Principles and steps for dust determination of paper and paperboard
1 definition
(1) Dust
Fiber bundles and other impurities that can be seen on the paper that are significantly different from the color of the paper under any irradiation angle .
(2 ) Dirt Count
Per square meter of paper or cardboard, it is expressed by the number of dust with a certain area or the equivalent area (mm3) of paper or cardboard dust per square meter.
2 instruments
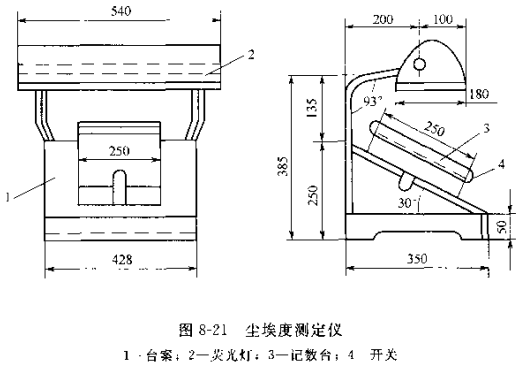
The Dirt Count measuring device is shown in Figure 8-21. Including the following parts.
① Lighting device. 20 W fluorescent lamp, the irradiation angle should be 60".
② Rotatable sample plate. Milky white glass plate or translucent plastic plate, the area of the sample plate is 270mm×270mm.
③Standard dust picture.
3 experimental steps
① Sampling shall be carried out according to the standard method, and at least four samples of 250 mm × 250 mm shall be cut.
②Put a sample on a rotatable sample board, tighten it with the four corners of the board, and inspect the dust visible to the naked eye on the paper surface under the fluorescent lamp. The visual distance of the eye is 250~300 mm. Circle different areas of dust with different markers. Use the standard dust picture identification paper ": the size of the dust area. It can also be used to record the number of dust in the same area according to the size of different areas.
③Then rotate the sample plate 90', and mark the newly discovered dust after each rotation. Until it returns to the original position , then check the other side of the sample according to the above method.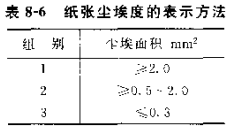
④ Measure the remaining 3 samples according to the above steps.
4 test results
According to Table 8-6, calculate the number of dust in each group on the front and back of each sample. If the paper is used on one side, only the dust on the use side is measured, and the four samples are counted. Then convert it into the number of dust per square meter, and round the calculation result to an integer.



