Definitions of several common viscosity
When there are dispersed particles in the liquid, the flow of the liquid must be disturbed by the particles, and additional energy needs to be consumed to overcome the internal friction generated by the particles, so the viscosity of the dispersed system is higher than that of the pure liquid. For ease of discussion, a few commonly used nouns are introduced first, and the definitions are as follows:
(1 ) The relative viscosity η r is the ratio of the viscosity η of the dispersion or solution to the viscosity η 0 of the pure solvent , expressed as: η r = η/η 0
(2) Increased specific viscosity η sp is the viscosity increase, which represents the contribution of dispersed particles to viscosity. η sp = η r -1
(3) Reduced viscosity, also known as reduced viscosity or viscosity number, is the contribution of dispersed particles per unit concentration to viscosity, expressed in n sp /C, where C is the mass concentration.
(4) Inherent logarithmic viscosity is the ratio of the natural logarithm of the relative viscosity to the concentration, expressed by ln η r /C.
(5) Intrinsic viscosity [ η ] extrapolates the reduced viscosity or logarithmic viscosity to the value when the concentration is zero, namely
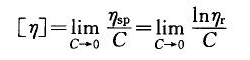
- 1Viscosity of polypropylene (PP) amide measured by NDJ Viscometer
- 2Which Viscometer to Choose for Licorice Extract Viscosity Testing? How to Test?
- 3Application of Rotational Viscometer in juice viscosity test
- 4Working Principle, Classification and Application of Capillary Viscometer
- 5Principle, Characteristics and Application of Dial Viscometer
- 6Basic Principle and Application of Ceramic Viscometer
- 7Principle, Characteristics and Application of QND Viscometer
- 8Determination of epoxy resin viscosity by Rotational Viscometer
- 9Rotational viscometer selection suggestions