The working principle of British thermax TMC temperature test paper
A common application associated with wax melt temperature indicating technology is self-adhesive labels, which consist of a series of heat-sensitive elements sealed between heat-resistant substrates with clear windows. Each element changes color noticeably above its rated temperature. These changes are irreversible and provide a temperature history of the surface being monitored. When removed for reference, the label will not delaminate and can be attached to the inspection report for a permanent record of the temperature achieved. Typically used in industrial environments.

Working principle of thermometer paper
The temperature-sensitive element is a color-changing indicator that uses the well-defined melting points of a series of specially purified organic chemicals to provide a unique, high-precision color-changing effect. Each temperature element uses a different compound and is made individually by applying a coating containing the chemical to a special absorbent paper substrate, usually black. When the rated temperature is exceeded, the chemical melts and is absorbed by the substrate, causing a permanent discoloration to black. Up to ten elements can be grouped together on a label.
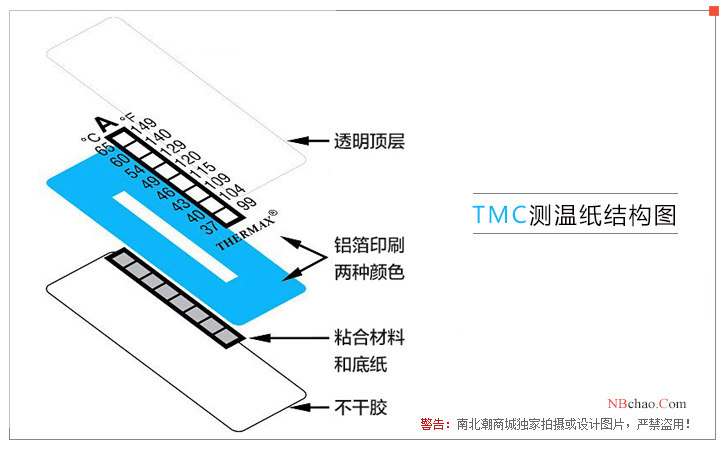
Material composition of temperature measurement label
| Material | thickness |
| printing foil | > 10µ |
| Melinex polyester film (171℃ and below) | 50µ |
| KALADEX membrane (177°C to 204°C) | 50µ |
| Kapton polyimide membrane (210¬℃ and above) | 50µ |
| Adhesive & Carrier (No Liner) | 75-85µ |
| black coated paper | > 150µ |
| Release liner | 75µ |














