How does the Bekk test measure paper and cardboard smoothness?
(1) Test principle
The test principle of the Bekk test method is shown in Figure 2-5. The sample is placed on a circular glass anvil, and a certain pressure is exerted on the sample. A certain volume of air is passed through the central hole of the annular glass anvil, and the smoothness of the paper is expressed by measuring the time required for the air to pass between the sample and the glass anvil. For paper with a rough surface, the gap between it and the glass surface is relatively large, and air can easily pass through the concave part of the paper surface. Therefore, the shorter the time required to pass a given volume of air, the less smooth the paper surface is.
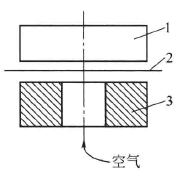
Figure 2-5 Principle of Air Leakage Method
1-gland 2-sample 3-glass anvil
The national standard GB 456 "Measurement of smoothness of paper and cardboard (Buick method) is applicable to most paper and cardboard, but not suitable for measuring paper with a thickness above 0.5mm or with a large air permeability.
(2 ) Ordinary Bekk smoothness meter test method
①Structure and working principle
The ordinary Bekk smoothness Tester consists of a pressurized part, a closed system and a testing part, as shown in Figure 2-6 . When the three-way valve points to "P", both air cylinders are connected to the Vacuum Pump; when it is pointed to "P0", only the small cylinder is connected to the Vacuum Pump, and the air in the cylinder is pumped out, and the mercury column in the glass tube rises immediately. Altitude is indicated by a graduated scale. During the test, first raise the mercury column to the specified height, then rotate the three-way valve to "M", and the outside air enters the small cylinder through the gap between the sample and the glass contact surface or enters the two cylinders at the same time. The mercury column falls accordingly. The smoother the sample, the tighter its contact with the glass surface, the slower the air enters the cylinder, the slower the mercury column falls, and the longer the falling time, the greater the smoothness, otherwise the smaller the smoothness.
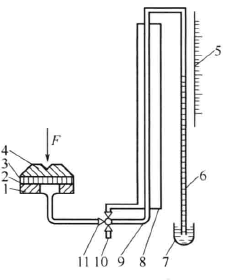
Figure 2-6 Ordinary Bekk smoothness meter
1-glass; 2-sample; 3-rubber sheet; 4-gland; 5-scale scale; 6-glass tube; 7-mercury; 8-large cylinder; 9-small cylinder; 10-Vacuum Pump interface; 11 -Three-way valve
② Calibration procedure
a. Check the tightness of the three-way valve.
b. Calibrate the height of the mercury cylinder, which should be within the range of (380 ± 0.5) mm.
c. Check the volume of the large and small tubes.
d. Proofread test area. First use a vernier caliper to measure the outer diameter of the test surface [should be within the range of (37.4 ± 0.05) mm] and the inner diameter of the test surface [should be within the range of (11.3 ± 0.05) mm], and then calculate the test area [should be within the range of ( 10 ± 0.05 ) mm ] 0.05) cm2 range].
e. Check the pressure on the test surface.
f . Check the seal of the Vacuum Pump.

③Test method
a. Sample collection and processing. Sampling according to GB450, cut 50mm×50mm samples along the transverse direction of the paper web, 10 pieces on the front and back sides, and ensure that there are no wrinkles, cracks or other defects on the sample surface. According to the requirements of GB 10739, carry out temperature and humidity pretreatment on the samples.
b. Take out the sample and put it on the glass, the surface to be tested is close to the glass anvil, and cover the film and the metal cover.
c. Adjust the pressure device to apply a certain pressure to the sample.
d. Open the valve on the instrument to the specified position, use a Vacuum Pump or an air pump to pump out the air in the container, so that the mercury column rises above 380mm. Then stop pumping, and quickly tighten the relevant valve.
e. Under the above-mentioned vacuum degree, the outside air will enter the container along the space between the sample surface and the glass anvil surface, causing the mercury column to descend. When the mercury column drops to 380mm, start the stopwatch and stop the stopwatch timing until the mercury column drops to 360mm. The stopwatch reading is the smoothness value of the sample. If a small tube is used, the stopwatch reading is multiplied by 10 to indicate the smoothness value of the sample.
The principle of using large and small tubes is: use a large tube for a sample whose smoothness value is less than 300s, otherwise use a small tube. If the smoothness value is less than 15s, use a large tube to measure the time required for the mercury column to drop from 482mm to 282mm, and then divide the stopwatch reading by 10 to indicate the smoothness value of the sample.
The test results are expressed by the arithmetic mean, maximum value, minimum value of the smoothness of the positive and negative surfaces of the tested samples, and the difference between the smoothness of the positive and negative surfaces.
-
CHINA BLD-PH10 Smoothness Meter$ 1695.00
-
- 1Determination Principle and Maintenance of Paper Smoothness Instrument
- 2Vertical and horizontal identification methods and front and back identification methods of paper and paperboard
- 3What are the common physical properties of paper?
- 4What is calcium plastic paper?
- 5What is paper smoothness?
- 6What are the paper physical properties testing instruments? How to maintain
-
-
CHINA BLD-PH10 Smoothness Meter$ 1695.00
-
-




