What is a drop ball viscometer?
When measuring the viscosity of a fluid with a falling ball viscometer, it is based on measuring the speed at which a ball falls through the measured fluid. The measurement is relatively simple, and relatively accurate viscosity data can also be obtained after proper mathematical processing.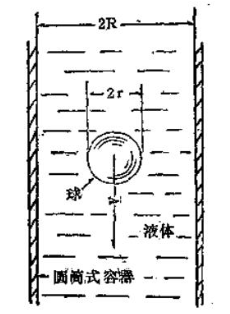
Equation is a theoretical expression for calculating the viscous resistance (force) encountered when a ball passes through a fluid at a constant velocity (Stokes' Law - Sto-kes Iaw):
F= 6πrηv
In the formula: F=viscosity resistance (force) resistance (dyne);
r = radius of the ball (cm);
η = viscosity (poise);
v = velocity (cm/s).
In deriving this expression, Stokes assumed that the ball was in an infinite fluid. After changing this formula, the viscosity of the fluid can be determined by the free falling ball method in a certain range of containers (see figure).
First consider the derivation of the basic formula of the falling ball viscometer: suppose the radius of the ball is r, the density is Ps, and the volume is v, which is equal to 4πr³/3. When it is put into a fluid with density P, the weight of the ball Just pull the ball down and pass through the fluid. At this time, the elastic force of the fluid reacts and pushes the ball up. The final effect is the net force (that is, the force after offsetting the balance), which is equal to the following formula:
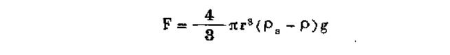
Under the influence of gravity, when the ball falls freely through the fluid, the direction of its acting force (calculated by Equation 3-46) is opposite to that of the viscosity resistance force (calculated by Equation 3-46). Falling at constant velocity v, adjust these two forces to be equal to each other at constant velocity:
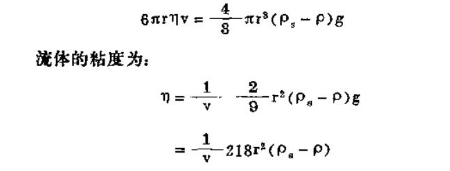
These formulas are applicable to free-falling balls in infinite fluids, free-falling balls in a cylindrical container with a certain range (radius R), and the viscosity calculated according to the formula needs to be multiplied by the wall correction coefficient:
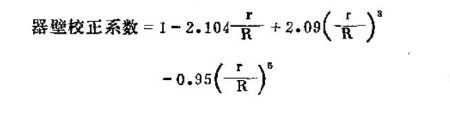
In the formula, r = the radius of the ball (cm)
R = inner radius of the cylindrical container (cm).
The falling ball viscometer is a relatively simple instrument, and it is also generally used to measure transparent Newtonian fluids, which can be expressed in units of "Poise". Heppler (appler) falling ball viscometer is a relatively precise instrument, which is characterized in that the tube is inclined at a certain angle, so that the ball can slide steadily along the wall of the tube to avoid the possibility of the ball falling vertically . Deviations cause errors.
- 1Viscosity of polypropylene (PP) amide measured by NDJ Viscometer
- 2Which Viscometer to Choose for Licorice Extract Viscosity Testing? How to Test?
- 3Application of Rotational Viscometer in juice viscosity test
- 4Working Principle, Classification and Application of Capillary Viscometer
- 5Principle, Characteristics and Application of Dial Viscometer
- 6Basic Principle and Application of Ceramic Viscometer
- 7Principle, Characteristics and Application of QND Viscometer
- 8Determination of epoxy resin viscosity by Rotational Viscometer
- 9Rotational viscometer selection suggestions