tubes and measuring the time it took for a volume of liquid to travel through the length of the tube. These developments, which were in place at the turn of the 20th century, were known as Ostwald or Uberold viscometers.
Zane Cup
Similar to this method is the Zahn Cup, which is a small container with a handle and a small hole in the bottom. The time required to empty the cup through the hole is viscosity related. Zahn cups are commonly used in the paint industry.
Falling Ball Viscometer
Another technique is the falling ball viscometer, in which a sphere of known density is dropped into a fluid sample and the time it takes for the sphere to fall to a designated point is recorded. This method is already used on ships to monitor the quality of fuel entering the ship's engines. A similar product is the Falling Piston Viscometer.
Vibration Viscometer
A vibratory viscometer measures the damping of an oscillating electromechanical resonator immersed in a fluid. The technology is often used in-process to provide continuous readings in product streams, batch containers or other process applications.
Rotational Viscometer
A Rotational Viscometer measures the torque required to turn an object in a fluid as a function of the fluid's viscosity. This method is frequently used in quality control and production laboratories.
Simple liquids that respond to flow rate and time in a simple manner are called pure liquids or Newtonian fluids. These pure liquids include water and milk. Newtonian fluids are usually measured by capillary viscometers, Zahn cups or falling ball viscometers.
Non-Newtonian fluids respond to changes in flow velocity and time in very different ways. Techniques for measuring these viscosities require complex testing methods offered by other types of instruments, Rotational Viscometers being popular.
- 1Viscosity of polypropylene (PP) amide measured by NDJ Viscometer
- 2Which Viscometer to Choose for Licorice Extract Viscosity Testing? How to Test?
- 3Application of Rotational Viscometer in juice viscosity test
- 4Working Principle, Classification and Application of Capillary Viscometer
- 5Principle, Characteristics and Application of Dial Viscometer
- 6Basic Principle and Application of Ceramic Viscometer
- 7Principle, Characteristics and Application of QND Viscometer
- 8Determination of epoxy resin viscosity by Rotational Viscometer
- 9Rotational viscometer selection suggestions







