Talking about the use of Rotational Viscometer
introduction
Viscosity is a characterization of the fluidity of oil, reflecting the strength of the interaction of liquid molecules in the process of movement. When the fluid is flowing, there is relative motion between adjacent fluid layers, and there will be frictional resistance between the two fluid layers, which is called viscous force (Newtonian internal friction force). Viscosity is a , which is determined by the type of substance, temperature, concentration and other factors. In industrial production, viscosity measurement is one of the main reference data for process calculation, and viscosity is one of the important parameters for evaluating oil properties.
1. Oil Viscosity Measurement Method
The measurement of oil viscosity is carried out according to GB/T 10247-2008 "Standard Test Method for Determination of Kinematic Viscosity and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity of Petroleum Products ". This standard stipulates the measurement of fluid movement by capillary method, falling ball method, rotation method and vibration method General method for viscosity and dynamic viscosity [1].
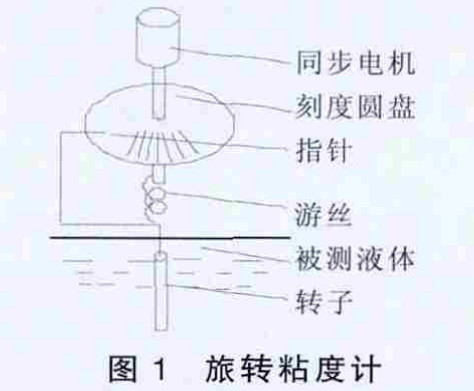
2 Working principle of Rotational Viscometer
The synchronous motor rotates at a stable speed, connects the scale disc, and then drives the rotor to rotate through the hairspring and the rotating shaft. As shown in Figure 1, if the rotor is not resisted by the liquid, the hairspring, pointer and scale disc rotate at the same speed, and the reading indicated by the pointer on the dial is "0"; on the contrary, if the rotor is subjected to viscous resistance of the liquid, Then the hairspring generates torque, which competes with the viscous resistance and finally reaches a balance . At this time, the pointer connected with the hairspring indicates a certain reading on the dial (that is, the torsion angle of the hairspring) [2]. Multiply the reading by a specific coefficient to get the viscosity of the liquid (mPa·s).
3 Rotational viscometer use
(1) Accurately control the temperature of the measured liquid.
The main factor is temperature. For example, the dynamic viscosity of water at 20°C is 1.005cp, and the dynamic viscosity of water at 21°C is 0.981cp. If the temperature changes by 1°C, the error will reach 2.4°C, so special attention should be paid to the measured liquid The temperature is constant around the specified temperature point . When in use, immerse the rotor in the measured liquid for a long enough time and keep the temperature constant so that it can be consistent with the temperature of the measured liquid, reducing the influence of temperature fluctuations on the measurement accuracy [3].
(2) Rotor selection.
First roughly estimate the viscosity range of the sample to be tested. For high- viscosity samples, choose small-volume (No. 3, No. 4) rotors and slow speeds. For low-viscosity samples, choose large-volume (No. 1, No. 2) rotors and fast speeds. The percentage scale (torque) of each output is a normal value between 20% and 90%, and the viscosity value measured in this range is the correct value. At the same time, the measurement should place the rotor in the center of the container as much as possible to reduce the measurement error caused by the rotation bias.
(3) The performance index of the viscometer needs to meet the national measurement verification regulations
It is required that the viscometer in use should undergo periodic verification, and if necessary (the viscometer is frequently used or in a qualified critical state), an intermediate self-inspection should be carried out to ensure that its measurement performance is qualified and the coefficient error is within the allowable range, otherwise accurate data cannot be obtained.
(4) Prevent air bubbles from adhering to the bottom of the rotor when the rotor is immersed in liquid.
There are often air bubbles when the rotor is immersed in the liquid. Most of them will float up and disappear after a period of time after the rotor rotates. Sometimes the air bubbles attached to the lower part of the rotor cannot be eliminated. The existence of air bubbles will bring large deviations to the measurement data. When using The rotor should be dipped into the sample holder at an incline slowly, which can effectively reduce generation of air bubbles. Ensure the uniformity of the liquid.
(5) Selection of range, coefficient, rotor and speed.
First roughly estimate the viscosity range of the liquid to be measured, and then select the appropriate rotor and speed according to the range table ; for example , the following combination can be used when measuring a liquid of about 2500mPa·s: No. 2 rotor is 6 rpm; No. 3 rotor is 30 rpm. When the approximate viscosity of the liquid to be tested cannot be estimated, it should be assumed to be a higher viscosity, and the rotor from small to large and the speed from slow to fast should be tried. The principle is to use a small rotor (high rotor number) and slow speed for high-viscosity liquids; use a large rotor (low rotor number) and fast speed for low-viscosity liquids. When measuring, the reading indicated by the pointer on the dial needs to be multiplied by the specific coefficient on the coefficient table to obtain the measured viscosity (mPa·s).
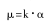 (1)
(1)
In the formula, Zi is the viscosity; K is the coefficient; A is the reading (deflection) pointed by the pointer.
(6) If the power frequency is not on time, it should be corrected according to the correction formula
For some instruments in Japan, Europe and the United States , the nominal frequency is 60Hz, and frequency correction is required, otherwise a 20% error will occur. The correction formula is: actual viscosity = (indicated viscosity + nominal viscosity) / actual frequency (2) For domestic instruments, the nominal The frequency is 50Hz, and the current power supply frequency in our country is also 50Hz, so the general measurement does not need frequency correction
(7) Make sure the rotor is clean.
The measuring rotor (including the outer cylinder) should be clean and free of dirt. Generally, the viscometer should be cleaned in time after the measurement. Pay attention to the cleaning method, soak it in a suitable organic solvent, and never use a metal knife to scrape hard, because serious scratches on the rotor surface will affect the measurement accuracy .
(8) Choice of measuring container
For the dual-cylinder Rotational Viscometer, read the instrument manual carefully. Different rotors (inner cylinders) match the corresponding outer cylinders, otherwise the measurement results will deviate greatly. For a single-cylinder Rotational Viscometer, the outer cylinder radius is required to , and the inner diameter of the outer cylinder, that is, the measuring container, is required not to be less than a certain size in actual measurement [4].
(9) Other precautions.
Most instruments need to adjust the level, pay attention to the level problem at any time after replacing the rotor and adjusting the height of the rotor and during the measurement process , otherwise it will cause reading deviation or even no reading ; Otherwise it will cause reading deviation.
4 Conclusion
Rotational viscometer has been widely used in viscosity measurement, and its measurement accuracy is mainly affected by human factors and physical factors. The latter is easy to solve, but it is usually not easy to find out. Only when the deviation of the measurement results is obvious, it will be noticed. If it is not used correctly, a qualified instrument cannot obtain accurate measurement results, which will affect product quality and even cause negative effects.
- 1Rotational viscometer - principle, classification, application and calibrating
- 2Application of NDJ-8S digital Rotational Viscometer in viscosity measurement of cosmetic raw materials
- 3NDJ-5S digital Rotational Viscometer accurate measurement of natural oil viscosity
- 4Application of HBDV-1H swirl/spin High Temperature Viscometer in Viscosity Determination of Plastic Particles
- 5Rotational viscometer selection guide: How to choose the right viscosity equipment for you?
- 6Principle, type and accuracy control of Rotational Viscometer
- 7Which Viscometer to Choose for Licorice Extract Viscosity Testing? How to Test?
- 8Application of Rotational viscometer in Waterborne Polyurethane Adhesive
- 9Application of Rotational Viscometer in cellulose material






