Application scheme of Abbe refractometer for oil detection
When light enters different substances from the air, the ratio of the sine of the incident angle to the sine of the refraction angle is constant, but the value of this constant is different, and its value is related to the material itself, which is a reflection of the property of the material. Every homogeneous substance has its inherent refractive index. For the solution of the same substance, the refractive index is also related to its concentration. Generally speaking, the refractive index is directly proportional to its concentration.
Therefore, the type, purity and concentration of the oil can be judged by measuring the refractive index of the oil by using the property of the refractive index of the substance . Natural oils are all mixtures of mixed glycerides. Oils and fats from various sources contain different glycerides, each with its own unique refractive index. Therefore, different oils have different refractive indices. For each natural oil, its refractive index is a physical constant. When the quality of the oil changes, such as contamination, rancidity, etc., the refractive index will also change. Oil with a high relative density has a high refractive index. When the acidity of the oil increases, that is, the density decreases, the refractive index decreases. Therefore, measuring the refractive index of oil is an important means to identify the composition and quality of oil.
Experiment preparation
2.1 Test equipment: Yidian Wuguang WYA-3S

2.2 Experimental reagents:
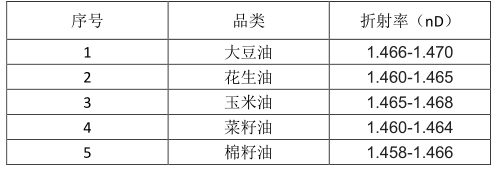
1) soybean oil
2) Peanut oil
3) corn oil
4) Canola oil
5) Cottonseed oil
2.3 Reference standards
"Method for Determination of Refractive Index of Animal and Vegetable Fats and Fats GB/T5527-2010"
Experimental procedure
3.1 Sample test
1) Connect the WYA-3S digital Abbe refractometer to a constant temperature Water Bath, and when the temperature is controlled at 20°C, use distilled water to correct the refraction index of the digital Abbe refractometer to 1.3330.
2) Separate the two prisms, add a small amount of sample (1 drop to 3 drops) to the fixed prism surface with a straw, and close the prism immediately. Wait a few minutes for the sample to reach the temperature of the prism.
3) Adjust the spiral handwheel of the prism until the field of view is divided into two parts, bright and dark, and turn the compensator knob (dispersion handwheel) to eliminate iridescence and make the dividing line between light and dark clear. Continue to adjust the spiral handwheel to align the light and dark dividing line on the crosshair.
4) Click the test button, the instrument will automatically display the refractive index of the sample, and then re-read it immediately , take at least two readings for each sample, and take the arithmetic mean.
5) Clean and dry both prisms completely, and take the above sample for the second measurement. Take the average value of the two measurements, which is the refractive index of the sample.
Results and discussion
4.1 Test interface

4.2 Experimental results
4.3 Discussion
Refractive index is one of the main parameters reflecting the purity of edible oil. For example, the refractive index of fatty acids increases with the increase of molecular weight and unsaturation. Therefore, some short-chain saturated fatty acid esters have low refractive index, while linseed oil and the like do not An oil with a high content of saturated acid has a high refractive index. Refractive index is an essential parameter for quality control and quality inspection of edible oil. In the quality inspection industry, the method of refractive index detection can also be used to quickly detect counterfeit products. For example, the industrial and commercial system uses WYA-3S digital Abbe refractometer to quickly test the content of sunflower oil in peanut oil.
- 1Tips for finding the light and dark boundary of Abbe refractometer [including video explanation]
- 2Measurement of oil refractive index by Abbe refractometer
- 3Suoguang WYA-2S Digital Abbe Refractometer Operation Manual
- 4Abbe refractometer operation method and precautions
- 5Abbe refractometer related introduction
- 6Optical Path Seat Analysis of Fully Automatic Abbe Refractometer
焦艳艳; 吴建民 - 《一种新型折射仪的光路座分析》
- 7Comparative analysis of several common oil fat detection methods
曹玉华; 杨慧萍; 孙香玲 - 《几种油料粗脂肪测定方法的对照》
- 8Introduction to several methods of liquid refractive index
辛督强;朱民;解延雷;张涛 - 《测量液体折射率的几种方法》
-
-
-
-
INESA WYA-2S digital Abbe refractometer$ 1700.00
-
-






