Waterborne epoxy resin curing
The curing of epoxy resin mainly depends on the epoxy group and hydroxyl group on the main chain that can react with various groups to form a three-dimensional cross-linked network structure. The ternary structure of the epoxy group has a strong deformability and a polarized charge distribution, and the reactivity is high. Due to the characteristics of the oxygen atom, the charge distribution in the epoxy ring is biased towards the oxygen atom, which increases the reactivity of the structure. When heating or other conditions meet certain requirements, the charge is easily transferred in a directional manner to cause a ring-opening reaction. Alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids, and thiols are easily reactive with epoxy groups. There are many types of curing agents for epoxy resins, mainly of latent type and explicit type. The latent curing agent means that it will not react with the epoxy resin under normal circumstances, and will only cure when certain conditions are met, so the latent curing agent can be fully mixed and stable after being added to the epoxy resin. The obvious type curing agent is mainly divided into polymerization type and catalytic type. After the polymeric curing agent contacts with the epoxy resin, it will attack the epoxy group to open the ring, and participate in the curing and crosslinking itself. The number of active groups inside the curing agent and the amount of active agent added affect the curing of the epoxy resin. The main factor of crosslinking. The catalytic curing agent only provides sufficient energy for the epoxy group when it opens the ring, and does not participate in the crosslinking and curing reaction itself. It has less influence on the crosslinking and curing of the epoxy resin than the polymeric curing agent. . Commonly used epoxy resin curing agents are: polyamine type, acid anhydride type, phenolic type, polythiol type, etc.
The curing mechanism of water-based epoxy resin is different from the curing of general polymer emulsion. The general polymer emulsion film-forming process is mainly a physical change process. The general polymer emulsion is with the volatilization of the solvent, and the polymerization in the polymer emulsion The particles will form a tight packing structure and aggregate into a film under pressure. Water-based epoxy resin emulsion crosslinking can be divided into high temperature crosslinking, UV crosslinking and room temperature crosslinking according to the crosslinking method. High-temperature crosslinking requires a lot of heat, and the scope of application of UV crosslinking is limited, while room temperature crosslinking not only saves resources but also applies to any coating substrate and construction conditions.
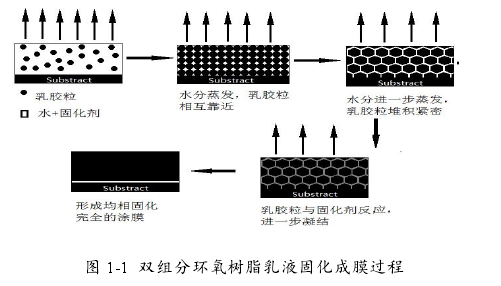
According to the packaging method, there are two kinds of two-component and one-component: the two-component water-based epoxy resin emulsion is to add a curing agent when the water-based epoxy resin is used, and stir the curing agent and emulsion evenly to form a uniform system. Evaporation, the epoxy group in the epoxy resin and the curing agent occur
The chemical reaction produces a dense three-dimensional structure. Because the reaction is carried out between molecules, the reaction is complete, and the performance of the emulsion film is very good. The film-forming process of two-component epoxy resin emulsion is shown in the figure. One-component water-based epoxy resin emulsion is a monomer with self-crosslinking function grafted on the molecular chain of epoxy resin, so that the system is stable without crosslinking under the condition of water. As the pH value of the system changes, the crosslinking monomers begin to self-crosslink to form a dense and uniform three-dimensional structure, thereby endowing the coating with good water resistance, hardness and adhesion. Two-components need to be packaged and stored separately before use, and they are prepared and used immediately when they are used, and the curing agent needs to be used as soon as possible after adding the epoxy resin, but there is no such defect in the single-component, so the cross-linking of the single-component Curing technology has broad market prospects and application value.
- 1Discussion on film thickness and accuracy in epoxy resin coating
- 2Experimental test of performance of epoxy resin film coated on metal iron plate by small coater
- 3Epoxy resin floor coatings key performance and detection method
- 4Epoxy resin Coating characteristics, uses and performance testing
- 5What is epoxy resin?
- 6Performance Testing Subjects and Testing Instruments of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Coatings
- 7Epoxy resin coating
- 8What are the main types of epoxy resin emulsions
- 9Epoxy vs Polyurethane: Which Coating is Better?