Effect of Dispersants on Coating Dispersion
Dispersants are surface-active substances that can improve the stability of coating dispersions. The dispersant added to the paint can be adsorbed on the surface of the pigment that has been crushed into fine particles, forming an adsorption layer, generating charge repulsion and steric hindrance, preventing the dispersed pigment particles from flocculating again, and keeping the dispersed system in a stable suspension state. . If the dispersant is used properly, it can also improve the leveling property, prevent the pigment from floating and fading, obtain a uniform color coating film, improve the coloring power and hiding power of the pigment, and increase gloss of the coating film.
The dispersion process of pigments is generally considered to be divided into three stages, namely wetting, crushing and stabilization. These three stages are not categorically separated, but intersect with each other . The wetting process can also be said to be the beginning . The wetting process still exists during the pulverization and grinding process. The pigment particles pulverized into fine particles will immediately absorb the resin polymer or added dispersant compound in the paint, that is to say, the stable The fixed stage also started.
There are basically two mechanisms for pigment dispersion stability, namely DLVO theory and steric hindrance effect. The basis of DLVO theory is that the colloidal particles are charged to form an electric double layer, and the stability of the dispersion system is formed due to the charge repulsion. If the surface of the pigment particle is charged, a layer of to form an electric double layer. A double layer formed by charged particles can be regarded as charged particles surrounded by an ionic atmosphere. When the Brownian motion causes the ion atmosphere of two particles to overlap each other, the charge concentration in the overlapping area changes and will be redistributed, resulting in the repulsion of the charges between the two particles. If the repulsion is greater than the van der Waals attraction, the particles will be repelled and the dispersion will be in a stable state. Otherwise, the two particles will coagulate with each other, and many problems will appear in the dispersed system, such as precipitation and blooming. This stabilization mechanism works well . In organic media, the polarity is rather low and thus the effectiveness of charge stabilization is less, usually explained by the theory of steric hindrance.
Classification of wetting and dispersing agents used in the experiments.
1. Synthetic polymers. Most of these additives are composed of long-chain polyaminoamides and salts of various carboxylic acids. They are electrically neutral surfactants, compatible with most coating resins, and have a wide range of applications. It has more adsorption groups, which can form a thicker and firm adsorption layer on the surface of the pigment, which improves the stability of the pigment dispersion and prevents floating and blooming.
2. Polyvalent carboxylic acids. They impart a structural viscosity to coating dispersions that can be pseudoplastic or thixotropic. It is especially effective in preventing paint from floating and blooming.
3. Block polymer copolymer. This type of dispersant has the adsorption part of the pigment and the extension part , with strong adsorption firmness and large thickness, so it has a good steric hindrance effect, which can ensure the stability of the paint dispersion system and prevent the paint from floating and fading. The purpose of flowering and precipitation.
4. Special vinyl polymers. This kind of dispersant is an oligomer, which belongs to polymer active substance, and contains carboxyl group in the molecule, so it has excellent dispersibility.
The amount of pigment dispersant used in the experiment is estimated by the addition curve method. The method is: into a thick water slurry made of a certain amount of pigment or pigment mixture, add a thicker pigment dispersant solution drop by drop under stirring, and measure the viscosity every time you add it. As the pigment dispersant amount / viscosity curve , the viscosity decreases with the gradual addition of the pigment dispersant, and rises after a minimum point ( flocculation due to the introduction of too much charge). This nadir serves as a good dosage of pigment dispersant for this pigment water slurry. The dosage curve of pigment dispersant may only be applicable to the pigment water slurry itself. If this amount is used in latex paint, the degree of dispersion stability is often insufficient, and more is needed in actual application. The effect of dispersant 5-1 .
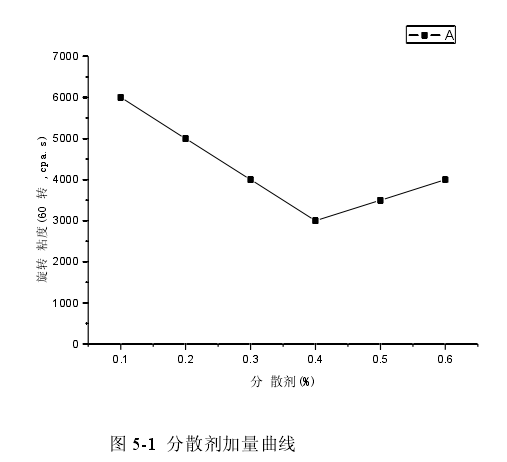
It can be seen from Figure 5-1 that with the increase of the dispersant content, the viscosity of the system decreases gradually. When the dispersant content reaches
When the dispersant content is 0.4 %, the viscosity is the lowest. When the dispersant content exceeds 0.4 %, the viscosity of the system will gradually increase due to re-flocculation.
- 1Why use dispersants in paints and coatings
Performance Coatings Team
- 2What is a dispersant?
- 3Effect of Wetting Agent on Coating Dispersion
李琴 - 《吉林大学》
- 4Composition and structure of coating liquid
- 5Basic process and configuration points of water-bomecoating production
- 6Coating stability detection dispersion method
- 7Effect of Shading Principle and dispersant on Low Titanium Dioxide
伍文君;熊喜竹;刘丽莉 - 《电镀与涂饰》





