Preparation of Antifog Film by Wire Bar Coater
Using the raw materials listed in Table 3.1, the anti-fog coating and its anti-fog film were prepared by multi-layer coating. The bottom layer of the anti-fog film is a polyester layer. The molecular chain structure of WPE0.1 polyester is similar to that of PET. According to the principle of similar compatibility, the underlying polyester layer has good adhesion to the surface of the PET substrate. At the same time, N-propidine and corona treatment also increase the of adhesion. The preparation method of the primer is as follows: take the WPE0.1 water-based polyester , stir at 80°C and 500r/min for 20min until the water-based polyester is completely dissolved, and then cool naturally for later use. Weigh the amino resin and isopropanol, dissolve them evenly, and add them dropwise to the cooled polyester aqueous solution while stirring. Finally, the catalyst and the wetting agent are added dropwise, and stirred evenly to obtain the bottom layer solution.
The upper layer of the anti-fog film is a hydrophilic layer. Because Tween-20 contains a large number of terminal hydroxyl ethers in its molecule and has a spatial structure, it can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules to significantly reduce the water contact angle, and the cured coating has extremely high transparency, so it is suitable for use Hydrophilic modification of transparent materials. . The preparation method of the upper coating is as follows: take Tween-20, deionized water, and stir at 500r/min at normal temperature. Weigh the amino resin and isopropanol, dissolve them evenly, and add them dropwise into the Tween-20 aqueous solution while stirring. Finally, the catalyst and the wetting agent are added dropwise and stirred evenly to obtain the upper layer solution.
The preparation process of the anti-fog film is shown in Figure 3.1: on the corona-treated PET substrate, the N-propidine ethanol solution with a wet film thickness of 4 μm was applied by scraping at a speed of 2 mm/s. The solid content is 0.5wt.%. After the ethanol volatilized, the bottom polyester solution with a wet film thickness of 100um was coated on the surface-activated PET substrate with the same coating process . Take it out after being partially cured in a vacuum Drying Oven, and apply the upper hydrophilic layer solution with a wet film thickness of 100 μm in the same coating process . The anti-fog film is obtained after curing completely in a vacuum Drying Oven.
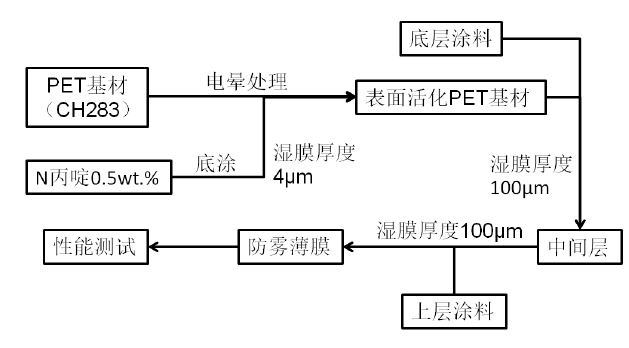
Figure 3.1 Flow chart of anti-fog film preparation
During the preparation of the anti-fog film, a large number of carboxyl groups and hydroxyl groups will be generated on the surface of the corona-treated PET substrate, which can react with the amino resin crosslinking agent in the underlying polyester layer to increase the adhesion of the coating. The amino resin crosslinking agent can react with the terminal hydroxyl groups of WPE0.1 to form a three-dimensional network structure, providing the necessary water resistance and mechanical properties . Part of the amino resin crosslinking agent in the bottom layer can react with the terminal hydroxyl group of Tween -20 in the upper hydrophilic layer, so that the upper hydrophilic layer and the lower polyester layer form a whole, thereby improving the durability of the overall coating. Figure 3.2 shows the chemical reaction between the amino resin and the corresponding groups in the process :
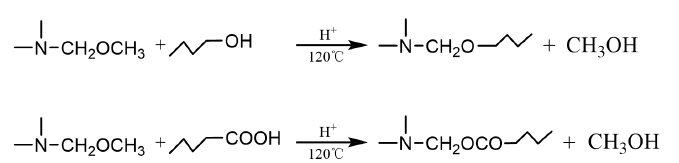
Figure 3.2 Chemical reactions that occur during the curing process of amino resins
- 1Advantages of Bar Spreader in corrosion coating prepative
- 2How Flat Film Applicators Can Build a New Generation of Functional Materials on Fabrics
- 3NVP anode film FAQ and solution
- 4Application Technology of Laboratory Film Applicator in Dielectric Thin Film
- 5Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Three Heating modes for Laboratory Film Applicators
- 6Application and selection of laboratory coater in PDMS thin film prepative
- 7Scraping machine selection case: film substrate large size high accuracy scraping solution
- 8Application of Film Applicator in PEM Research and Preparation
- 9Application of Film Applicator in PVDF-HFP Material Research






