Effect of Synthetic Polymer Thickener on Viscosity of Styrene Acrylic Latex Paint
In order to investigate the effect of synthetic polymer thickeners on the viscosity of latex paints, acrylic acid alkali-swellable thickeners (ASE), alkali-swellable associative thickeners (HASE) and associative polyurethane thickeners (HEUR ) as a thickener, use different amounts of thickener to prepare latex paint, and test the viscosity of the newly prepared latex paint after 2 days and 7 days. The viscosity of latex paint is tested according to the Stormer viscometer method stipulated in the national standard GB/T 9269-2009, and the results are shown in Figure 3-16, Figure 3-17, and Figure 3-18.
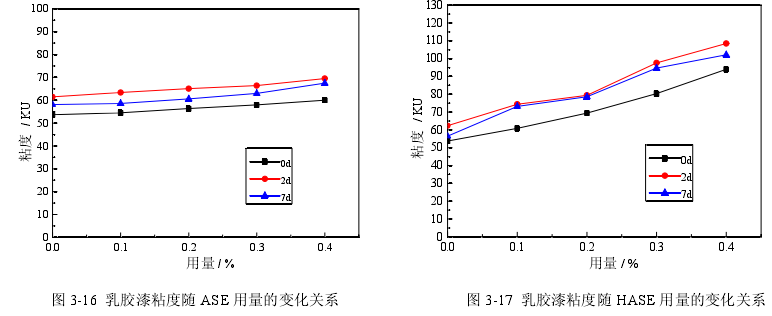
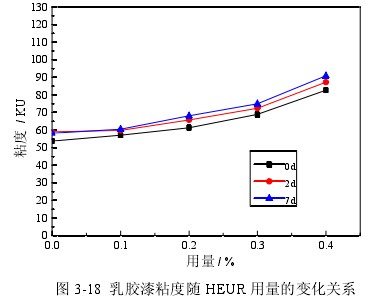
It can be seen from Figure 3-16, Figure 3-17, and Figure 3-18 that with the increase in the amount of three synthetic polymer thickeners, the viscosity of latex paint increases, and the viscosity of latex paint increases with different types of thickeners. The trends are also different. The increasing order of latex paint viscosity with the increase of three thickeners is as follows: HASE>HEUR>ASE. The viscosities of the latex paints prepared with the three thickeners after being placed for 2 days and 7 days were higher than those when they were just prepared. In Figure 3-16, when ASE is used as a thickener, the viscosity of latex paint after 7 days of storage is smaller than that of 2 days after storage. In Figure 3-17, when HASE is used as a thickener, the viscosity of latex paint after 7 days of storage is close to the viscosity of 2 days after storage, and the drop is small. In Fig. 3-18, when HEUR is used as a thickener, the viscosity of the latex paint remains basically unchanged after 7 days and 2 days. The reason for the above phenomenon is that ASE is a non-associated anionic type, which is a polyacrylate alkali-swellable emulsion containing carboxyl groups. In an alkaline system, a neutralization reaction occurs, the resin is dissolved, and the carboxyl groups make the polymer under the action of electrostatic repulsion. The chain stretches, and the molecular chain elongates from a helical shape to a rod shape, which increases the viscosity of the water phase and increases the viscosity of the system. With the increase of its dosage, the content of carboxyl groups is also large, and the formation of rod-shaped molecular chains is also large, so the viscosity is also large. HASE is also an anionic thickener. On the basis of ASE thickening, surface-active associative monomers are introduced into its main structure with acrylate as the main chain to participate in copolymerization, and the side chains are grafted and have hydrophobic groups. The long-chain structure of groups and hydrophilic groups can form a large micelle structure in water, and carry out mutual adsorption and association within or between molecules. In addition, the hydrophilic groups in the main chain and side chains can adsorb with water molecules through hydrogen bonds, and the hydrophobic groups not only adsorb each other, but also adsorb with latex particles and hydrophobic groups of various additives, forming a large The range of three-dimensional network structure increases the viscosity of the system, and the thickening efficiency of HASE is higher than that of ASE. HEUR It is a non-ionic hydrophobic modified ethylene oxide polyurethane block copolymer, which is a three-block polymer in the form of "lipophilic-hydrophilic-lipophilic". The chain end is usually an aliphatic hydrocarbon group, and the middle is a water-soluble Hydrophilic segment of polyethylene glycol. In the water-based system, when the concentration of the thickener is greater than the critical micelle concentration, the lipophilic end groups are associated into micelles, the hydrophilic groups are coupled with water, and the end groups forming micelles are adsorbed on different micelles through two lipophilic ends. On the particles, the thickener molecules form bridges between the particles, and associate with the polymer particles of the emulsion and the pigment particles that have absorbed the dispersant to form a network structure, which is interlinked and intertwined to increase the viscosity of the system. In addition, since one molecule carries several micelles, this structure reduces the mobility of water and increases the viscosity of the aqueous phase. The viscosity of the latex paint prepared by the above three thickeners after being placed for 2 days and after being placed for 7 days is higher than that of the latex paint just prepared because the molecular chain structure of the thickener after being placed for a period of time is fully extended. Mutual entanglement causes the viscosity to increase. When using HEUR as thickener, the viscosity of latex paint increases slower than that of HASE, because the molecular weight of HEUR is low and the thickening effect is not significant. The viscosity of latex paint prepared with ASE after 7 days is lower than that after 2 days, while the viscosity of latex paint prepared with HASE and HEUR has little change, because the former cannot form a stable network structure and the viscosity is stable The latter two can form a three-dimensional network structure during the thickening process, and have high stability.
- 1Stormer Viscometer (KU): Accurate measurement and multi-domain applications
- 2Determination of viscosity of architectural coatings: application of the Stormer Viscometer method
- 3Analysis of factors affecting viscosity
- 4The relationship between viscosity and shear rate
- 5Viscosity and surface tension
- 6How to measure the viscosity of glue
- 7The relationship between viscosity and rheology
- 8Effect of viscosity on inks wettability
- 9How to ensure accurate Stormer Viscometer measurements? with calibration method
-
-
-
-
-
-
JFL QNZ Stormer Viscometer$ 518.00












