How does a circulating cooler work?
The basic principle of a recirculating cooler is that the temperature of a system or object is controlled by the heat flowing in and the heat flowing out. There are many sources of heat entering a system, including electrical, mechanical, radiation or chemical, that need to be overcome to maintain a constant temperature.
When is chilling usually required?
Desire to keep samples/systems reliably at or below ambient temperature
Samples/systems with heat sources that need to be counteracted and cooling is used to keep the sample/system at a stable temperature
Cooling gas to liquid state while distilling and condensing
The diagram below shows how the heat exchanger in the unit works, without the two liquids touching, cold water is pumped through the coil which cools the surrounding fluid.
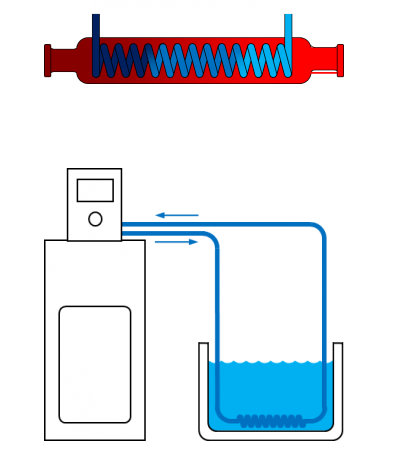
Calculations are required to calculate the set temperature of the circulator to be able to maintain the desired sample temperature. The flow rate, the speed at which the coolant circulates in the circuit, and practical conditions such as the length of the pipes and the limitations of the pipes need to be considered.







