The principle of natural convection and forced convection in oven
Principle of natural convection
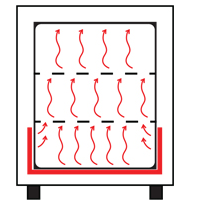
In a natural convection oven, a stream of hot air flows from top to bottom, spreading the temperature evenly (see image above). There is no fan that actively blows the air inside the box. The advantage of this technology is the ultra-low air turbulence for gentle drying and heating.
Principle of mechanical convection
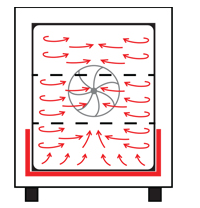
In mechanical convection (forced-air driven) ovens, an integrated fan actively drives the air inside the oven to achieve even temperature distribution throughout the oven (see image above). One of its major advantages is that it has good temperature uniformity and high reproducibility of experimental results, which is suitable for applications such as material testing and drying schemes with very strict temperature requirements. Another advantage is that the drying process is much faster than natural convection. After opening the door, the temperature inside the mechanical convection oven will quickly return to the set temperature level.

- 1Principle, application and selection of Electric Oven
- 2Principle, application and selection of vertical Electric Forced Air Drying Oven
- 3Principle, application and selection of Electric Oven
- 4Principle, application and selection of pigment Drying Oven
- 5Principle, application and selection of ozone sterilizing oven
- 6Principle, application and selection of electric heating air Drying Oven
- 7Principle, application and selection of tunnel oven
- 8Principle, application and selection of vacuum electric Drying Oven
- 9Principle, application and selection of nitro paint Drying Oven














