Application of Coating Thickness Gauge in Textile Material Measurement
The coating Thickness Gauge can non-destructively measure the thickness of the non-magnetic coating on the magnetic metal substrate and the thickness of the non-conductive coating on the non-magnetic metal substrate. It has the characteristics of small measurement error, high reliability, good stability, and easy operation. It is a testing instrument needed to control and ensure product quality, and is widely used in testing fields such as manufacturing, metal processing, chemical industry, and commodity inspection. In this experiment, we tried to use the instrument in the textile industry to measure yarn, fiber diameter and fabric thickness, and compared the measurement results of this method with the results of traditional measurement methods.
Yarn Diameter Test
The yarn is tested in two ways: one is the conventional method, using the MVS300 fiber projector to measure the diameter of the yarn; the other is using a coating Thickness Gauge. The specific method is as follows: the yarn is evenly wound on the surface of the iron substrate, that is, only one layer of yarn is spread on the surface of the substrate, and the calibration plate used for instrument calibration is placed on the surface of the yarn. In the test, we put the probe lightly on the surface of the standard plate. According to the principle of the coating Thickness Gauge, the instrument reading is the sum of the apparent diameter of the yarn and the thickness of the calibration plate.
The point of the calibration plate is to average the pressure on the yarn surface. The calibration plate we use is relatively hard and light, and because it is the calibration plate used in the test, the thickness is fixed.
Lightly place the probe on the surface of the test material and get a reading of 684 μm, then remove the yarn and put the calibration plate on it to get the reading of the calibration plate. Thus, if the calibration plate reads 239 μm, the approximate diameter of the yarn derived from the test is 684 μm - 239 μm = 445 μm.
10 sets of data are obtained for each measurement, and the average value obtained from the measured values at different points is the yarn diameter data. The instrument can automatically obtain the variance of 10 sets of data, and the stability of the yarn data can be known. Since the reading of the obtained yarn adopts the difference method, no matter whether the calibration is accurate or not, the difference between the two values obtained under the same instrument state is always certain.
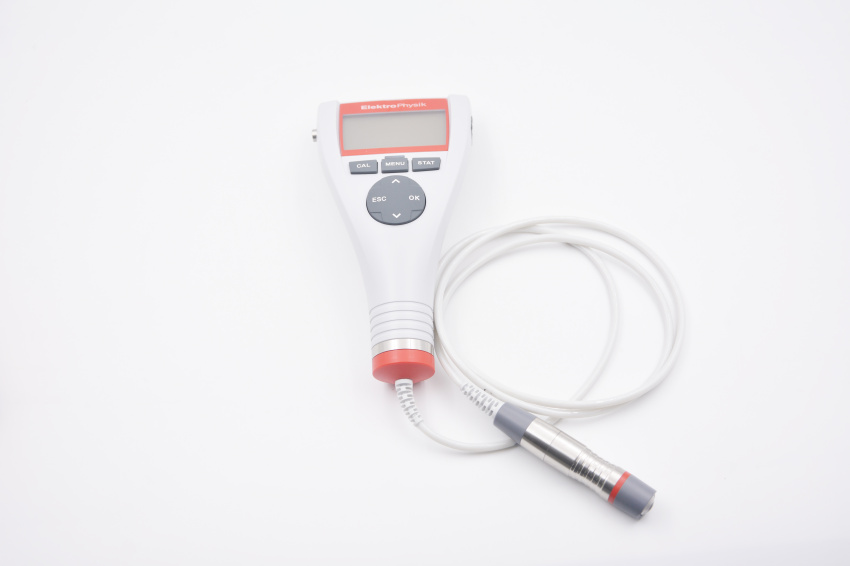
Fiber diameter test
Taking wool fiber as an example, two methods are used to test its diameter: one is the conventional method, that is, the MVS300 fiber projector is used to measure the diameter of the fiber [2]; the other is to measure the fiber diameter with a coating Thickness Gauge. The specific method is as follows: flatten the fiber soaked in liquid paraffin on the substrate, and put a suitable calibration plate on the fiber to buffer the artificial pressure and reduce the error caused by the fiber gap, so as to ensure a smooth surface under the probe . Gently place the probe on the calibration plate to read
The reading is the sum of the fiber diameter and the thickness of the calibration plate.
In the fiber test, iron and aluminum substrates were used to understand the influence of the substrate material on the test data.
Fabric Thickness Test
Two methods are used to test the thickness of the fabric: the first one uses the YG141D digital fabric Thickness Gauge to measure the thickness of different fabrics, and selects representative fabrics with different thicknesses [3]; the second one uses a coating Thickness Gauge to measure the thickness of different fabrics. Measurement. The specific method is as follows: put the cloth sample on the iron substrate, and put a suitable calibration plate on the cloth sample to buffer the artificial pressure and the error caused by the unevenness of the cloth sample surface.
Gently place the probe on the calibration plate to read, the reading is the sum of the thickness of the cloth sample and the thickness of the calibration plate.
- 1Nondestructive measurement Coating thickness
- 2Principle, application and selection of traffic coatings Coating Thickness Gauge
- 3Principle, Application and Selection of Eddy current Coating Thickness Gauge
- 4Principle, Application and Type Selection of Electronic Coating Thickness Gauge
- 5Explore the principle, application and selection of phosphating layer Coating Thickness Gauge
- 6Principle, Application and Type Selection Analysis of Chrome Coating Thickness Gauge
- 7Principle, Application and Selection of Coating Thickness Gauge for inner wall of small pipe
- 8Basic principle and application scenario of steel Coating Thickness Gauge
- 9Principle and Application Analysis of Coating Thickness Gauge














