Types and uses of pH electrodes
The first pH electrodes had a glass bulb or bubble filled with a strong electrolyte, with an Ag/AgCl (silver/silver chloride) half-cell inside, with Ag wires as contacts.

The original pH electrode and the way modern electrodes work hasn't changed much, but as technology has improved, new designs have emerged such as combination electrodes, double junction electrodes, gel filled electrodes, Calomel junctions, solid state electrodes, ion selective electrodes and epoxy resin body electrodes.
Most pH electrode types today are called combination electrodes. Combination electrodes have a glass hydrogen ion (H+) sensitive electrode and an additional reference electrode in one housing.

How does a pH electrode or combination electrode work?
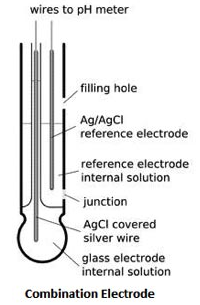
Combination electrodes or pH electrodes measure the potential difference between two sides of a glass electrode. To measure potential, it needs to be closed. The circuit is closed by the internal solution of the electrode and the external solution to be measured and the pH meter.
When the electrode is immersed in the test solution, the glass bulb senses hydrogen ions in millivolts (mV) due to their positive charge. The electrolyte or internal solution picks up the mV signal from the glass bulb. This signal is then passed to the internal electrodes. The Ag/AgCl wires then carry this signal to the electrode cable leading to the meter.
A reference electrode containing an electrolyte or fill solution produces a constant mV which is transferred to the Ag/AgCl wire. The wires then carry a signal, which can be thought of as a "control," to the electrode's cable.
This circuit is closed by the trace internal solution in the reference electrode flowing through a porous membrane made of a ceramic core. This membrane or junction is called the electrode body.
A pH meter measures the difference (in millivolts DC) between the internal electrode and the reference electrode. The meter then takes this mV reading and displays it in pH units.
How do double junction electrodes work?

As mentioned above, the combined electrode is separated from the solution under test by the junction where the electrolyte flows out. Under unfavorable conditions, the solution being measured may be strongly acidic or basic, or under high pressure or temperature, the forward flow of electrolyte through the junction may be reversed. Once reversed, the measured sample will flow into the reference chamber, contaminate the reference electrode, and eventually destroy the electrode.
在可能发生电解液逆流的应用中,使用双结。为了保护参比不受污染,在电极中内置了第二个结。第二结,即众所周知的双结电极,在被测溶液和参比电极之间有一个额外的腔室。在测试溶液的污染到达参比电极之前,它首先需要不仅扩散通过原始结,而且还扩散通过第二结。附加腔室用作缓冲液,减慢参比电极电解液的变化。双结电极的优点是它们使用寿命更长,并且在不利条件下也能正常工作。
Calomel电极如何工作?
由银线,氯化银和氯化钾(KCl)电解质构成的通用电极在大多数不与银反应的水溶液中都能很好地工作。当使用含有重金属,蛋白质,Tris缓冲液,有机物和低离子溶液的溶液时,它们都会与银发生反应,因此会缩短通用电极的寿命。
Calomel组合电极的参比电极由汞和氯化汞制成,并具有KCl电解质。它与上述解决方案的反应性较弱,并且可以延长电极的使用寿命。
Calomel电极的缺点是其所含的汞和汞化合物。它们被认为是有害物质,需要特殊的处置方法。
双结电极构造技术的进步消除了对Calomel电极的需求。
离子选择性场效应晶体管(ISFET)如何工作?
离子选择性场效应晶体管(ISFET)或固态电极依靠硅芯片,当与测试溶液接触时,该硅芯片可检测并测量其表面与下面的半导体材料之间的可变电势。此可变电位与样品中的氢离子浓度成正比,并用于确定pH值。
ISFET电极耐用且易于维护。探头由不锈钢制成,由于没有玻璃,因此非常适合食品工业。它们几乎是牢不可破的。
ISFET电极的其他优点包括:可以用牙刷清洁的坚固的pH感应区域; 它们可以干燥存放;具有快速的响应时间,可用于测试pH等级上极端水平的酸或碱。
ISFET的缺点是其价格是传统电极的2至3倍。它们提供的稳定性和准确性不如玻璃电极。它们存在一个已知的漂移问题,并且大多数仅适用于适用于ISFET技术的pH计。
离子选择电极如何工作?
Ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) are commonly used to measure specific ion concentrations in solutions in real time. The electrodes consist of a sensor that converts the activity of ions dissolved in solution into an electrical potential. Traditional pH electrodes can only measure the potential of dissolved hydrogen ions. The ISE can measure the ionic potential of many substances; some common examples are ammonia, cadmium, calcium, bromide, fluoride, copper and cyanide dissolved in solution.
The ISE can only be used with pH meters that display readings on both a millivolt scale and a pH scale. Measurements are converted to parts per million (ppm).
Instead of a glass bulb, the sensing part of the electrode is made into an ion-specific membrane together with an ion-specific reference electrode. When using ISE Ionic Strength Adjusters, ion-specific calibration solutions and replacement electrolyte solutions are required.
ISE is used in water treatment plants, manufacturing facilities and laboratories where real-time measurement of specific ions is required for purification results, quality control and solution analysis.
- 1PH meter composite electrode type
- 2How to use and maintain pH electrodes?
- 3What is a pH electrode?
- 4Ark custom PH electrode model Daquan
- 5Customized pH electrode structure, function and type [Common sense]
- 6How to choose the right PH electrode? [Selection Guide]
- 7Classification of pH Electrodes
- 8pH Electrode FAQ
- 9pH Electrode Routine Maintenance Guide